* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Congenital Hypothyroidism
Survey
Document related concepts
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Sex reassignment therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Hypopituitarism wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
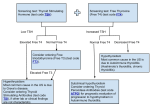
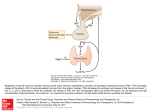
Congenital Hypothyroidism Department of pediatrics Xin Ying Definition and Summary Hypothyroidism results from deficient production of thyroid hormone or defect in its receptor. The characteristics is retardation in growth and mental development. Category Sporadic Hypothyroidism results from hypoplasia or aplasia of the thyroid gland. Endemic Hypothyroidism (Cretinism) is due to iodine deficiency during mother pregnancy. Synthesis of Thyroid Hormone Thyroid hormone triiodothyronine (T3) thyroxine (T4) Materials iodine, tyrosine Steps 1. Iodine trapping 2. Iodine oxidized 3. Tyrosine iodinate 4. Iodotyrosine condensation Regulation of Thyroid Function Hypothalamus TRH Pituitary TSH TRH thyrotropin-releasing hormone TSH thyroid-stimulating hormone negative feedback Thyroid T3, T4 Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Thyroid Axis 甲状腺素合成和释放的调节 TRH TSH T3,T4 Actions of Thyroid Hormone ¾ Increase oxygen consumption and heat production ¾ Accelerate growth and development ¾ Promote central nervous system development ¾ Influence metabolism of lipids, carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids and vitamins ¾ Have important effects on other hormone actions Etiology Thyroid dysgenesis (aplasia, dysplasia, ectopic) 90%~95% Defective synthesis of thyroid hormone Genetically determined enzymatic defects, thyroid enlargement is present TRH or TSH deficiency Unresponsiveness of tissues to TSH or thyroid hormone Iodine deficiency Clinical Manifestations Early symptoms and signs (1~2 month of life) ¾ Postmature infant, large for gestational age ¾ Prolongation of physiologic icterus ¾ Feeding difficulties, poor appetites, constipation, hypothermia ¾ The anterior and posterior fontanels are widely open *Typical Features of Hypothyroidism ¾Characteristic facies Eyes seem to be widely spaced Bridge of nose is flat and broad Eyelids swollen Mouth is kept open and the thick and broad tongue protrudes from it Skin is dry and myxedema may be present ¾ The child is stunted in growth Short stature, infantile skeletal proportions with short extremities Protuberant abdomen, umbilical hernia Delayed closure of fontanels Retarded dental eruption *Typical Features of Hypothyroidism ¾ Mental retardation ¾ Diminished physical activity hypothermia, bradycardia, sluggish, poor appetite, constipation, umbilical hernia, poor muscle tone, hoarse voice or cry, anemia Before Treatment After Treatment Before Treatment After Treatment Manifestations of Endemic Cretinism ¾ Nervous endemic cretinism Mental deficiency, deaf-mutism, sometimes with neuro-muscular disorders, but without severe hypothyroidism ¾ Myxedematous endemic cretinism Hypothyroidism associated with dwarfism and mental deficiency Manifestations of Secondary Hypothyroidism • The symptoms are mild • The majority of affected infants have multiple pituitary hormone deficiencies and present with hypoglycemia, micropenis Laboratory Findings Screening Programs for Neonatal If TSH>20mU/L, hypothyroidism is suspicious Serum FT3, FT4, TSH Measurement Primary hypothyroidism: TSH T4 Secondary hypothyroidism: TSH T4 normal value FT3 2.3~6.3 pmol/L FT4 10.3~24.5pmol/L TSH 0.4~4.0mIU/L TRH Stimulation Test Objective To diagnosis secondary hypothyroidism Methods TRH 7μg/kg iv,TSH was measured at 0, 15, 30, 60 and 90 min after injection. Pituitary Hypothyroidism subnormal TSH response Hypothalamus Hypothyroidism Delayed TSH response Skeletal x-ray Bone age is delayed. Bone age < Chronologic age Location: < 6m knee >6m wrist B ultrasound scanning for thyroid gland ECG may show low voltage P and T waves with diminished amplitude of QRS complexes. Cholesterol level is usually elevated. 14岁 女孩 骨龄 7岁 Differential Diagnosis ¾Rickets ①No mental retardation ② Bone age is normal ③ No characteristic facies ¾Trisomg-21 (Down’s syndrome) ① Retardation of growth and development ② No myxedema ③ Form another characteristic facies 佝偻病 21-三体综合征 Differential Diagnosis ¾Growth Hormone Dificiency ①The extremities are well proportioned ②Intelligence is normal ¾Congenital Giant Colon Distension, constipation ¾Achondroplasia Treatment Principle ¾Treatment of hypothyroidism requires exogenous thyroid hormone. ¾It should be used early, whole life, adequate dose, and from smaller dose to adequate dose. Sodium-L-thyroxine (L-T4) Newborn 10 μg/kg · d Infant 6~8 μg/kg · d Child 5μg/kg · d Dry Throid Starting dose Infant 5~10mg/d Child 10~20mg/d Every 2~4 weeks add 5~10mg/d Constant dose 4~8mg/kg·d Follow Up The best guide to adequacy of therapy is periodic measure of circulating levels of T4 and TSH. The history and physical examination are important in follow up. The growth rate should accelerate within a few months after therapy. Overtreatment produces thyrotoxicosis. Prognosis ¾ Early diagnosis and adequate treatment from the first weeks of life results in normal linear growth and intelligence comparable with that of unaffected siblings. ¾ Delay in diagnosis, inadequate treatment, and poor compliance result in variable degrees of brain damage. ¾ Without treatment, affected infants become mentally deficient dwarf.