* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download congenital Hypothyroidism - Baylor College of Medicine
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
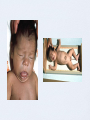
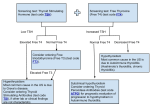
congenital Hypothyroidism Baylor College of Medicine Anoop Agrawal, M.D. Case study- C.V. C.V. is a FT, 4kg, 7 day old hispanic infant girl, born to a 22 yo female, NSVD, GBS negative, APGARS 9/9. You receive a call from the Texas Department of Health stating C.V. has an abnormal thyroid study on her newborn screen. What is your course of action? Background Thyroid development begins around 17th day of gestation. Hypothalamus releases TRH by 20th week of gestation. T3 levels remain relatively low until the 30th week. Fetus is protected by increased activity of deiodinase enzymes in the brain and maternal thyroid hormone transfer across the placenta. Placenta is impermeable to TSH. incidence In US - 1 : 3,500 live births Females to Males - 2:1 ratio Hispanic - 1:2000, White infants - 1:4000, African American - 1:32,000 Children with Down syndrome have 35 fold increase risk. Congenital Hypothyroidism is the most common treatable cause of mental retardation. etiology of C.H. What are the causes that result in lifelong hypothyroidism? Thyroid Dysplasia (agenesis, hypoplasia, or ectopy) - incidence is sporadic in 85% of cases Dyshormonogenesis - inborn error of thyroxine synthesis - 10% of cases Secondary or Central Hypothyroidism (1:25,000 - 100,000) Etiology of C.H. What are the causes of transient hypothyroidism? Maternal or neonatal drug exposure Iodine deficiency (in Europe 1:100 vs. in US 1:50,000 due iodized salt in foods) Maternal antibodies - this form resolves in 1 to 3 months as antibodies are cleared Gestational hyperthyroidism Clinical manifestations macroglossia large fontanelles hypotonia umbilical hernia prolonged unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia hoarse cry Clinical Findings Finffmanifestations 95% of newborn will have no evidence of disease Can be associated with other congenital malformations - mainly cardiac renal and urologic deformities also seen Newborn screening All states screen for hypothyroidism - type of testing is variable: T4 with TSH backup vs. TSH alone 4 million infants are screened annually in US, of which 1,600 will be diagnosed with congenital hypothyroidism Evaluation case - c.v. State TSH screen reported to be >400. C.V. was called into the office the next day. Thyroid function tests were performed via venipuncture. TSH > 54, free T4 - QNS, thyroglobulin <1 Started on thyroxine 10 mcg/kg/day - or 40 mcg per day. Referred to Endocrine Clinic. Treatment Start at 10-15 mcg/kg/day as single daily dose. Initiation of hormone replacement with lthyroxine can wait until diagnostic labs completed. Certain milks and drugs can interfere with thyroxine absorption: soy formulas, iron, calcium, sucralfate, aluminum hydroxide, bile acid sequestrants. Treatment How should thyroxine be administered to the infant? It is available only as a tablet DO NOT HAVE THE PHARMACY COMPOUND THE TABLET INTO A SOLUTION. Tablet should be crushed and given in a small amount of milk or water. Permanent vs. transient How do you determine if child has permanent vs. transient hypothyroidism? After 3 years of age, discontinue therapy for 30 days. If low free T4 and high TSH are found, then permanent is confirmed. Thyroid scan or u/s - uncommonly performed. If TSH rises above 20 mU/L after the first year of life in setting of insufficient T4 therapy, then likely to be permanent. Follow-up care AAP recommends the following schedule: at 2 and 4 weeks after initiation of T4 treatment every 1 to 2 months during first 6 mos. every 3 to 4 months between 6 mos and 3yrs every 6 to 12 months thereafter until growth is complete 2 weeks after any change in dose Follow up care Serum T4 concentration should become normal within 1-2 weeks of treatment. Serum TSH should be normal within 1 month of treatment. Pedi endocrine In HCHD, pediatric endocrinologist available at Casa de Amigos no outpatient pedi endo at BTGH Depending on the type of Medicaid, a child may be referred to either Casa de Amigos or Texas Children’s. conclusion Congenital hypothyroidism is seen most commonly in females, hispanics. Thyroid dysgenesis is most common cause in the US. Iodine deficiency in the maternal diet is #1 cause worldwide. Initiation with hormone replacement should not be delayed. Overall, long term outcomes are good.