* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NERVE INJURIES OF THE LOWER EXTREMITY STACY RUDNICKI, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OF
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
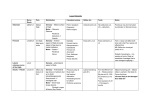
NERVE INJURIES OF THE LOWER EXTREMITY STACY RUDNICKI, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OF NEUROLOGY Dermatomes of the Leg Root Innervation of the Leg • Hip Flexion – L 1, 2, 3 • Knee Extension – L 2, 3, 4 • Foot Dorsiflexion – L 4,5 • Foot Plantar Flexion – S1, 2 • Knee Flexion – L5, S1, S2 • Hip Extension – L5, S1, S2 Clinical Principles • Detecting subtle weakness – Get up from squat • Quadriceps/Gluteus maximus – Stand on tip toes • Gastrocnemius/Soleus – Stand on heels • Tibialis Anterior Reflexes • Knee Jerks - evaluates – Quadriceps muscle – Femoral Nerve – Primarily L4 nerve root (also L2, L3) • Ankle Jerk - evaluates – Gastrocnemius muscle – Tibial Nerve – Primarily the S1 nerve root (also S2) CASE 1 History • 20 yo college student involved in an MVA • She suffers multiple pelvic fractures • She complains of weakness and numbness of the right leg • She is aware that her right foot is “dropped” relative to the left, and that she must lift her foot up higher to clear her toes Exam • She has weakness of: – Foot dorsiflexion – Foot eversion – Toe extension • Strength is normal in: – Foot plantar flexion – Foot inversion – Toe flexion • There is just a hint of weakness in knee flexion SENSORY LOSS Localization Finding Involved Ft Dorsiflex Grt toe ext Toe ext Foot eversion Knee flex Spared Foot plant flex Toe flex Foot inv Muscle Nerve Root TIB ANT EHL EDL, EDB FIB L, B Mult FIB FIB FIB FIB TIB/Fib L4,5 L5 L4,5 L4,5 L5S1S2 GASTROC, TIB SOLEUS FDL/FDB TIB POST TIB TIB S1,2 L5,S1 L4,5 Localization Finding Involved Ft Dorsiflex Grt toe ext Toe ext Foot eversion Knee flex Spared Foot plant flex Toe flex Foot inv Muscle Nerve Root TIB ANT EHL EDL, EDB FIB L, B Mult FIB FIB FIB FIB TIB/Fib L4,5 L5 L4,5 L4,5 L5S1S2 GASTROC, TIB SOLEUS FDL/FDB TIB POST TIB TIB S1,2 L5,S1 L4,5 Common Fibular (Peroneal) Nerve Common Fib Short head BF Deep Fib Superficial Fib Fib Longus Fib Brevis Tib Ant EHL Fib Tertius EDB Differentiating b/w L5 radiculopathy and Fibular Neuropathy • Motor exam – Foot inversion - Posterior tibial muscle • Spared - Fibular neuropathy • Involved - L5 • Sensory exam Sensory loss in deep fibular, common fibular, and L5 disease Final Diagnosis Sciatic neuropathy with selective involvement of the fibular (peroneal) nerve fibers at the level of the pelvis Pearl: The fibular component of the sciatic nerve is more susceptible to traumatic injury than the tibial component - “false localization” CASE 2 History • The patient is a 45 yo man who complains of burning pain in his right lateral thigh • He is otherwise healthy, though over the last 2 years, he has gained 30 pounds because he can’t find time to exercise Exam • He has normal strength in all muscles of his leg • Reflexes are normal SENSORY LOSS Localization Finding Muscle Nerve Root Sens loss -- Lat fem cut <<L2 Final diagnosis Lateral femoral cutaneous neuropathy (AKA: Meralgia Parasthetica) Pearls: This nerve does not come from the femoral nerve but rather the L-S plexus There is no motor component It is trapped as it crosses the pelvic brim, and wt loss or gain can precipitate sxs CASE 3 History • A 27 yo man is shot at multiple sites in the thigh, popliteal fossa, and foot • He complains of burning pain in the foot and weakness of the foot Exam • He has weakness of: – Foot plantar flexion – Foot inversion – Toe flexion • Strength is normal in: – Knee flexion – Foot dorsiflexion – Foot eversion • His foot has a “cocked up” appearance and is everted compared to the other foot SENSORY LOSS Exam Finding Involved Ft plant flex Toe flex Foot inv Sens loss Spared Ft dorsiflex Foot ever Knee flex Muscle PN Root GASTROC FDL, FDB POST TIB ---- TIB TIB TIB MP+LP (tib) S1, S2 L5, S1, S2 L4, L5 <S1 TIB ANT FIB L, B, T HS SHBF FIB (per) L4,5 FIB (Per) L5S1 SCIATIC L5, S1, S2 (Tib and Fib) Exam Finding Involved