* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Galaxies
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Physical cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Dark matter wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Gamma-ray burst wikipedia , lookup
Space Interferometry Mission wikipedia , lookup
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Planetary system wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Accretion disk wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Globular cluster wikipedia , lookup
Observable universe wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Open cluster wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Structure formation wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Lambda-CDM model wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
High-velocity cloud wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
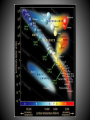
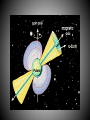
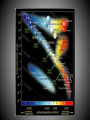
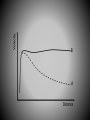
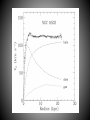
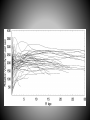
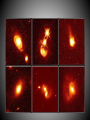
SIZE OF MILKY WAY Kapteyn all visible stars – 30,000 parsecs sun close to center Shapley globular clusters – 100,000 parsecs sun 2/3 toward rim Population I – blue, young, found in disk particularly in arms, circular orbits, high concentration (3%) heavy elements Population II – red, old, found in bulge and halo, elliptical orbits, low concentration of heavy elements Probably smooth transition between end members (i.e. the sun). ? Population III ? – pure H and He TWO MODELS OF STAR FORMATION Density wave model Self-propagating star formation model Galaxy Shapes spiral (S) barred spiral (BS) spiral with no arms (S0) elliptical (E) irregular (Irr) Rotation of Galaxies all stars follow velocity/gravity relationships all galaxies have too little visible mass for rotation speeds Any model for the formation and evolution of galaxies must account for collisions! Other types of galaxies Radio Galaxies Seyfert Galaxies Quasars probably all black holes with accretion disks Stars are grouped in clusters and galaxies Galaxies are grouped in clusters. Even clusters of galaxies are clumped together.