* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Solar System
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Equation of time wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
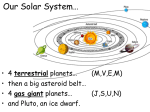
Solar System The sun • The sun’s mass is 99.8% of all the mass in the solar system. • The sun is a ball of glowing gas that is about ¾ hydrogen and ¼ helium. The Sun • Although the Sun looks very large in our sky, it is an average size star. • There are many stars larger than the Sun, but the Sun looks much bigger because it is so much closer to Earth. • The Sun is at the center of our solar system and is the only star in our solar system. How big is the Earth? INNER PLANETS • Small • Rocky Surface • Called “Terrestrial” Planets • Solid • No rings • Short Revolution OUTER PLANETS • No solid surfaces • Called “Gas Giants” • Might have partly solid core • Have lots of moons and satellites • Long revolution • Have rings