* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Civil War - Northwest ISD Moodle
Battle of Perryville wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Cumberland Church wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Malvern Hill wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Stones River wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Big Bethel wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Donelson wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Sumter wikipedia , lookup
Battle of White Oak Road wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Port Royal wikipedia , lookup
Ulysses S. Grant and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fredericksburg wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Appomattox Station wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Roanoke Island wikipedia , lookup
Red River Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Fort Sumter wikipedia , lookup
Second Battle of Corinth wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Lexington wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Antietam wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Cedar Creek wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Vicksburg wikipedia , lookup
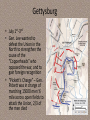
Civil War 1861-1865 Civil War • Causes of the War – States’ Rights, Sectionalism, Slavery • Ft. Sumter • Antietam • Emancipation Proclamation • Gettysburg and the Address • Vicksburg • Appomattox Courthouse • Lincoln’s Assassination Civil War • Causes: – States’ Rights – power belong to states or federal government • Nullification Crisis • Expansion of slavery • Missouri Compromise, Compromise of 1850, KansasNebraska Act, Fugitive Slave Law – Sectionalism – extreme devotion to ones region • Political, Social, and Economical differences – Slavery • South wanted to expand, North want to eliminate North • Advantages – More people – Industrial – More Money – More Railroads – More Telegraph lines • Disadvantages – Weaker Generals – Offensive War – Had to win the War – Support for war divided South • Advantages – Best Generals – Defensive battle – Did not have to win – Fighting on homeland • Disadvantages – Fewer People – Agrarian economy – Little Industry – Few Railroads and telegraph lines Civil War Railroad Lines Fort Sumter • April 12th, 1861 • Confederate officials began seizing federalmint branches, arsenals, and military posts. • Fort Sumter was a Federal outpost in Charleston, SC. • Confederate forces asked for its surrender. • Lincoln refused and sent ships with supplies. Fort Sumter • Confederate cannons began firing on April 12, 1861. • Fort Sumter fell 34 hours later. 85 Union soldiers surrendered, Abner Doubleday fired the first shots in defense of the fort • The Civil War began. 1st Bull Run • Confederate Soldiers defeated the Union soldiers • General Jackson was epitomized by the name Stonewall because of his slow response to aid other troops • Stonewall Jackson also ordered the first rebel yell during the attack • The number of casualties and ferocity of the fighting gave evident that this was not going to be quick, decisive war Shiloh • Union victory after a Confederate surprise attack • 23,000 casualties, level of violence shocked both sides • Realized more that the war would not end quickly • Citizens began sending Grant cigars (10,000) after his victory, he eventually died of lung cancer after being President Antietam • Sept 17, 1862 – 1st battle fought on Union soil • Single bloodiest day in American Military History, more than 22,000 casualties • Although considered a draw, the Union chose to declared victory, though had his Generals chose to advance using their full force the battle would have been different • This “victory” encouraged Lincoln to give his Emancipation Proclamation Emancipation Proclamation • July 1st 1863 after the Union victory at Antietam • Freed the slaves in the South • War now included the freeing of the slaves and preserving the Union • Lincoln believed this was his crowning achievement Ticket out the door • Explain the importance of the battle of Antietam to the Civil War? • What was the purpose of the Emancipation Proclamation? How was this to help the Union? • Which side had the greatest advantage? Why? Gettysburg • July 1st-3rd • Gen. Lee wanted to defeat the Union in the North to strengthen the cause of the “Copperheads” who opposed the war, and to gain foreign recognition • “Pickett’s Charge” – Gen. Pickett was in charge of marching 15000 men ¾ mile across open fields to attack the Union, 2/3 of the men died Gettysburg • Union claimed victory and General Lee offered President Jefferson Davis his resignation, but was refused • This battle turned the tide of the Civil War to that of the Union, due to heavy Confederate loses they would never again advance onto northern soil Gettysburg Address • One of Lincoln’s