* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Digestive Systems
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
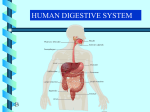
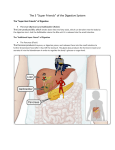
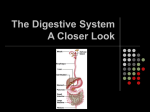
Digestive System Part II Digestive Organs- the Stomach Digestion is regulated by hormones and the Nervous System Stomach hormone: Gastrin produced in the presence of protein-containing food in the stomach stimulates the release of gastric juices and muscular contractions of stomach & intestine Chemical Digestion Accessory Digestive Organs Structure of the small intestine Small Intestine Small intestine is 20-23’ long: 1) duodenum 8-10” 2) jejunum 8’ 3) ileum 12’ duodenum – most active in digestion jejunum & ileum – absorption Digestion in Small Intestine Digestion is regulated by hormones and the Nervous System Duodenal hormones 1) secretin – stimulates pancreas & liver to secrete 2) cholecystokinin (CCK) – triggers release of enzymes from pancreas and gall bladder (amylase, lipase, etc.) Activation of protein-digesting enzymes in the small intestine Accessory Organs: Liver largest internal organ = 3 lb chemical factory processes food by the Hepatic Portal Vein delivered from digestive tract though the liver performs many functions Liver Functions 1) Filter blood for wastes to produce urea 2) Maintain a Constant glucose level in bloodstream Remove excess sugar from blood or release it when needed Glygogen (Liver) Glucose (Blood) Will also metabolize amino acids to make glucose if necessary!! 2) Detoxification blood of drugs & alcohol 3) Production of bile – to emulsify fat in the duodenum 4) Destroy old Red Blood Cells 5) Make blood proteins 6) Regulation of cholesterol & other fats Chopping up Protein Cut off the NH2 to supply glucose Bile produced by liver, stored in gall bladder enters small intestine by duct from gall bladder fat emulsifier contains bilirubin (breakdown hemoglobin) Jaundice occurs when bilirubin isn’t broken down neutralizes stomach acid, contains sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) Jaundice Yellow tinge to skin or whites of eyes occurs when rbc’s bilirubin is not broken down properly by the liver Other Liver Disorders 1. Viral Hepatitis 2. often cause jaundice Hep A often transmitted by infected water, shellfish, etc Hep B often associated with exposure to contaminated blood products. This one will destroy the liver over time Cirrhosis Long term disease of the liver where liver becomes fatty. Alcoholism is leading cause of cirrhosis as the toxin (ethanol) is difficult to break down over time Cirrhosis of the Liver The Digestive Enzymes Enzymes are hydrolytic, meaning they introduce water to break the molecular bonds of nutrients (protein, fats, carbs, etc) In the Mouth Starch + H2O ----------------------> Maltose salivary amylase Stomach Protein Digestion Low pH turns pepsinogen into active enzyme pepsin Protein + H2O ----------------------> Peptides (AA chains) pepsin Small Intestine (duodenum first) Neutralization, then Absorption Pancreatic juice (amylase) enters. It contains sodium bicarbonate which neutralizes acid from the stomach Starch + H2O ----------------------> pancreatic amylase maltose Protein + H2O ----------------------> trypsin peptides Starch + H2O ----------------------> bile salts/lipase glycerol + 3 Fatty Acids Small Intestine Further Breakdown … Peptides are further broken down into Amino Acids Maltose is broken down into glucose, the simplest sugar Source: peptidase & maltase secreted by intestine villi Peptides + H2O Maltose + H2O ----------------------> peptidases ----------------------> maltase Amino Acids Glucose Enzymes of the Digestive System The Essential Amino Acids There are 20 amino acids we require 9 cannot be made in our bodies and must be supplied by diet Sources: Complete Protein ---> Meat - supplies all 20 AA’s Incomplete Protein ---> Vegetable products - must use combinations to supply all 20 AA’s - ex. Beans and Rice - Soy protein is excellent but not complete by itself Recommended Daily Allowances 120 lb. female needs 44 grams per day 144 lb. male requires 56 grams per day Servings Cup of milk Roast beef slice (3oz) Mmmm… = 8g = 25g The Essential Fatty Acid Fats were the enemy in the 1990’s At 9.3 cal/g, reducing fat was identified as a “fad” method to drop weight Reducing fat intake, while increasing exercise is a good idea to maintain weight, but cutting fat all together is foolish Why? Fats are necessary for the production of hormones and cell membranes Essential Fat linoleic acid. Without it, we cannot produce phospholipids for cell membranes OBESITY 61% of North Americans are overweight or obese. Defined as 20% above desirable weight. Can lead to diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipemia, cancer, cardiovascular disease, sleep apnea and gout. Very complex condition. Never the result of just one factor, but has many causes, which may include: genetics, environmental/social lifestyle, food selection, inactivity, and behavioral conditions. WEIGHT LOSS What works? Moderate calorie restriction, regular aerobic exercise, combined with strength training, low fat/high fiber diet, and behavioral changes. WEIGHT LOSS Body fat reduction Must include both nutrition and exercise. Educate and encourage a healthy weight loss plan. Exercise Long duration, low intensity aerobic. At least 30 min., but 45 min. is the best. GOAL FOR WEIGHT LOSS With a 500 cal decrease per day = 3500 per week = 1lb. of fat. When combined with increased activity level, provides 1-2 lbs. weight loss per week. Monitor yourself (food/PT log) Calorie control: Meal planning (Exchange system/Food guide pyramid) Encourage healthy balance of nutrients, portion control, variety and choices. Enzyme Problems / Deficiencies Lactose Intolerance 75% of African Americans do not have sufficient levels of LACTASE to digest lactose into glucose/galactose sugars Result is painful cramps, diarrhea and bloating as the milk ferments in the digestive tract Vitamin Deficiencies cause Diseases Vitamin Niacin C - Scurvy (B3)- Pellagra (Skin Disease) Vitamin D - Rickets Vitamin A - Night Blindness Vitamin K - Blood clotting problems Ricketts – Vitamin D deficiency B6 Deficiency Mild deficiency Cheilosis Mouth soreness Seborrhea – oily face/ scalp Weakness Irritability Severe Angular Cheilosis Recommended Sodium Intake 400-3300 mg per day More salt makes blood hypertonic Water from surrounding tissues is pulled in by osmosis BP increases! This can create hypertension, leading to heart attacks, aneurisms and strokes