* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Constellations
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Orion (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
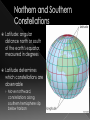
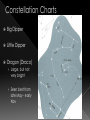
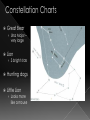
http://www.voxnovus.com/composer/ voisey/constellations/pic/constellation_ map.gif Constellation: Group of stars that form a distinctive pattern in the sky › International Astronomical Union (IAU) designated 88 constellations Asterism: Smaller groups of stars that form patterns within a constellation, from the Greek word aster, meaning star The larger the ‘dot’, the brighter the star Apparent magnitude: star’s brightness as seen from Earth › If all were placed at same distance from Earth Apparent magnitude scale first developed by Greek astronomer (around 130 BCE) He assigned a magnitude of 1 to the brightest star he could see › Faintest star was 6 Today, stellar magnitude extends well beyond 6 and into the minus range › Sun now recognized as -26 Stars in constellations appear to be close together – same line of sight › May be light years apart! Light year – represents the distance light travels in one year › At 300 000km/s, light travels about 9.5 x 1012 km in one year Best known group of stars (Asterism) › Not a constellation! Part of a large constellation, Ursa Major Recognized by many cultures › Ancient Chinese – chariot › Early Egyptians – bull leg › Aboriginal - bear The Big Dipper’s two end stars are known as pointer stars › Help to navigate the night sky › Point toward Polaris Polaris (“North Star”) points toward the North › Does not appear to move › Stars appear to rotate counterclockwise around Polaris Latitude: angular distance north or south of the earth's equator, measured in degrees Latitude determines which constellations are observable › Move northward, constellations along southern hemisphere slip below horizon More Constellations – The Twins The Twins as you see them in the sky Allegorical representation More Constellations – The Twins Graphically Geometrical Note: the stars are still in the exact same position, but now the shape has meaning! Constellation Charts Big Dipper Little Dipper Dragon (Draco) › Large, but not very bright › Seen best from late May - early Nov Constellation Charts Great Bear › Ursa Major – very large Lion › 3 bright stars Hunting dogs Little Lion › Looks more like a mouse Constellation Charts Cassiopeia › In the milky way › “W” shape – easy to remember › Draw a line from where handle joins bowl, through Polestar and beyond Cepheus Giraffe › Hard to see Learning Check: Please answer the following questions on a separate sheet of paper: 1. What does the term “celestial object” mean? 2. What unit of time does one revolution of Earth around the Sun correspond to? 3. Explain how calendars were helpful to ancient civilizations 4. Imagine you are standing at the North Pole and see a star directly overhead. Where do you think the star would be if you were standing at the equator? 5. Compare and contrast the terms constellation and asterism in a Venn diagram 6. What is a star’s apparent magnitude? 7. Define the term light year