* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BELLWORK
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
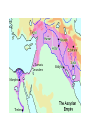
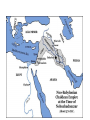
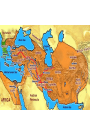
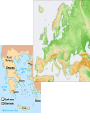
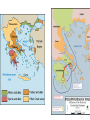
BELLWORK 8/31 1. Explain the causes & effects of the Israelites move to Egypt. 2. Who were the Chaldeans? 3. Describe the strengths of the Persians. 4. Define tyrant. 5. Define oligarchy. 6. THINKER: What is a democracy? (HINT: The U.S. government is a democracy) Middle Eastern Empires • The Israelites gave the world their language, law, and religious beliefs, but they lacked the military power of their neighbors. • Eventually, four warlike empires with strong armies came to rule over the Fertile Crescent. • Why do you think so many civilizations fought to control the Fertile Crescent? • Hittites • Assyrians • Chaldeans • Persians Hittite Empire – 2000BC Assyrian Empire – 650BC Chaldean Empire – 612 BC Persian Empire – 539 BC Ancient Greece • The Greeks took over the Mediterranean region and contributed greatly to the way we live today. • Ancient Greece included the southern part of Europe’s Balkan Peninsula and islands in the Aegean Sea. • Greece’s mountain ranges protected against invaders but also limited communication. • Greece is surrounded by sea, which encouraged the Greeks to become traders, and expand their empire. Greek Civilization • Originated in Minoan and Mycenaean civilizations between 3000BC to 1000BC. • Early on, they developed legends of gods and heroes. • Main themes throughout Greek civilization: bravery, honor, dignity, and the love of beauty. • In religion, the Greeks worshiped gods and goddesses Temple built for Apollo (God of music, prophecy, archery & medicine) – 4th Century B.C. The Polis • Polis, or city-state, emerged as the political unit of Greek civilization. • A Polis included a city and surrounding villages and fields. • Citizens within a polis government could vote, hold public office, own property, and speak for themselves in court. • In return, they were expected to defend the polis in time of war. • Greek women had no political or legal rights. Greek Government • By the 700s BC, Kings were losing their powers and being challenged by lower classes. • As unrest increased, tyrannies arose in the citystates. (Tyrant: one man who seized power and ruled the polis on his own) • Tyrants ruled until 500BC until city-states became either: • Oligarchy: rule by a few wealthy people • Democracy: government and rule by the citizens BELLWORK 9/1 1. How did Greece’s geography impact their civilization? List two ways! 2. Who was Athena? 3. What is a polis? 4. THINKER: What makes Greek civilization different than other ancient civilizations? The Persian Wars • Persia and Greece were enemies that fought for control of trade/travel routes. • Between 490-480B.C., the rivals go to war three times. • 7,000 Greeks (Spartans/Athenians) vs. 100,000 Persians This will be our focus next week, so stay tuned…… The Peloponnesian War • War between Sparta and Athens that lasted from 431BC to 404BC. • Sparta allied with the Persians • A plague struck Athens and killed 1/3 of their population • Persian-financed Spartan navy destroyed Athens fleet. • Athenians surrendered Engineering an Empire • Citizens of ancient Greece constructed many temples, statues, and buildings, but how did they do it? • In this video, you are going to learn about the history of the Greek city-states and the construction of these magnificent structures! • As you watch the video, answer the 15 questions on the worksheet. • Be ready to discuss!