* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Where We Were to Where We Are: The History of Astronomy
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Gamma-ray burst wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Patronage in astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Shape of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy in the medieval Islamic world wikipedia , lookup
Fine-tuned Universe wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Physical cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Structure formation wikipedia , lookup
Expansion of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
Lambda-CDM model wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
International Year of Astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Observable universe wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Chronology of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
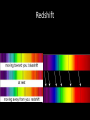
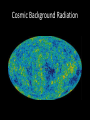
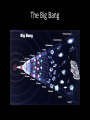
Where We Were to Where We Are: The History of Astronomy May 19th 2015 Announcements • Your post-test will be Thursday May 19th • Today is your last day to present your 2nd brief Early Astronomy Questions • People did not have youtube, I-Pads, phones, etc. • To entertain themselves they looked at the stars Constellations The Zodiac Constellations What They Thought… Geocentric Model Why don’t we see the same constellations all year long? Clue #1 That we are not at the center of the universe Galileo • If we are at the center of the universe, how can Jupiter have moons? • This was really controversial! • Clue # 2 that we are not at the center of the universe Foucault’s Pendulum Clue #3 that the Earth is not at the center of the Universe Heliocentric Model • This model put the Sun in the center of the solar system • The earth rotates around its axis and revolves around the sun Astronomy Today • Today’s telescopes are much bigger, more powerful and can see in many wavelengths This is How We Know What We Know Fusion in Super Giants Supernova •Gravitational Collapse of a Star due to extreme pressure on the core. •This stellar explosion sends shockwaves into space (gamma rays, xrays) Supernovas can become Black Holes or Neutron Stars • Black holes – Gravity has collapsed so much that nothing can escape it’s pull, not even light • Neutron Stars - Remaining core after a supernova - They are the densest and smallest stars Questions? Responsibility Team Section 2 Team 1 Team 2 Team 3 Team 4 Team 5 Team 6 Anam Mikauly Chris Dajana Jennifer Daze Junior Ramzi Sarmad Keny Yanvier Mosammat Victoria Abdullah Z. Besare Humayera A. Maridania Perla Jubayer Geovani Abdullah N. Kaylin Smarlyn Seme Kagbe Laura Blendi Jokely Himyard Earth Milky Way Galaxy Solar System Observable Universe Astronomers Noticed a Doppler Effect Spectroscope • An instrument used to see which wavelengths of light are absorbed by specific elements known to be in space Every Element is Different Elements absorb light at specific wavelengths of light…it is like a Fingerprint Redshift Cosmic Background Radiation If Everything is Moving Away… • There must have been a beginning The Big Bang Where We Are • Most of what we know about Astronomy and Space we learned in the last 20 years • In your lifetimes there will be much, much more that we understand and learn • Never stop asking questions and wondering why? And how? • This is how we got to where we are today 2027? Responsibility Teams Section 1 Team 1 Team 2 Team 3 Team 4 Team 5 Antoneta Megany Alimatou Thanya Robert Zoha Obniel Maisha Sharna Daiana Misha Gabriela Khady Sadia Henood Keyzie Carolina Harold Kimberly Reyson Sandeilis Marbelin Scarlett Nathi Responsibility Team Section 2 Team 1 Team 2 Team 3 Team 4 Team 5 Team 6 Anam Mikauly Chris Dajana Jennifer Daze Junior Ramzi Sarmad Keny Yanvier Mosammat Victoria Abdullah Z. Besare Humayera A. Maridania Perla Jubayer Geovani Abdullah N. Kaylin Smarlyn Seme Kagbe Laura Blendi Jokely Himyard