* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download LAB #2: First-Order System Behavior
Spectral density wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope types wikipedia , lookup
Tektronix analog oscilloscopes wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
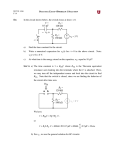
LAB #2: First-Order System Behavior Equipment: Oscilloscope (Tektronix 2211) Digital Multimeter (FLUKE 8050A) Function Generator (Tektronix CFG250) 1.5 V Battery RC Box Objectives: In this experiment you will learn to use the transient-capture (single-shot) feature of the oscilloscope, and you will apply this technique to study the response characteristics of a first-order system (in this case, an RC network). You will also apply your knowledge of uncertainty analysis in evaluating the accuracy of your measured data. 1 Preparation 1.1. Scope Setup: You will use CHannel 1. Be sure that all buttons in both the “cursor” section and the “acquisition” section are Out. In the “vertical” (i.e., CH 1 VOLTS/DIV) section, set the switch to DC and the input amplitude knob to 0.5 volt/div. In the “time” (i.e., SEC/DIV) section, set the sweep rate to 0.1 ms/div. In the “trigger” section, set the SLOPE switch to positive slope and the MODE switch to AUTO. Now turn on the scope. You should see a line (trace) on the scope screen. 1.2. First-Order System: As a first-order system we will study the basic RC circuit is shown in Fig. 1. (See also the class handout entitled REVIEW OF ELECTRIC NETWORKS.) We will study how the system responds to a transient input in the form of a step voltage and how it responds to sinusoidal input. Here, system response refers to how the output voltage across the capacitor, vo(t), varies with time. 1 2 Transient Response of a First-Order System 2.1. Find the RC Box (a small box with three capacitors and five resistors). The arrangement of capacitors and resistors in the box is shown in Fig. 2. The units for the capacitors are microfarads ( +/- 10%), and the units for resistors are ohms ( +/- 10%). Note that the time constant of the circuit is = RC. Connect the (+) terminal of the battery to the black connector of the 10 K. resistor, and the ( - ) terminal of the battery to the 0.01 F capacitor (black connector). Connect the 0.01 F capacitor (black) to the ground terminal of the scope. Connect the red terminal of the 0.01 F capacitor to the CH 1 input terminal. Now you have completed the circuit for measuring the output voltage across the 0.01 F capacitor. Ask your Lab Instructor to check your setup if you are not completely sure that what you have done is correct. Figure 1: A simple RC circuit. 2 2.2. Switch the switch for CH 1 to GND. The line on the screen is your reference line (i.e., v(t) = O V). Put the line at a convenient place by turning the POSITION knob above the CH 1 VOLT/DIV dial. Now, move the switch for CH 1 back from GND to DC. You will see a shift of the line. The amount shifted (approximately 1.4 volts) is the output DC voltage from your RC circuit. Now, disconnect the line from the (+) terminal of the battery to the resistor of your RC circuit by pulling out the banana plug from the black resistor post. You are now ready to measure the transient response of the RC circuit. Switch the MODE switch in the “trigger” section to SGL SWP, the COUPLING switch to DC, and the SOURCE switch to CH 1. (Remember that your circuit output is connected to CH 1.) At this time the scope trace should disappear from the screen. At the top edge of the scope screen there is a display of the Trig voltage. Turn the LEVEL knob in the trigger section to set the trigger voltage. Note that the trigger voltage should be set at less than the DC voltage (1.4 V) from your RC circuit. (Try to set the trigger voltage to 0.4 V.) Push the RESET button, and a green ready light should turn on. Now apply a step voltage to the RC circuit by quickly, but firmly, touching the banana plug (one end of which is connected to the (+) terminal of battery) to the black terminal of the 10 K resistor. You should see a signal flashing on the screen of your scope, and the trigger ready light will go off. However the signal is too quick for you to really see, so you will need to store the signal on the screen. Push to On (In) the 25% button and the STORE button in the ACQ section. Now you are ready to store your transient signal. Be sure that the green ready is on. Generate a transient signal by quickly, but firmly, making contact between the banana plug and the resistor terminal. (This is a crude switch.) On the screen you should see a typical transient response signal of the first-order system. If you are not satisfied with the signal, press the RESET button and try again. When you get an acceptable first-order response trace on the scope, ask the Lab Instructor to look at it; then sketch the scope trace in your lab notebook. Be sure that you: (a) record the sweep speed and the amplitude settings of the scope, and (b) record the values of R and C for your circuit. Use the V and T cursors to measure the time constant, , from the scope trace. 3 You are encouraged to play with the signals by changing the combination of R and C and the scope settings until you are comfortable with the procedure. 3 Frequency Response of a First-Order System 3.1. Set the channel selection switches in the “vertical” section to BOTH, NORM, and CHOP so that your scope will display two signals simultaneously. Set the coupling switches for both channels to AC. Set the MODE switch in the trigger section to AUTO. Be sure that all buttons in the cursor and acquisition sections are Out. You should see two traces on the scope screen. Slowly turn the POSITION knob for each channel and observe the vertical movement of the signal trace for each channel. 3.2. “Drive” the RC circuit with a sine wave by using a BNC-to-dual-banana-plug cable to connect the output of the function generator to the input of the RC box (just as you did in the transient signal study). Then, connect the output from the RC box to CH 1, and the output from the function generator to CH 2 of your scope. Set both CH 1 and CH 2 VOLTS/DIV dials to 1 V/div and the SEC/DIV to 0.1 ms/div. 3.3. Set the frequency dial of the function generator to a sine wave of 1000 Hz. Turn on the function generator. You should see two signals. The signal in CH 1 is from your RC circuit, and the signal in CH 2 is from the function generator used to drive your RC circuit. Thus, the signal in CH 1 is the output signal, vo(t), and the signal in CH 2 is the input signal, v(t). 3.4. Starting at a frequency several times lower than l/RC, drive the RC circuit with a sine wave and compare the amplitude and phase angle of the input and output signals. Increase the frequency and record frequency, the two amplitudes, and phase angle between the two sine waves for at least five frequencies. You may need to adjust the amplitude and time settings for a good display of signals. (A good practice is to show two cycles of a signal on the screen.) Be sure to make use of the amplitude-measuring (V) and time-measuring (T) cursor features of the scope. 4 3.5. Drive your RC circuit with a square wave and observe the differences between the input and the output signals. Sketch the output shape at several different frequencies and explain. 4 Homework 1. Using the nominal resistance and capacitance values, calculate the time constant, , for the RC circuit. Also, calculate the probable error in the computed time constant due to uncertainties in the values of R and C. 2. Determine a measured time constant from your lab data. Discuss the agreement (or disagreement) between the predicted and measured time responses in light of your error analysis. 3. Discuss how poor response characteristics of a measuring system could introduce errors into measurements. Discuss the importance of knowing the time constant for a first-order system. 4. Most temperature sensors behave as first-order systems in responding to temperature changes. To assure that the measured temperature will always be within 2% of the actual value, what time constant would you specify for a temperature sensor to be used in a gas turbine engine in which the temperature may fluctuate sinusoidally at a frequency of up to 10 Hz. 5. Plot the ratio of (Output Amplitude)/(Input Amplitude) and the phase angle data collected in Step 3.4, and discuss their significance in light of the theoretical behavior of first-order systems. RC. Revised 9/97; PDF 11/99; MSWORD 1/00. 5