* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Endocrine System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
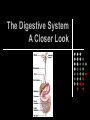
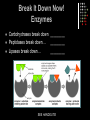
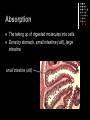
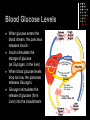
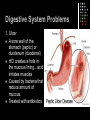
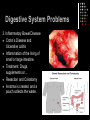
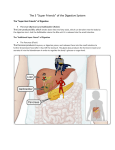
The Digestive System A Closer Look QOTD – Label Me! Answers 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Tongue Esophagus Stomach Duodenum Pancreas ileum Large Intestine Rectum Purpose: To enable the absorption of the nutrients needed for growth, maintenance and repair Components of Digestion Ingestion = the taking in of nutrients = enters by mouth Digestion = the breakdown of complex organic molecules into smaller components by physical & chemical means Mechanical – done by teeth, and stomach Chemical – done by the mouth, stomach, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, small & large intestine. Break It Down Now! Enzymes Carbohydrases break down ________ Peptidases break down… ________ Lipases break down… ________ SEE HANDOUTS! Absorption The taking up of digested molecules into cells Done by stomach, small intestine (villi), large intestine small intestine (villi) Absorption The Small Intestine is designed to have a large surface area. The inner membrane is folded like a fan The entire surface is covered with villi (villus) Each villus is covered with microvilli Absorption involves diffusion and active transport Anatomy of a Villus Proteins Microvilli Capillary Lacteal BEFORE DIGESTION… Starches TOO BIG!! AFTER DIGESTION… SMALL ENOUGH!! Lipids Water Minerals TO BLOOD Water soluble vitamins (B, C) Glucose Amino Acids Glycerol TO LYMPH Fatty Acids Fat soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) Elimination The removal of waste from the body Done by large intestine, rectum and anus Control Mechanisms Regulation through feedback Done by hormones (chemical messengers) Thermostat Example: -Too hot, shuts down -Too cold, starts furnace Digestion of Fats When fats enter the duodenum, the hormone CCK (Cholecystokinia) is released which causes the gall bladder to release bile. Fats are emulsified Acidic Chyme When acidic chyme enters the small intestine, the hormone secretin is released which causes the pancreas to release bicarbonate ions. The acid is then neutralized! Blood Glucose Levels When glucose enters the blood stream, the pancreas releases Insulin. Insulin stimulates the storage of glucose (as Glycogen, in the liver) When blood glucose levels drop too low, the pancreas releases Glucagon. Glucagon stimulates the release of glucose (from Liver) into the bloodstream Blood Sugar Levels Check out Page 270! Digestive System Problems 1. Ulcer A sore wall of the stomach (peptic) or duodenum (duodenal) HCl creates a hole in the mucous lining…acid irritates muscles Caused by bacteria that reduce amount of mucous. Treated with antibiotics Digestive System Problems 2. Cirrhosis of the Liver. Scar tissue in liver. Caused by excessive alcohol consumption and/or hepatitis virus. Results in jaundice (yellow skin), nausea, pain, fluid in abdomen Treatment…stop drinking!, vitamins, transplant. Read Page 273! Digestive System Problems 3. Inflammatory Bowel Disease Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative colitis Inflammation of the lining of small or large intestine. Treatment: Drugs, supplements or… Resection and Colostomy A stoma is created, and a pouch collects the waste. Digestive System Problems 4. Acid Reflux •Stomach acid burns the tissue of the esophagus •Caused by a weak cardiac sphincter Digestive System Problems 5. Constipation Too much water is removed from feces Usually because waste is moving too slowly…bunged up! Treatment: Eat fibre! (cellulose), laxatives, suppositories. A CURE FOR CONSTIPATION?