* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Anatomy & Physiology II
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
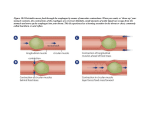
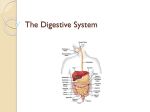
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Chapter 19 GASTROINTESTINAL (GI) TRACT Tube that includes: mouth, Pharynx, Esophagus, Stomach, Small intestine, Large intestine Accessory organs: teeth, tongue, salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas FIGURE 19.1 OVERVIEW- OPERATIONS Ingestion: eating Secretion: release of water, enzymes & buffers Mixing & propulsion: movement along GI tract Digestion: mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods Absorption: getting it into the body Defecation: dumping waste products = defecation WALL LAYERS- EVERYWHERE 4 layers Mucosa- epithelium, connective layer, glands, muscularis mucosae Submucosa- connective tissue, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, enteric nervous system Muscularis- circular layer, longitudinal layer In mouth, pharynx & upper esophagus –skeletal muscle Also in external anal sphincter Serosa or Visceral peritoneum FIGURE 19.2 FIGURE 19.3A FIGURE 19.3B MOUTH Formed by cheeks, hard & soft palate & tongue Soft palate at back includes a “hangy down” part = uvula During swallowing uvula prevents entry into nasal cavity Tongue muscular accessory organ maneuvers food for chewing Adjusts shape for speech & swallowing Lingual tonsils at base of tongue SALIVARY GLANDS 3 pairs of salivary glands Ducts empty into oral cavity Parotid inferior & anterior to ears Submandibular in floor of mouth, medial & inferior mandible Sublingual Beneath tongue submandibular to and superior to Saliva contains 99.5% water, salivary amylase, mucus and other solutes Dissolves food & starts digestion of starches FIGURE 19.4 TEETH Accessory organs in bony sockets of mandible & maxilla 3 external regions: 3 Crown- above gums Root- 1 or more parts embedded in socket Neck – between crown and root near gum line layers of material Enamel- covers crown Dentin- majority of interior of tooth Pulp cavity - nerve, blood vessel & lymphatics FIGURE 19.5 DIGESTION IN THE MOUTH Mechanical breakdown- chewing Mixed with saliva by tongue Salivary amylase chemically breaks down polysaccharides (starch) maltose and larger fragments Continues in the stomach until acidified Rounds up food into a soft bolus for swallowing PHARYNX & ESOPHAGUS On swallowing: Bolus of food oropharynx Laryngopharynx esophagus Muscular contractions in pharynx help Upper Skeletal muscle –controls entry to esophagus Lower esophageal sphincter (UES) esophageal sphincter (LES) Smooth muscle- regulates entry to stomach FIGURE 19.6A,B SWALLOWING Voluntary: bolus forced into oropharynx Triggers oropharyngeal stage Involuntary & breathing interrupted Soft palate move up-close nasopharynx Epiglottis seals off larynx Bolus moves into esophagus through UES Esophageal stage peristalsis moves it toward stomach FIGURE 19.6C STOMACH J- shaped enlargement of tract Serves as mixing chamber and holding reservoir Very elastic & muscular 4 regions Cardia- surrounds upper opening Fundus- superior & to left of cardia Body – large central portion Pylorus- lower part leading to pyloric sphincter & duodenum FIGURE 19.7 STOMACH WALL Mucosa: Folds called rugae Epithelium- simple columnar mucous Form gastric glands lining gastric pits Secretory cells: mucous neck cells Chief cells inactive enzyme pepsinoge Parietal cells HCl & intrinsic factor Collectively = gastric juice Muscularis- 3 Layers: longitudinal, circular & oblique FIGURE 19.8 FIGURE 19.9 DIGESTION & ABSORPTION Food entry stretch & rise in pH Nerve impulses secretion & mixing waves Food mixed with juice Chyme Small amount pushed through pyloric sphincter = gastric emptying- Carb. foods fastest, lipids next & proteins slowest Entry in duodenum feedback inhibition of stomach activity Pepsin digests protein peptides Little absorption- water, ions & some drugs PANCREAS Behind stomach- Produces pancreatic juice in acinar cells to duodenum via pancreatic duct Neutralize stomach acid and dilutes chyme Proteases: chymotrypsinogen, trypsinogen, et. al. Activated by entreokinase from intestine Starch digesting- pancreatic amylase Pancreatic lipase Nucleotidases – RNAase & DNAase NaHCO3 solution (pH 7.1-8.2)– 1000ml/day Panceas digestive enzymes LIVER & GALL BLADDER Largest organ after the skin On right below diaphragm Functional unit is lobule Hepatocytes around central vein Open capillaries = sinusoids Bile canaliculi ducts hepatic duct Gall bladder =Pear-shaped organ on front (stores bile) cystic duct common bile duct BILE Bicarbonate, bile salts & waste. – 1000 ml/day Important for emulsifying fats Increases surface area for digestion Pigment is bilirubin- from broken-down heme during RBC recycling Digested to strecobilin- brown color Bile salts reabsorbed at end of small intestine- ileum recycle to liver in portal circulation FIGURE 19.10 FIGURE 19.11A FIGURE 19.11B LIVER FUNCTION Maintains blood glucose Stores as glycogen Uses absorbed sugars & Converts acids glucose Lipid metabolism Produces cholesterol amino & triglycerides, makes bile Makes lipoproteins for lipid transport Excretion of bilirubin Processes drugs and other Store fat soluble vitamins Make active vitamin D chemicals SMALL INTESTINE 3 parts: duodenum, jejunum, ileum Where most of the digestion occurs Essentially all of the nutrient absorption Ends in ileocecal sphincter FIGURE 19.12A FIGURE 19.12B WALL STRUCTURE Same 4 layers Epithelial- simple columnar Absorptive cells with microvilli Goblet cells- secrete mucus Intestinal glands- intestinal juice & hormones Secretin, cholecystokinin (CCK), Glucosedependent-insulinotrophic peptide (GIP) Lymphatic tissue- defense WALL STRUCTURE (CONT.) Duodenal glands- alkaline mucus Helps neutralize stomach acid Circular folds- increase surface area Villi- finger like projections of mucosa Increase surface area for absorption Include lacteals for lipid absorption FIGURE 19.13 MOTILITY & SECRETIONS Secretions: alkaline, some enzymes Peptidases-breaks small peptides Disaccharidases attached to wall Water and salt to balance osmolality ~2000 ml/day Segmentation activity- for mixing Peristalsis for movement after most absorption completed- slow waves DIGESTION & ABSORPTION Chyme enters with partially digested carbohydrates & proteins Bile + pancreatic juice + intestinal juice completes the job Absorption is of monosaccharides; amino acids; phosphate sugar & bases of DNA & RNA; fatty acids & monoglycerides CARBOHYDRATE DIGESTION Amylases: Starch & dextrin maltose Disaccharidases at surface: Maltose: maltose glucose Sucrase: sucrose glucose & fructose Lactase: lactose glucose & galactose PROTEIN & FAT DIGESTION Trypsin, chymotrypsin, elastase, carboxypeptidase & pepsin Proteins small Peptidases at surface: peptides Peptides amino acids & di- & tripeptides Lipase: glycerides fatty acids & monoglycerides ABSORPTION By diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis & active transport Carbohydrates monosaccharides Via portal system to liver Proteins acids (jejunum & ileum) amino Via portal system to liver Lipids reformed to triglycerides Packaged in chlyomicrons with protein Via lacteals lymphatics ABSORPTION (CONT.) Water & salt Primarily osmotic movement along with other nutrients Vitamins: Fat soluble absorbed with fat Water soluble with simple diffusion B12 combines with intrinsic factor & absorbed by active transport in ileum FIGURE 19.14A FIGURE 19.14B LARGE INTESTINE Cecum, colon, rectum, anal canal Ileocecal canal large intestine Below is cecum with appendix Few folds , little specialization for absorption Colon- ascending, transverse, descending & sigmoid rectum anal canal Standard 4 layers with mucus secretion Muscularis: circular + bands of longitudinal muscle FIGURE 19.15A FIGURE 19.15B FIGURE 19.16 DIGESTION & ABSORPTION Slow emptying of ileum Slow peristalsis Mass peristalsis with food in stomach Moves from middle of colon rectum Bacterial digestion Produce some B-vitamins & Vit. K Produce gases= flatus Colon absorbs salt & water DEFECATION REFLEX Stretch of rectum wall neural reflex contraction of longitudinal muscle Combined pressure + parasympathetic activity relaxing of internal anal sphincter External anal sphincter is voluntary Contraction of diaphragm & abdominal wall muscles aid defecation CONTROL Rule: activate forward and inhibit behind three phases: Cephalic, gastric, intestinal Cephalic- smell, sight, thought of food Neural signals stimulates salivary glands & gastric glands Gastric stretching, pH of stomach Gastrin activates stomach & LES & CONTROL (CONT.) Intestinal- duodenum responses to food entering neural & endocrine CCK stimulated by AA & Pancreatic enzyme release fats Gall bladder contraction Contraction of pyloric sphincter Acid stimulates secretin Stimulates HCO3- ions in pancreatic juice Inhibits gastrin action in stomach AGING Decreased secretion, motility, strength of responses loss of taste, periodontal disease, hiatal hernia, gastritis & peptic ulcer disease Increased incidence of gall bladder problems, cirrhosis of liver, pancreatitis, constipation, hemorrhoids & diverticulitis