* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plume Poppy
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Indigenous horticulture wikipedia , lookup
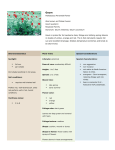
Plume Poppy Herbaceous Perennial Flower Also known as Tree Celandine Macleaya cordata Papaveraceae Family Synonym: Bocconia cordata, Bocconia japonica Tall and striking, Plume Poppy makes a great border background with its unique foliage and spikes of fluffy blooms. Very aggressive and requires considerable effort to keep under control. Site Characteristics Plant Traits Special Considerations Sunlight: Lifecycle: perennial Special characteristics: full sun Ease-of-care: moderately difficult part shade Tends to be more aggressive in large clumps. Control spread over perennial beds. by dividing every 3 to 4 years and deadheading to prevent self-seeding. Height: 6 to 8 feet Soil conditions: Spread: 2 to 3 feet tolerates low fertility rich soil. Hardiness zones: 4 to 9 non-invasive not native to North America Native to China and Japan. requires well-drained soil May be too aggressive if planted in aggressive - Rapidly forms Requires effort to keep from taking shade. deer resistant Bloom time: mid-summer late summer Flower color: white Foliage color: dark green Foliage texture: coarse Heart-shaped leaves are large (8” to 12" wide) and lobed. Shape: upright Shape in flower: flower stalks with upright spikes Fluffy blooms borne along tall, erect stems. Growing Information How to plant: Propagate by seed, division or separation - Divide in the spring to propagate and reduce clump size. Self-seeds readily. Maintenance and care: Very aggressive. Consider planting in its own bed. Divide to keep clump size manageable. Cut back by half in spring for shorter plants and delay flowering. Deadhead to prolong bloom and prevent self-seeding. Usually does not require staking. More growing information: How to Grow Perennials ©2006 Cornell University. All rights reserved.