* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Enterprise Applications - Texas Tech University Departments
Information privacy law wikipedia , lookup
Expense and cost recovery system (ECRS) wikipedia , lookup
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Operational transformation wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
Enterprise content management wikipedia , lookup
Business intelligence wikipedia , lookup
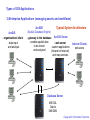
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 26: Enterprise Applications Enterprise Applications of GIS - enterprise applications of GIS are usually designed to manage assets and organization work flows Understanding the GIS Job Market - in 2004 the U.S. Department of Labor identified three new high-growth emerging technologies - they noted that there was an insufficient workforce in the U.S. to meet the demand in these areas - the three technologies were 1) nanotechnology, 2) biotechnology and 3) geospatial technology - to address this workforce issue, they developed the High Growth Training Initiative - the initiative was designed to help meet the workforce demand in these three areas - we can see this demand reflected in the job postings for the GIS industry (e.g. The GIS Jobs Clearinghouse) - while an understanding of GIS is sufficient for some jobs (e.g. GIS analyst), many job listings want much more - these additional job requirements often include: - ArcSDE (Spatial Database Engine) - the gateway to relational database management systems - RDMS (Relational Database Management Systems) - Microsoft SQL, Oracle, IBM DB2 - and the programming skills necessary to manage an enterprise geographic information system (especially web programming skills for the development of Internet mapping applications) Geospatial Technology Competency Model - the Geospatial Technology Competency Model was developed by industry to help people understand the skill sets that are necessary for positions in the geospatial field - the model is structured with basic skills at the bottom and more advanced skills at the top Management Competencies / Occupation Specific Requirements (varies with position) Industry Sector Competencies (either data acquisition, analysis and modeling, or application development) Industry-Wide Technical Competencies (core geospatial abilities and knowledge - this class) Workplace Competencies (e.g. teamwork, creative thinking, problem solving, business fundamentals) Academic Competencies (e.g. reading, writing, math, geography, science, critical thinking, basic computer) Personal Effectiveness Competencies (e.g. interpersonal skills, integrity, dependability, professionalism) Understanding the GIS industry - to understand the GIS industry, we need to recognize that there are three types of GIS applications 1) Project Applications (research) - GIS is used as a tool to complete a specific research project - this is the most common use of GIS in a university environment - GIS is used a research tool in many different disciplines - we also see project applications of GIS used in government, business and industry - e.g. site suitability analysis 2) Department Applications - GIS is used in a single department to support the department’s functions - e.g. to support the daily functions of the tax assessor or water utility department in a city 3) Enterprise Applications - GIS is used throughout an organization - used by multiple departments with data shared across the organization - GIS is used to manage assets and is an integral part of the organization’s workflow Copyright © Kevin Mulligan, Texas Tech University Enterprise Applications - departments within an organization operate on information (data) - this can be a business - or local, state or federal government - or any other large organization - this information (data) is stored in a database - MS Excel - limited to 1 million records and a single user - MS Access - limited to 2 GB of data - multi-user database - most large organizations use a RDMS (relational database management system) - e.g. MS SQL, Oracle, IBM DB2 - unlimited records and data storage - multi-user databases - problem: these database systems are not designed to map information - solution: GIS applications can be developed to manage assets and the workflows within an organization System Architecture - the diagram below shows a typical system architecture - ArcGIS is used for data input and spatial analysis (on internal organization clients) - ArcSDE allows ArcMap/ArcCatalog to connect to a database server - database server stores the data (often using a RDMS such as MS SQL, Oracle or IBM DB2) - ArcGIS Server is used to distribute web applications (to either internet or external Internet clients) Copyright © Kevin Mulligan, Texas Tech University GIST 3300 / 5300 Geographic Information Systems Enterprise Applications of GIS (Managing Assets and Work Flows) Understanding the GIS job market Geospatial Technology Competency Model Understanding the GIS industry Types of GIS Applications Enterprise applications of GIS Geographic Information Systems Enterprise Applications of GIS U.S. Department of Labor - in 2004 the DOL identified three new high-growth emerging technologies - noted that there was an insufficient workforce to meet demand - nanotechnology, biotechnology and geospatial technology - developed High Growth Job Training Initiative - designed to help meet the workforce demand in these three areas Geographic Information Systems Enterprise Applications of GIS GIS Jobs Clearinghouse - we can see this in the job postings for the GIS industry Geographic Information Systems Enterprise Applications of GIS Geospatial Technology Competency Model Geographic Information Systems Types of GIS Applications - to understand the GIS industry - we need to recognize that there are three basic types of GIS applications 1) Project Applications (research) - GIS used as a tool to complete a specific project 2) Department Applications (serving department needs) - GIS is used in a single department to support department functions 3) Enterprise Applications (managing assets and workflows) - GIS is used throughout an organization - multiple departments with data shared across the organization Geographic Information Systems Types of GIS Applications 1) Project Applications (research) - GIS used as a tool to complete a specific project - most common use in a university environment - GIS is used as a research tool - also used in business, government and industry (site analysis) - optimum location of a distribution center Geographic Information Systems Types of GIS Applications 2) Department Applications - GIS is used in a single department to support department functions - e.g. tax assessor or water utility departments in a city Geographic Information Systems Types of GIS Applications 3) Enterprise Applications (managing assets and workflows) - departments within an organization operate on information (data) - either a business – or local, state and federal government - marketing, sales, product distribution, logistics - information stored in a database - MS Excel (limited to 1 million records and 1 user) - MS Access (limited to 2 GB - multi-user database) - most large organizations use RDMS - Relational Database Management Systems (RDMS) - e.g. MS SQL, Oracle, IBM DB2 - unlimited records and multi-user problem: - these database systems are not designed to map information - not designed to conduct any type of spatial query or analysis solution: - GIS applications can be developed to help manage the assets and the work flows within an organization Geographic Information Systems Types of GIS Applications 3) Enterprise Applications (managing assets and workflows) ArcGIS - organizational client - data input and analysis Typical System Architecture ArcSDE (Spatial Database Engine) - gateway to the database ArcGIS Server - enables spatial data - web server Internet Clients to be stored - custom applications web users and analyzed (Intranet or Internet) and map services Database Server MS SQL Oracle IBM DB2 Geographic Information Systems Types of GIS Applications 3) Enterprise Applications - GIS is used throughout an organization - multiple departments with data shared across the organization Geographic Information Systems