* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nutrition powerpoint
Thrifty gene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Vegetarianism wikipedia , lookup
Waist–hip ratio wikipedia , lookup
Cigarette smoking for weight loss wikipedia , lookup
Gastric bypass surgery wikipedia , lookup
Calorie restriction wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbohydrate diet wikipedia , lookup
Adipose tissue wikipedia , lookup
Body fat percentage wikipedia , lookup
Fat acceptance movement wikipedia , lookup
Food choice wikipedia , lookup
Overeaters Anonymous wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Human nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Obesity and the environment wikipedia , lookup
Abdominal obesity wikipedia , lookup
Diet-induced obesity model wikipedia , lookup
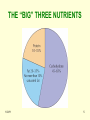
1/21/11 1 NUTRITION INFLUENCES 4 SPECIFIC AREAS Health Appearance Behavior Mood 1/21/11 2 THE ROLE OF NUTRIENTS IN DIET Growth and development Provide energy Regulate metabolism 1/21/11 3 NUTRIENT CLASSES • Carbohydrates • Fats • Proteins • Minerals • Vitamins • Water 1/21/11 4 THE “BIG” THREE NUTRIENTS 1/21/11 5 CALORIC CONTENT IN FOOD Carbohydrates 4 cal/g Protein 4 cal/g Fats 9 cal/g Alcohol 7 cal/g 1/21/11 6 CARBOHYDRATES • Simple (Soda, candy, sweets, fruit) – Increase blood sugar – Promotes fat deposition • Complex (Pasta, rice, breads, potatoes) – Contribute nutrients and fiber • Eat at least 3 ounces of whole-grain every day • Eat more dark green and orange vegetables and beans • Eat a variety of fruits 1/21/11 7 FATS • Saturated (Animal sources) – Solid at room temperature • Unsaturated (Vegetable sources) – Liquid at room temperature • Less than 10% of calories in diet from saturated fat – Total dietary fat between 20-35% of calories • Substitute lean meat, fish, poultry, nonfat milk and other low-fat dairy products for high-fat foods – Reduce fried foods & foods high in cholesterol 1/21/11 8 PROTEIN • Sources of Protein – Animal (complete) • meats, dairy – Vegetable (incomplete) • beans, nuts, legumes, grains • Consume at least 2 servings/day • Dietary supplements of protein (tablets & powders) are NOT recommended 1/21/11 9 MINERALS • Inorganic elements found in food that are essential to life processes • A diet containing recommended servings of carbohydrates, fats and proteins will meet the RDA standards • Extra servings of green and yellow vegetables may be beneficial • Salt should be limited in the diet 1/21/11 10 VITAMINS • Organic substances that regulate numerous and diverse physiological processes in the body • Do not contain calories • Two types – Fat soluble – Water soluble • A balanced diet containing recommended servings of carbohydrates, fats and proteins will meet the RDA standards • If you eat a balanced diet, you do not need to take supplements 1/21/11 11 WATER • • Vital to life (60% of body weight) Life Processes/functions • Drink at least 8 – 8oz glasses a day • Limit daily servings of beverages containing caffeine to no more than three • Limit sugared soft drinks; they contain empty calories • If you choose to drink alcohol, do so in moderation – – – – – 1/21/11 Chief component of blood plasma Aids in temperature regulation Lubricates joints Shock absorber in eyes, spinal cord and amniotic sac Active participant in many chemical reactions 12 http://www.my pyramid.gov/ 1/21/11 13 Guidelines for Healthy Eating • Make half your grains whole • Vary your veggies & Fruits • Know your fats/reduce intake • Get your calcium-rich foods • Go lean with protein • Minimize reliance on fast foods/processed foods • Limit artificial sweeteners • Restrict “empty” calories/ Healthy Snacks • Learn the difference between a craving and hunger • Eat smaller, more frequent meals/avoid binging 1/21/11 14 READING LABELS 1/21/11 15 Portion Distortion • http://hp2010.nhlbihin. net/oei_ss/PD1/downl oad/ppt/PD1.ppt 1/21/11 16 BODY FAT/BMI INDEX CHARTS 1/21/11 17 State Obesity Trends • http://www.cdc.gov/nc cdphp/dnpa/obesity/tr end/maps/index.htm 1/21/11 18 Health Risks Associated with Being Overweight • Coronary heart disease (Ex. Stroke, Heart Attack) • Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) • High Cholesterolemia (High Cholesterol) • Diabetes • Premature death • Physical fitness provides protection from the health risks of obesity 1/21/11 19 REGIONAL FAT DEPOSTION • Abdominal body fat poses greater health risks than fat stored in other areas • Males store more fat centrally and have increased health risks associated with body fatness 1/21/11 Male (apple) Higher health risk Female (pear) Lower health risk 20 OBESITY CLIPS YouTube - The Obesity Epidemic (Obesity #1) YouTube - Consequences of Obesity (Obesity #2) 1/21/11 21 Disorders Associated with Being Underweight • Anorexia Nervosa (not consuming enough calories) • Bulimia Nervosa (binging and purging, eat and throwing up) • Anorexia Athletica (no longer enjoys exercising, but feels obligated to do so, overexercising) • Female Athlete Triad (emphasizes leanness and low body weight) • Muscle Dysmorphia (males) (too low body fat) • Fear of Obesity 1/21/11 22 WARNING SIGNS FOR EATING DISORDERS • • • • • • • • • • Drastic change in weight Pre-occupied with calorie counting Weighing themselves several times a day/week Excessive exercise Binge eating or purging Odd food rituals (small bites, pushing food around plate) Eating alone or skipping meals Using laxatives Using drugs to curb appetite (smoking) Warped view of themselves 1/21/11 23 Health Risks Associated with Underweight Eating Disorders • Hair Loss • Drastic weight loss • Loss of menstrual period • Blood thickens • Sleeping Issues • Loss of muscle tissue • Heart attack • Muscle/joint issues 1/21/11 24 EATING DISORDER CLIPS YouTube - Anorexia's Living Face (CBS News) YouTube - 'Man-orexia' On The Rise 1/21/11 25 FACTORS THAT INFLUENCE WEIGHT & FAT CONTROL • Heredity / Genetics • Lifestyles – Consumption of excess calories – Lack of regular physical activity • Environment – Easy access to high calorie food makes it harder to eat properly – Modern “conveniences” make activity less likely 1/21/11 26 Prevalence of Dieting • 40% of all women • 25% of all men Diet products are a 33 billion dollar industry 1/21/11 27 Almost All Diets are Unsuccessful • 50% regain all weight within 2 years • 5-10% keep weight off permanently Why do diets fail? 1/21/11 28 Problems with Fad Diets • Weight loss is often water loss • Supplements may be dangerous • Diet may lack essential nutrients • Metabolism may slow down if caloric intake is very low • Most (if not all) simply do not work for people long term! 1/21/11 29 Formula for Losing Body Fat Need to create a caloric deficit (2 ways to do it!) – Eat less! – Exercise more! 1/21/11 30 Weight Loss Calculations 1 pound of fat = 3500 calories Maximum weight loss should be no more than 1-2 pounds per week 1/21/11 31 BENEFITS OF EXERCISE FOR WEIGHT CONTROL • Burns calories • Maintains lean body mass (LBM) • Increases metabolism • Promotes greater fat loss • Suppresses appetite 1/21/11 32 SUMMARY TOPICS • Dieting • Eating Disorders • Healthy Eating • Nutrients 1/21/11 33