greatest speeches, 272 words given in less than 2 minutes • Speech given to honor those who died at Gettysburg and consecrate a cemetery Gettysburg Address "Fourscore and seven years ago our fathers brought forth on this continent a new nation, conceived in liberty and dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal. Now we are engaged in a great civil war, testing whether that nation or any nation so conceived and so dedicated can long endure. We are met on a great battlefield of that war. We have come to dedicate a portion of that field as a final resting-place for those who here gave their lives that that nation might live. It is altogether fitting and proper that we should do this. But in a larger sense, we cannot dedicate, we cannot consecrate, we cannot hallow this ground. The brave men, living and dead who struggled here have consecrated it far above our poor power to add or detract. The world will little note nor long remember what we say here, but it can never forget what they did here. It is for us the living rather to be dedicated here to the unfinished work which they who fought here have thus far so nobly advanced. It is rather for us to be here dedicated to the great task remaining before us--that from these honored dead we take increased devotion to that cause for which they gave the last full measure of devotion--that we here highly resolve that these dead shall not have died in vain, that this nation under God shall have a new birth of freedom, and that government of the people, by the people, for the people shall not perish from the earth." Vicksburg • May 18 – July 4 • 6 weeks siege of the City • Surrendered due to lack of food; men were left to eat mules, rats, and boiled leather • During the siege many of the inhabitants lived in caves to hide away from the constant bombing • There were roughly 20,000 casualties combined and the Union took 37,000 POWs • “The Father of Waters again goes unvexed to the sea.” Abraham Lincoln Vicksburg • The victories of Grant and the Union (North) in Vicksburg (gaining control of the Mississippi River and dividing the South) and at Gettysburg were the turning point of the war Ticket out the door • Why was the battle of Gettysburg and Vicksburg important to the Union campaign? Sherman’s March to the Sea • Nov 15 – Dec 21 • After Sherman captured Atlanta (the pride and joy of the Confederacy), the railroad hub and industrial center of the South, he chose to begin his 270 mile march to Savannah, GA • It begun with the burning of Atlanta and the singing of Glory!Glory!Hallelujah • Total War – war plan in which Sherman chose to destroy all things in their path; barns, animals, farms (they did not destroy towns), and to destroy southern morale, making the people of the south feel what war was like, be terrorized and helpless Sherman’s March to the Sea The Surrender • April 9th, 1865 Gen. Lee surrendered to Grant at Appomattox Court House • Lee was defeated by Grant and lost Richmond to the North and attempted to meet up with additional troops in NC but was cut off • Lee and Grants messaging • As Lee left the Courthouse the Union soldiers began to celebrate but Grant stopped them saying “The war is over, the rebels are our countrymen again.” Appomattox Court House • Although the war was officially over the Confederates defeated the Union at the battle of Palmito Ranch in Texas a month later Lincolns Assassination • At wars end John Wilkes Booth, a southern sympathizer assassinated Lincoln at Fords Theatre during the comedy show My American Cousin. This began the largest federal man hunt that resulted in the killing of the assassin and the hanging of his coconspirators Ticket out the door • Explain how the Civil War ended? • How did Lincoln want to treat the Confederates? Why? • Create a flow map of the battles. Include a picture with a brief caption 1. Explain the importance of the battle of Antietam to the Civil War? 2. What was the purpose of the Emancipation Proclamation? How was this to help the Union? 3. Which side had the greatest advantage? Why? 4. Why was the battle of Gettysburg and Vicksburg important to the Union campaign? 5. What was the name of the Lincolns military strategy to defeat the Confederates • Create a flow map of the battles. Include a picture with a brief caption Quiz 1. Complete flow map Ft. Sumter to Shermans march to the sea 2. Which side do you think had the greatest advantage? Why? 3. What was the importance of the Emancipation Proclamation? 4. Who issued the Gettysburg Address? 5. What was the first battle of the Civil War? 6. What battles were considered the turning point of the War Reconstruction Begins TEST 1. Summarize the important points of Lincoln’s 1st and 2nd Inaugural Address 2. Summarize the Union’s War strategy and how it was implemented? 3. What battles turned the tide for the War? How might the War ended had the Confederates won those battles? Why?