* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Renaissance
Brancacci Chapel wikipedia , lookup
Northern Mannerism wikipedia , lookup
Spanish Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Art in early modern Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Waddesdon Bequest wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance philosophy wikipedia , lookup
French Renaissance literature wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance in Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance music wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance architecture wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance Revival architecture wikipedia , lookup
Italian Renaissance wikipedia , lookup
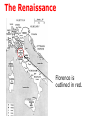
The Renaissance Quick facts about the Renaissance It was a re-birth of learning that first focused on finding the learning of Ancient Greece and Rome Renaissance artists and scientists accepted the study of the human condition as a valid field of study. It generally began in Italy during 13001350 period. It spread rapidly in some areas. slowly in others. The Renaissance Four areas of Renaissance learning we will examine in class are: Artwork Science and Math Navigation & Exploration Architecture The Renaissance Four areas of Renaissance learning we will examine in class are: Artwork Michelangelo, Leonardo, Donatello, Raphael Science and Math Navigation & Exploration Architecture The Renaissance Four areas of Renaissance learning we will examine in class are: Artwork Michelangelo, Leonardo, Donatello, Raphael Science and Math Galileo, Copernicus, Vesalius, Gutenberg Navigation & Exploration Architecture The Renaissance Four areas of Renaissance learning we will examine in class are: Artwork Michelangelo, Leonardo, Donatello, Raphael Science and Math Galileo, Copernicus, Vesalius, Gutenberg Navigation & Exploration Henry the Navigator, Magellan, Columbus Architecture The Renaissance Four areas of Renaissance learning we will examine in class are: Artwork Michelangelo, Leonardo, Donatello, Raphael Science and Math Galileo, Copernicus, Vesalius, Gutenberg Navigation & Exploration Henry the Navigator, Magellan, Columbus Architecture Brunelleschi The Renaissance Quick facts about what the Renaissance was not It was not a single event. It was not universally popular throughout Europe. It was not monolithic; it had many parts and nuances to it. It did not stay localized to Italy. It was not embraced by all the kings of Europe with great enthusiasm. The Renaissance The Renaissance began in Florence, Italy among crafters of the arts guilds. An especially important guild was that of the textile industry. The fine wool fabric made in Florence was sold all across Europe. As a result, interest in creating beautiful fabric in Florence grew. This expanded to included the creation of other works of art as well. The fabric market and the powerful banks centered in Florence made some of the Florentine families very rich. Some of these families became patrons to the arts. The Renaissance In order for artists and scientists to devote time to ideas they needed money to travel and live. This is where wealthy patrons came in to play. A patron is a person who offers money for a service. One of the most famous patrons of Renaissance artists was the Medici family of Florence. Florence was situated in northwestern Italy. The government of Italy at the time allowed the City-States of Italy a large degree of autonomy or self rule. The Renaissance Florence is outlined in red. The Renaissance These patrons helped establish schools where artists and scientists were free to pursue many fields of study that would not have been allowed a hundred years earlier. The schools were known as the Florentine schools. There were many conflicting ideas about how art should be studied and taught but out of the Florentine schools came many of the masters of the time who are still known today. -In part because of turtles. The Renaissance One of the chief artistic techniques of the time involved the use of perspective, or the ability to create the illusion of depth in a painting. Previously it had been common to paint the most important item in a painting as the largest regardless of its location. This often made paintings prior to the Renaissance look absurd to the eye but with the use of perspective the viewer could become part of the artwork. In other words the viewer became important. The Renaissance The Trinity by Massaccio, 1428, is an excellent example of perspective. Note the lines in the painting. They point to the foot of the cross upon which Christ is hung. The illusion of depth behind the cross comes from the receding nature of the vault or room in which the artist has placed the cross. The Renaissance The Great Cathedral of Florence is an excellent example of Renaissance architecture. Here the architect Brunelleschi designed a huge vaulted dome supported by steel ribs that extended high above the supporting structure below. This was the first use of the vaulted dome. It is now a dominant style of architecture for religious and government buildings around the world. The Renaissance United States Capitol Building The Renaissance Idaho Capitol Building The Renaissance Utah Capitol Building The Renaissance Here the lines are drawn over the painting to show the illusion depth created by perspective in the painting.