* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Quadriceps Strain
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
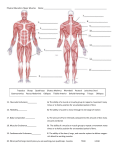
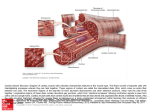
Quadriceps Strain OVERVIEW You have been diagnosed with a quadriceps strain, which is a partial tear of the large muscle in the front of the thigh. The quadriceps muscle is a group of large, powerful muscles that span the front of the thigh, from the groin to the back of the knee. Treatment of a quadriceps tear depends on the severity of the injury, but usually includes limited activity, ice, compression, and pain medications. Crutches may be needed. Recovery takes several weeks and it is important not to return to activities too soon. BACKGROUND The quadriceps is the important muscle that functions to extend the knee and helps to flex the hip joint. The quadriceps is an important muscle for standing, walking, running, and climbing. It is used heavily in many sporting activities, as well as during normal daily activities. Sports that commonly cause a quadriceps injury are sprinting and jumping sports that involve sudden deccelerations. These include track and field, soccer, and basketball. A muscle strain, or "pulled muscle", is a tear of the muscle fibers. In less severe strains, or grade I injuries, the tearing is microscopic. The muscle fibers are essentially stretched too far, and some bleeding occurs within the muscle. In very severe muscle strains, grade III injuries, the muscle can completely rupture, and may require surgery to repair the torn ends of the muscle. Muscle strains and tears most commonly occur because of what is called an "eccentric contraction." When this occurs, the muscle is trying to contract while another force (the ground, another player, etc.) is forcing the muscle in the opposite direction. This creates tremendous force on the muscle, and if the force is strong enough, it will tear the muscle fibers. CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND DIAGNOSIS The symptoms of a pulled quadriceps depend on the severity of the injury. The quadriceps injury is usually sudden and painful. Other common symptoms include: Skin: Small tears within the muscle cause bleeding, but usually this is deep. Sometime bruising will reach the skin, sometimes after 24-48 hours. Swelling: The accumulation of blood from the muscle injury causes swelling of the thigh. There can sometimes be a soft (fluctuant) OrthoInfo Quadriceps Strain Page 1 of 2 collection of blood, which is called a hematoma. This can also become a firm solid mass. This can make further muscle contraction difficult and painful. Wearing a compressive bandage can help control the swelling and the potential for a hematoma. Spasm: Muscle spasm is a common and painful symptom of a muscle injury. Because of the trauma to the muscle, signals of contraction are confused, and the muscle may be stimulated. Difficulty Contracting: Extending the knee and flexing the hip is often painful after a pulled quadriceps, and can even prevent the patient from walking normally. If you are unable to contract the quadriceps, the muscle may be completely ruptured. TREATMENT Treatment of a quadriceps strain is dependent on the severity of the injury. Because of bleeding and swelling, athletes should stop their activity and rest immediately. An ice pack and compressive bandage can be applied to control swelling. Crutches may be necessary if walking is painful or if spasms are severe. If the pain is significant, or if the symptoms do not steadily resolve, medical evaluation should be obtained. Some steps to take include: Ice the injury Apply a compressive bandage Use crutches Gently stretch the hamstrings Massage the injured area Physical therapy MORE INFORMATION Further information can be obtained on the internet. Your local public library can help you explore these sources if you are interested. Two good sites for expert and peer reviewed information are the American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons at www.aaos.org and www.emedicine.com. FEEDBACK If you have questions or comments, please contact the office or submit them to the web site at www.pedortho.com. OrthoInfo Quadriceps Strain Page 2 of 2