* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CPDIGESTIVE
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
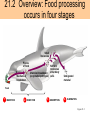
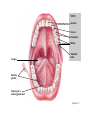
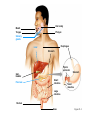
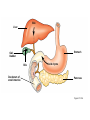
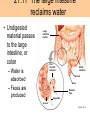
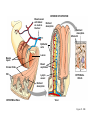
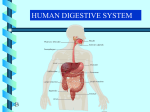
• Most animals ingest chunks of food Figure 21.1E 21 21.2 Overview: Food processing occurs in four stages Small molecules Pieces of food Mechanical breakdown Nutrient molecules enter body Chemical breakdown (enzymatic hydrolysis) cells Undigested material Food 1 INGESTION 2 DIGESTION 3 ABSORPTION 4 ELIMINATION Figure 21.2 TEETH Incisors Canine Premolars Molars Tongue “Wisdom” tooth Salivary glands Opening of a salivary gland duct Figure 21.5 • 21.4 The human digestive HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM system consists of an alimentary canal and When food is swallowed, it glands is moved through accessory the alimentary canal by peristalsis – Peristalsis is rhythmic muscle contraction in the walls of the digestive tract – Ringlike sphincter muscles regulate the passage of food Oral cavity Mouth Tongue Salivary glands Pharynx Esophagus Liver Stomach Pyloric sphincter Gallbladder Pancreas Small intestine Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Rectum Anus Figure 21.4 21.8 The stomach stores food and breaks it down with acid and enzymes • The stomach mixes food with gastric juice – The gastric juice contains pepsin, which begins the hydrolysis of protein 21 21 • major organ of chemical digestion and nutrient Alkaline pancreatic juice neutralizes stomach absorption acids – Its enzymes digest polysaccharides, proteins, nucleic acids, and fats • Bile emulsifies fat droplets for attack by pancreatic enzymes – It is made in the liver and stored in the gall bladder Bile Liver Stomach Gallbladder Bile Duodenum of small intestine Acid chyme Pancreas Figure 21.10A • The lining of the small intestine is folded and covered with tiny, fingerlike villi – Villi increase the absorptive surface • Nutrients pass through the epithelium of the villi and into the blood – The blood flows to the liver – The liver can store nutrients and convert them to other substances the body can use 21.11 The large intestine reclaims water • Undigested material passes to the large intestine, or colon Large intestine (colon) End of small intestine – Water is absorbed – Feces are produced Small intestine Rectum Anus Nutrient flow Appendix Cecum Figure 21.11 INTERIOR OF INTESTINE Blood vessel with blood en route to the liver Nutrient absorption Nutrient absorption Microvilli Epithelial cells Lumen Muscle layers Circular folds Villi Blood capillaries Lymph vessel EPITHELIAL CELLS Nutrient absorption INTESTINAL WALL VILLI Figure 21.10B