* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Renaissance Quiz
Waddesdon Bequest wikipedia , lookup
Mass (music) wikipedia , lookup
Spanish Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Art in early modern Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Art in the Protestant Reformation and Counter-Reformation wikipedia , lookup
French Renaissance literature wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance Revival architecture wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance architecture wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance in Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Italian Renaissance wikipedia , lookup
Italian Renaissance painting wikipedia , lookup
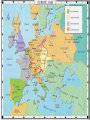
The Renaissance What was the Renaissance? • • • • Period following the middle ages (14001600) “Rebirth” of classical Greece and Rome Began in Italy Moved to northern Europe Causes of the Renaissance • Lessening of feudalism – – – • Fall of Constantinople – • • Church disrespected Nobility in chaos Growth of Middle Class through trade Greek scholars fled to Italy Education Nostalgia among the Italians to recapture the glory of the Roman empire Objectives During the middle ages – – Find God Prove pre-conceived ideas During the Renaissance – – Find man Promote learning Northern and Late Renaissance • RELIGION/POLITICS – Reformation; much political & religious violence • IDEAS – a skeptical Humanism • ART – a realism of everyday life: PORTRAITS, LANDSCAPES; oil painting • MUSIC – conservative perfection (Palestrina) & new approaches (madrigals) Renaissance • • • 1st period to name itself and say nasty things about earlier times: “Gothic” & “Dark Ages” Term means “Rebirth” Looking back to Classical culture – Ancient Greece and Rome Middle Ages - people were parts of a greater whole; members of a family, trade guild, nation, or Church Renaissance - human beings first began to think of themselves as individuals Timeline • • • • • • • Guttenberg Bible—1456 Columbus reaches America—1492 Leonardo da Vinci: Mona Lisa—c. 1503 Michelangelo: David—1504 Raphael: School of Athens—1505 Martin Luther’s 95 theses—1517 Shakespeare: Romeo and Juliet—1596 Humanism • Pursuit of individualism – Recognition that humans are creative – Appreciation of art as a product of man • Basic culture needed for all • Life could be enjoyable • Love of the classical past Renaissance Man • Broad knowledge about many things in different fields • Deep knowledge of skill in one area • Able to link areas and create new knowledge Realism That painting is the most to be praised which agrees most exactly with the thing imitated. - Leonardo da Vinci • Names! Artists known by name – 1st contemporary art historian (1550) • Individuality celebrated in this era Shakespeare Part of a general revival of theater, which we need to mention now, because OPERA is about to develop in the Baroque period. HAMLET - 1602 • Church is still the biggest power structure • Beginning of banking • Private fortunes & power • Starts in Italy – specifically Florence Josquin Ave Maria . . . Donatello David Michelangelo David Michelangelo Raphael Leonardo REFORMATION Renaissance timeline 1400 1500 1600 Summary – Italian Renaissance • POLITICS – Italian city-states; power from money • EARLY RENAISSANCE – Florence • HIGH RENAISSANCE – Rome • ART – Classical ideals revived; BIG 3 • IDEAS – Humanism returns • MUSIC – Josquin & imitative counterpoint Add a third active line that goes well with the cantus firmus and the other line The Old Way Add a nice active line that goes well with the cantus firmus Start with a bit of chant – a cantus firmus The Emerging Way? Still very “linear” in conception, especially in its emphasis on IMITATIVE COUNTERPOINT, but more “vertical” in organization? (Careful control of dissonance; favoring triads.) Basic structure • Words dominate • Tone painting • Printed in part-book or opposing-sheet format • Originated in Italy • English madrigal lighter & simpler • Intended for amateur performers (after dinner music) Josquin (to the tune of the Beatles’ “Michelle”) Josquin, the Man, Wrote smooth counterpoint as no one can, That guy Josquin. Josquin Desprez • 1st “Great Composer” glorified by contemporary and following generations • new approach to composition? a piece by Josquin Musical Notation • • • Invented to publish books of music Invented instruments Instrumental arrangements appeared The Reformation 1517 • • • • • • Martin Luther – a composer himself Effort to reform creates new church Sides with rulers against peasant revolts Printing press disseminates The Word Boost to individualism Consequences for music: Mass gone; hymns The Counter-Reformation Giovanni Palestrina • Adult life in Rome – • Reactionary period – – • Choirmaster, singer,/ director of music Church suppressed music that did not enhance words of the Mass Polyphony was distracting Works were conservative Giovanni Palestrina • Wrote over 100 masses – Gregorian chant – Mass in Honor of Pope Marcellus • • Influenced later music Buried in St. Peter’s Basilica – “The Prince of Music” Palestrina Chant a source of musical materials (revival & last gasp of cantus firmus technique) Very refined; no text painting Repetition avoided “16th Century Counterpoint” still taught today – why? To teach control, focus & line We usually celebrate innovators in history – Palestrina was a consolidator and perfecter of a soon-to-fade style Palestrina – a story The Church was about to ban polyphonic music from the church, because it obscured the sacred text. In response, Palestrina then composed the Missa Papae Marcelli, which, depite its 6-part texture, features very clear text-setting. The powers-that-be heard its merit & beauty and music was SAVED! Charming story, often told, but alas not true. Secular Music • • New instruments Chansons favored in the court – Courtly Love • Madrigals – Poetry and Music Music at Court Dances • Instrumentation unspecified; usually a consort (group) of a family of instruments of uniform timbre • Dances are collected into suites (Baroque) which evolve into symphonies (Classical) Instrumental Music • • • • • • Still subordinate to vocal music Used more often to accompany voices Sometimes played adapted vocal music alone Published music stated that parts could be sung or played Dancing became ever more popular Composers did not specify instrumentation Music at Court Madrigals Origin of term obscure A type of song for multiple voice parts Text is a rhyming poem, usually with sections of repetition & is usually about Love Music at Court Madrigals • • • • • Popular-at-court-&-wealthy-homes music In Italy and England Participatory, not passive music text-painting importance of words homorhythmic texture