* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download May 2005: Guide to the Horse's Gut
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
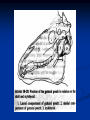
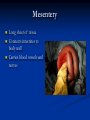
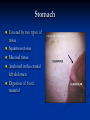
University of Tennessee College of Veterinary Medicine – Horse Owner Seminar 1-22-05 Benjamin R Buchanan, DVM Resident Large Animal Internal Medicine Resident Veterinary Emergency and Critical Care Guide to the Equine Gut Normal Equine Gastrointestinal Anatomy Divisions Oral Cavity Esophagus Small Intestine Proximal Mid Distal Cecum Large Colon Transverse Colon Small Colon Rectum Oral Cavity Oral Cavity Oral Cavity Oral Cavity Pharynx and Guttural Pouch Pharynx Epiglottis Arytenoids Opening to Esophagus GP Nerves control swalloing Esophagus Connects oral cavity to stomach Valve where it travels from thorax into stomach Swallowing unconsciously controlled Covered by squamous tissue Mesentery Long sheet of tissue Connects intestines to body wall Carries blood vessels and nerves Stomach Covered by two types of tissue Squamous tissue Mucosal tissue Anchored in the cranial left abdomen Digestion of food material Small Intestine Proximal Duodenum Connection for liver and pancreas Digestion of food material Short mesentery Mid Jejunum Digestion and absorption Long mesentery Small Intestine Distal Ileum Controls rate of flow into cecum/colon Tape worms Short mesentery Cecum Appendix Fermentation and fiber digestion Base and apex 8-10 gallons fluid and gas Anchored at base by mesentery Large Colon Modification of ascending colon Travels from right flank to liver to left flank back to liver back to right flank Anchored on right by short mesentery, free on left Ferementation and fiber digestion Transverse Colon Short connection of large colon to small colon Short mesentery Small Colon Descending colon Water reabsorption Fecal storage Long mesentery Rectum Abdominal and extraabdominal Short mesentary Fecal storage Route for abdominal palpation Glass Horse Questions