* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nineteenth lecture
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Gamma-ray burst wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Lambda-CDM model wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
High-velocity cloud wikipedia , lookup
Physical cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Observable universe wikipedia , lookup
Structure formation wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
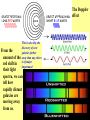
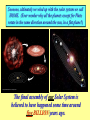
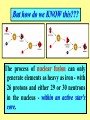
Origins of the Universe, the Solar System and the Earth, as we know it The "Big Bang" occurred 13.5-14 bya, according to astrophysicists & cosmologists (See? I told you geologists are happy to borrow!) THIS is believed to be the origin of the ENTIRE UNIVERSE, as we know it! What was there BEFORE the "Big Bang"? However, at this time, that's strictly conjecture ... Yeah, corny ..... everyone knows that with no air, there's no sound! You're undoubtedly already familiar with: E= 2 mc E = energy, m = mass, c = speed of light (299,792,458 meters/sec.) Turn this around a little, and you get: E/ 2 c =m IF you have almost unlimited energy, you can generate a lot of mass! Initially after the Big Bang, everything was pure energy Ultimately, subatomic particles coalesce to create protons, neutrons and electrons……. Even then, energy levels are so high that protons and neutrons bounce off each other. Deuterium colliding with a proton can produce , which with another neutron can become helium-4… OR ... Eventually, they cool down enough to be able to fuse, forming Deuterium, or 2H deuterium colliding with a neutron produces tritium, which can combine with another proton to produce helium-4. This Nuclear Fusion is what generates the energy of stars, producing the heat and light that we experience at 150 million kilometers' distance! Initially, matter was distributed surprisingly uniformly throughout the Universe, as much of it remains today. 90% of all matter in the known Universe consists of hydrogen and helium! These gases began condensing into clouds, now called nebulae (or nebulas)... YOU ARE HERE! The nebulae gradually collapse and commonly start rotating, to form galaxies, like the Andromeda Galaxy, pictured here. (Note the other galaxies also in the picture!) ( Our own Milky Way Galaxy is a spiral galaxy ) The first GALAXIES were probably forming within 1 billion years of the Big Bang. How many stars in a galaxy? Milky Way: 200 billion; Andromeda: 1 TRILLION! How many galaxies are out there? Galaxies aren't always completely isolated, either, but can interact! The Doppler effect This is also why the discovery of new galaxies farther away than any others is of major importance! From the amount of the red shift in their light spectra, we can tell how rapidly distant galaxies are moving away from us. Individual large pockets of gas within the spinning disc of a galaxy can create stars, if they have sufficient mass (i.e., ~10x the size of Jupiter). BUT here, the original star didn't last …. It gradually burned out, and then exploded in what is called a SUPERNOVA …. creating a new nebula that included much heavier elements than the old original star elements above iron in the Periodic Table of the Elements (the transferric elements). Much of our hydrogen and helium was lost to space, only some remaining in what would become the outer planets (Jupiter, Saturn, etc.). Heavier debris coalescing within this gas cloud produced solids, that coalesced into small bodies called planetesimals…. …. that then further coalesced to form larger solid bodies planets - rotating around a central star …. the Sun. Soooooo, ultimately we wind up with the solar system we call HOME. (Ever wonder why all the planets except for Pluto rotate in the same direction around the sun, in a flat plane?) The final assembly of our Solar System is believed to have happened some time around five BILLION years ago. But how do we KNOW this??? The process of nuclear fusion can only generate elements as heavy as iron - with 26 protons and either 29 or 30 neutrons in the nucleus - within an active star's core. Iron But if we look at the period table, we see LOTS of elements that are heavier than iron! The Supernova is required to generate the pressures and temperatures to create these heavier elements! Wednesday: The EARLY Earth