* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electricity and Magnetism
High voltage wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Insulator (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Electric current wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
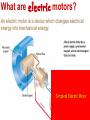
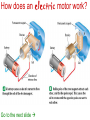
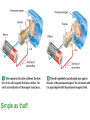
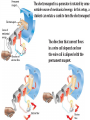
Electromagnetism Activity #6 Electricity and Magnetism – how are they related? 1.) When an electric current passes through a wire a magnetic field is formed. 2.) when a wire is moved across a magnetic field, an electric current is induced in the wire What is an electromagnet? When an electric current is passed through a coil of wire wrapped around a metal core, a very strong magnetic field is produced. This is called an electromagnet. What is a galvanometer? A galvanometer is an electromagnet that interacts with a permanent magnet. The stronger the electric current passing through the electromagnet, the more is interacts with the permanent magnet. Galvanometers are used as gauges in cars and many other applications. The greater the current passing through the wires, the stronger the galvanometer interacts with the permanent magnet. Activity #7 What are electric motors? An electric motor is a device which changes electrical energy into mechanical energy. How does an electric motor work? Go to the next slide Simple as that!! We have seen how electricity can produce a magnetic field, but a magnetic field can also produce electricity! How? What is electromagnetic induction? Moving a loop of wire through a magnetic field produces an electric current. This is electromagnetic induction. A generator is used to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy by electromagnetic induction. Carefully study the next diagrams: Activity #8 A look again at alternating current – Alternating current is electrical current which comes from a generator. As the electromagnet is rotated in the permanent magnet the direction of the current alternates once for every revolution. Go to this website and click the button for DC then for AC to visually see the difference between the two. You can see that the DC source is a battery – current flows in one direction. The AC source is the generator and the current alternates once for each revolution.