* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Planets
Impact event wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Life on Titan wikipedia , lookup
Naming of moons wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
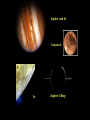
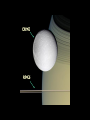
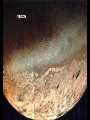
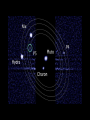
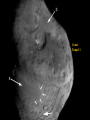
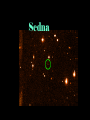
P l a n e t s The Solar System The Planets The word “Planets” comes from the Greek word for “wandering stars”. The stars are fixed in the sky, holding their same positions year after year, but the planets move over days across the background of the starry sky. The planets known to ancient people were often brighter than the stars, and were given the names of Gods. In the summer of 2006, the International Astronomical Union announced three criteria for an object to be labeled a “planet”: 1. 2. 3. It must be massive enough to be spherical It must orbit the Sun It must be dominant (massive) enough to have cleared all other objects out of its orbit Big objects not meeting these three criteria (like Pluto) Would be classified as “dwarf planets” There are five currently named “dwarf planets”: Ceres is the largest asteroid in the asteroid belt. Four are called “plutoids” and are beyond Neptune, Pluto, Haumea (2004), Eris (2005), and Makemake (2005). Mercury 1/3rd the size and mass of Earth, about the size of the Moon Grey/yellow in color, similar to the moon No atmosphere Day temperature: 800° F Day: 58.6 days night: -300° F Year: 88 days Only visible in the sky for a shortwhile before sunrise near the Sun or after sunset near the Sun, because Mercury is so close to the Sun. Looks like the Moon with lots of craters No moons or rings A little less gravity than Earth, a little bit smaller White in color Venus has a thick, cloudy atmosphere of carbon dioxide and sulfuric acid. Surface air pressure is 90 times that of Earth Surface temperature reaches 900° F 225 day year, 243 day retrograde “day” Earth’s “sister” planet The brightest object in the sky, besides the Sun and Moon. Venus is the “morning” or “evening” star, being a very bright, white “star” in the morning or evening sky. Venus Earth A blue and white planet Nitrogen / oxygen atmosphere Average temp.: 59° F 365.26 day “year” , 23.93 hour “day” One satellite called “the Moon”. The planet is often referred to as the Earth-Moon System, because the Earth and moon are similar in size and close to each other. The only planet known by humans to have “life” A mostly water planet 1/2 the size of Earth, 1/3 the gravity A red planet, because of a large amount of iron oxide (rust) in the soil Mars A VERY thin atmosphere, mostly CO2 Day: 24 hrs, 37 min. Year: 687 days The temperature on Mars ranges from about 0° to -100° F Two moons: Phobos and Deimos... both are very small (less than 30 miles across) and appear to be irregularly shaped asteroids captured by the Martian gravity Mars has polar ice caps, volcanoes and seasons Deimos and Phobos Taken by the “Spirit” Rover Asteroids 315x Earth’s gravity, 11x bigger Jupiter Gas Giant, atmosphere of mostly hydrogen and helium with a liquid metallic core Temperature in the upper clouds is -220° F, and increases as you approach the core to 43,000° F Year is 11.86 Earth years, day is 9.92 hours 63 known moons, the inner 4 being as large as Earth’s moon and visible with Earth telescopes Thin ring, 10 meters thick made of rock and dust Jupiter and Io Ganymede Io Jupiter’s Ring Tvashtar erupting on Io, 2/28/07 as New Horizons flew by 95x the gravity of Earth, 9x wider Atmosphere of hydrogen and helium with a liquid metallic core Average temperature of -300° F Year of 29.46 Earth years, day of 10.66 hours 60 moons, including Titan, a moon bigger than Mercury with a Nitrogen atmosphere and a solid and liquid surface. Saturn’s density is so low it would float on water Saturn Dione Rings Enceladus Icy H2O on its surface Lack of craters suggests it has been resurfaced Cassini photographed an H2O geyser Titan Methane rain with dry stream and lake beds where methane has flowed and then evaporated Nitrogen atmosphere 10x thicker than Earth A possible volcano Conditions like ancient Earth Huygens photographed dry river channels and lakebeds, presumably from raining methane Titan must have an internal source of methane, as UV light from the Sun turns it into solid organic material Huygens observed no actual liquid and only a few clouds through the haze Titan from Huygens 1/05 Cassini discovers Saturn’s 60th moon, July 2007. It is 1.2 miles across. This was filmed over 6 hours. Gravity 14.5x greater than Earth, 4x wider Methane atmosphere Surface temperature of -345° F Year: 84 Earth years Day: 17.24 hours Uranus Five major moons, at least 9 more smaller moons More on Uranus Has a ring system Tilted almost 90 degrees on it’s axis Each season lasts 21 years. In summer, the Sun would never set, in winter it would never rise. Neptune 17x the Gravity of earth, 4 x wider Atmosphere of methane, hydrogen and helium Temperature of -373° f Year of 165 earth years, day of 16 hours Neptune has 2 major moons 6 small ones and rings NeptuNe’s riNgs Neptune and Triton Triton Pluto Earth has 500x the gravity, and is 5.5x bigger Very thin atmosphere of methane and nitrogen Surface temperature of -390° f 248 years to revolve around the Sun, days to rotate 6.4 Pluto has a highly elliptical orbit orbit Five moons: Charon (1978), Hydra (2005), Nix (2005), P4 (2012), P5 (2012) The Kuiper Belt and Oort Cloud Comets Balls of ice and dust on highly elliptical orbits around the sun Comet Tempel 1 Sedna Sedna is three times farther than Pluto, a giant iceball on a highly elliptical orbit Quaoar (2002) is a another Kuiper Belt object Varuna is another about the same size UB313 2003 “Eris” Identified in the summer of 2005 as a “planet” Bigger than Pluto More than twice as far as Pluto, on average The Orbit of Eris (bigger than Pluto and sometimes closer)