Ft plant flex Toe flex Foot inv Sens loss Spared Ft dorsiflex Foot ever Knee flex Muscle PN Root GASTROC FDL, FDB POST TIB ---- TIB TIB TIB MP+LP (tib) S1, S2 L5, S1, S2 L4, L5 <S1 TIB ANT FIB L, B, T HS SHBF FIB (per) L4,5 FIB (Per) L5S1 SCIATIC L5, S1, S2 (Tib and Fib) Sciatic Nerve in Thigh/ Tibial Nerve in Leg Sciatic Nerve Semitendonous Semi Membranous Add Magnus Tibial Nerve Gastroc, Med Soleus Tibialis Post FDL Med Plantar AH, FDB, FHB Biceps Long Hd Biceps Short HD Common Fib Nv Popliteus Gastroc, lat FHL Lateral Plantar ADM, FDM, AH, Int Final Diagnosis Tibial neuropathy at the popliteal fossa Pearl: The appearance of the foot at rest may help distinguish b/w a fibular and a tibial neuropathy - unopposed action of spared muscles CASE 4 History • An 81 yo man with diabetes mellitus complains of onset of deep aching pain in his right thigh that evolved over a few weeks • He is having trouble walking because his knee “gives out” • He complains of numbness on the top of his leg Exam • He has weakness of: – Hip flexion – Knee extension • He has normal strength of: – Hip adduction – Hip abduction – Foot dorsiflexion/plantar flexion • His knee jerk is absent, his ankle jerk is preserved SENSORY LOSS Localization Finding Hip flex Knee Ext Sens Loss Hip Add Hip Abd Foot DF Foot PF Muscle IP/Rec Fem Quads --ADD L, B, M Add M Gl Med/Min Tib ant Gastroc/sol PN Fem Fem Fem Obt Sciatic Sup Glut Fib (Per) Tibial Root L1,2,3 L2,3,4 L2-4 L2,3,4 L5, S1 L5, S1, S2 L4,5 S1,S2 Localization Finding Hip flex Knee Ext Sens Loss Hip Add Hip Abd Foot DF Foot PF Muscle IP/Rec Fem Quads --ADD L, B, M Add M Gl Med/Min Tib ant Gastroc/sol PN Fem Fem Fem Obt Sciatic Sup Glut Fib (Per) Tibial Root L1,2,3 L2,3,4 L2-4 L2,3,4 L5, S1 L5, S1, S2 L4,5 S1,S2 Femoral nerve Iliopsoas Sartorius Rectus Femoris Vastus Lat Vastus inter Vastus Med Pectinius Distinguishing b/w a femoral neuropathy and L2 or L3 radiculopathy • Motor exam – Thigh adduction (obturator nerve) • Spared with a femoral neuropathy • Involved with L2,3 disease • Sensory exam – Loss extends below the knee (medial foreleg) with femoral neuropathy • Saphenous nerve Final Diagnosis Femoral Neuropathy Related to Diabetes Mellitus Pearl: The femoral nerve is also liable to injury during procedures involving the femoral artery or vein CASE 5 History • A 27 yo body builder complains of a 4 week history of low back and leg pain • Pain travels down the back of the leg and into the sole of the • He is unaware of weakness and he continues to lift weights Exam • His routine strength exam is normal • He can stand on his heels with ease • He can stand on his tiptoes on the right but not on the left • His left ankle jerk is absent, right is normal • Sensory exam – Decreased sensation of the sole of the foot, lateral distal leg, and lateral dorsum of the foot Localization Finding Muscle PN Stand toes Abs AJ Sens GASTROC/SOL TIB S1,2 GASTROC/SOL TIB S1,2 --MP, LP, SU S1 Stand Heels Foot Inv TIB ANT POST TIB FIB TIB Root L4,5 L4,5 Localization Finding Muscle PN Stand toes Abs AJ Sens GASTROC/SOL TIB S1,2 GASTROC/SOL TIB S1,2 --MP, LP, SU S1 Stand Heels Foot Inv TIB ANT POST TIB FIB TIB Root L4,5 L4,5 Differentiating b/w radicular disease and focal tibial neuropathy • Back pain that radiates into the leg highly suggestive of radicular process • Tibial nerve also innervates the foot inverters yet these are spared • Spontaneous (ie not associated with penentrating trauma) tibial neuropathies would be very unusual Final diagnosis S1 radiculopathy related to a herniated disc Pearl: The term sciatica is a misnomer - it is really a root based process, not one of the sciatic nerve Particularly in large muscles, weakness may be subtle and hence easily missed Final Comments • Overall, nerves in the leg are less liable to chronic compression/entrapment compared to those in the arms • Most common entrapment in the leg is a fibular (peroneal) palsy at the fibular head – May get the common, superficial, or fibular (peroneal) nerve • Traumatic nerve injuries related to penetrating injury / bony trauma (hip / pelvic fxs) are seen