* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulatory System - Madison County Schools
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
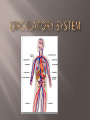
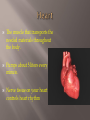
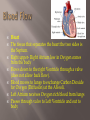
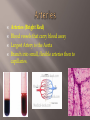
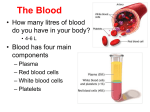
Transports food/ nutrients, oxygen, and chemicals to the cells. Removes Carbon Dioxide and waste from the cells. Transports cells to attack pathogens. The muscle that transports the needed materials throughout the body. Pumps about 5 liters every minute. Nerve tissue on your heart controls heart rhythm Heart The tissue that separates the heart the two sides is the Septum. Right upper- Right Atrium low in Oxygen comes from the body Flows down to the right Ventricle through a valve (does not allow back flow). Blood moves to lungs to exchange Carbon Dioxide for Oxygen (Diffusion) at the Alveoli. Left Atrium receives Oxygen rich blood from lungs Passes through valve to Left Ventricle and out to body Arteries (Bright Red) Blood vessels that carry blood away Largest Artery is the Aorta Branch into small, flexible arteries then to capillaries. Veins- have valves to prevent back flow. Dark Red and low in oxygen Blood is pushed back to the heart Capillaries Very thin-walled to allow diffusion Red blood cells pass single file Function to give up oxygen and take waste away Blood Contains four component Red blood cells, White blood cells, platelets, and plasma Plasma Yellowish fluid 90% water , 10% protein, fats, salts, and gases Regulates amount of water entering and leaving cell Antibodies fight off bacteria, viruses, and other substances Contains clotting factors Red Blood Cells Produced in Bone marrow and live about 120 days 2 million die per second Contains Iron protein (Hemoglobin)attaches to oxygen easily White Blood cells Larger than red blood cells and last months or years Develop in Bone marrow Function is to protect the body from pathogen by surrounding it and digesting it. Produces antibodies Platelets Collects around cuts Produces fibrin that burst apart to form clotting agents Catches blood cells and plasma to create clot/scab They are fragments of cells that are produced in the bone marrow Live 10 days