* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Schistosoma mansoni wikipedia , lookup
Ascending cholangitis wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
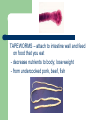
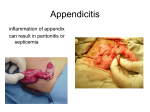
WARM UP 4/24 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. What organ stores bile? What does bile break down? What organ produces many digestive juices to help the small intestine? What is the main function of the large intestine? What does the rectum do? What is defecation? What are the 6 parts of the large intestine? Digestive System Problems and Diseases Notes Ch 21 4/24 PROBLEMS CIRRHOSIS or HEPATITIS – disease of the liver HEPATITIS – infection of the liver (virus) HEPATITIS A – infection due food eaten that has fecal waste in it HEPATITIS B - infection due to body fluids (sexual contact) HEPATITIS B - infection due to body fluids (sexual contact mostly) SYMPTOMS: fever, loss of appetite, loss of taste for cigarettes, and pain in the lower right chest or upper right abdomen. There is often a feeling of bloating in the abdomen, and bowel habits may change. The urine may appear dark or cola-coloured, and the bowel movement may appear clay-coloured. HEPATITIS C – contaminated blood transfusions HEPATITIS D – drug users HEPATITIS E - contaminated food or water * most common in world JAUNDICE – bile entering the body tissue SYMPTOMS – yellow skin and sclera WORMS – intestine parasites worms in stool coughing up worms loss of appetite fever shortness of breath abdominal distention (swelling of the abdomen) severe stomach or abdominal pain ASCARASIS - Round worms LIFE CYCLE 1. Eat eggs 2. Hatch in stomach 3. Move to intestines 4. Up throat and esophagus 5. Back in Intestines 6. Live in body tissues HOOKWORMS – attach to intestine wall and feed on tissues - fecal content in soil; bare feet - causes anemia TAPEWORMS – attach to intestine wall and feed on food that you eat - decrease nutrients to body; lose weight - from undercooked pork, beef, fish PINWORMS – •How is pinworm spread? •Pinworms live as parasites in the intestine. •At night, adult female pinworms migrate from the large intestine to the anal area, where they lay their eggs. •From the anus, pinworm eggs may be transferred to other surfaces: •Underclothes •Pajamas •Bedding •Towels •Toilets DIARRHEA – watery stools - food wastes are rushed through the large intestine before it has time to absorb water - usually caused by bacteria PROBLEM – causes dehydration CONSTIPATION – feces hard to eliminate - food wastes remains too long in the body, stools hard Caused by lack of fiber or “holding it” Ulcers Peptic ulcer - sore in the stomach lining Gallstones Bile is too concentrated and forms crystals COLON CANCER Cancer in the colon - 57,000 die each year from this - mostly over 50 yrs old - causes: too much fats in diet, genetics IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME Persistent diarrhea and constipation problems DIABETES Body does not produce enough insulin (pancreas) - need to eat low sugar diet LACTOSE INTOLERANT Lack of having enzyme lactase that breaks down milk - cramps, gas, bloating, dismfort, and diarrhea after eating milk products - 15% white 80-90% of African- american and Asians get this - ** Humans only species that drink another animals milk ANOREXIA NERVOSA Self- induced starvation - vomiting after a meal - low heart rate, dry skin, loss of bone mass, cavities, acid reflux, ulcers 10-15% die BULEMIA • Binge eating and then getting rid of food after - throw up or laxatives