* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Digestive System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
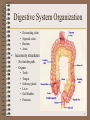
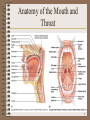
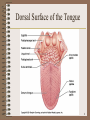
The Digestive System 1 Digestion • Processing of food • Types – Mechanical (physical) • • • • • Chew Tear Grind Mash Mix – Chemical • Catabolic reactions • Enzymatic hydrolysis – Carbohydrate – Protein – Lipid 2 Digestion • Phases – – – – – Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption Further digestion 3 Digestive System Organization • Gastrointestinal (Gl) tract (Alimentary canal) – Direct link/path between organs – Structures • • • • • • • • • • • Mouth Oral Cavity Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Duodenum Jejunum Ileum Cecum Ascending colon Transverse colon 4 Digestive System Organization • • • • Descending colon Sigmoid colon Rectum Anus • Accessory structures – Not in tube path – Organs • • • • • • Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas 5 Anatomy of the Mouth and Throat 6 Human Deciduous and Permanent Teeth 7 Dorsal Surface of the Tongue 8 The Major Salivary Glands 9 Deglutition (swallowing) • Sequence – Voluntary stage • Push food to back of mouth – Pharyngeal stage • Raise – Soft palate – Larynx + hyoid – Tongue to soft palate – Esophageal stage • Contract pharyngeal muscles • Open esophagus • Start peristalsis 10 Deglutition (swallowing) • Control – Nerves • Glossopharyngeal • Vagus • Accessory – Brain stem • Deglutition center – Medulla oblongata – Pons – Disorders • Dysphagia • Aphagia 11 Esophagus • Usually collapsed (closed) • Functions – Secrete mucous – Transport food 12 Esophagus • Sphincters – Upper – Lower 13 Stomach • Usually “J” shaped • Left side, anterior to the spleen • Mucous membrane – G cells – make gastrin – Goblet cells – make mucous – Gastric pit – Oxyntic gland – Parietal cells – Make HCl – Chief cells – Zymogenic cells • Pepsin • Gastric lipase 14 Anatomy of the Stomach 15 Stomach • 3 muscle layers – Oblique – Circular – Longitudinal • Regions – – – – Cardiac sphincter Fundus Antrum (pylorus) Pyloric sphincter • Vascular • Inner surface thrown into folds – Rugae • Contains enzymes that work best at pH 1-2 16 Stomach • Functions – Mix food – Reservoir – Start digestion of – Absorbs • Alcohol • Water • Lipophilic acid • Protein • Nucleic acids • Fats – Activates some enzymes – Destroy some bacteria 17 Small Intestine • Extends from pyloric sphincter ileocecal valve • Regions – Duodenum – Jejenum – Ileum • Movements – Segmentation – Peristalsis 18 Small Intestine • Absorbs – – – – – 80% ingested water Electrolytes Vitamins Minerals Lipids • Monoglycerides • Fatty acids 19 Structure of the Villi in the Small Intestine 20 Small Intestine • Control • Requires pancreatic enzymes & bile to complete digestion 21 Large Intestine • Extends from ileocecal valve to anus • Regions – Cecum – Appendix – Colon • Ascending • Transverse • Descending – Rectum – Anal canal 22 Anatomy of the Large Intestine 23 Large Intestine • Functions – Mechanical digestion • Haustral churning • Peristalsis – Chemical digestion – Bacterial digestion – Absorbs •More water •Vitamins – Concentrate/eliminate wastes • Ferment carbohydrates • Protein/amino acid breakdown 24 Feces Formation and Defecation • Chyme dehydrated to form feces • Feces composition – – – – – Water Inorganic salts Epithelial cells Bacteria Byproducts of digestion • Control – Parasympathetic – Voluntary • Defecation – Peristalsis pushes feces into rectum – Rectal walls stretch 25 Liver • Location • 4 Lobes – – – – Left Quadrate Caudate Right • Each lobe has lobules – Contains hepatocytes 26 Liver • Functions – Makes bile • Detergent – emulsifies fats • Contains – – – – – Water Salts Pigments Electrolytes Cholesterol 27 Liver – Detoxifies/removes • Drugs • Alcohol – Stores • • • • – – – – Glycogen Vitamins (A, D, E, K) Fe and other minerals Cholesterol Activates vitamin D Fetal RBC production Phagocytosis Metabolizes absorbed food molecules • Carbohydrates • Proteins • Lipids 28 The Organs and Positions in the Abdominal Cavity 29