* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac physiology wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Hormonal contraception wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Graves' disease wikipedia , lookup
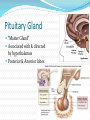
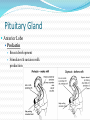
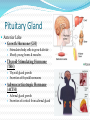
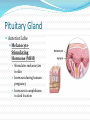
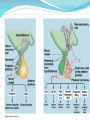
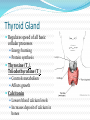
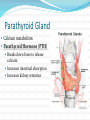
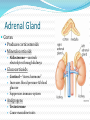
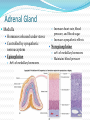
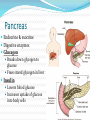
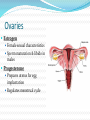
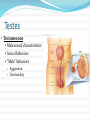
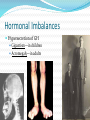
Integration & Control: The Endocrine System Endocrine System Works w/ nervous system to control all functions of the body Endocrine glands Ductless Hormones Pineal, pituitary, thyroid, pancreas, etc. Exocrine glands Ducts Non-hormones Salivary, sebaceous, sweat Endocrine System Hormones Chemical signals Carried in bloodstream Affect cells away from gland Homeostatic Hormones Positive feedback Increase in hormone stimulates further secretion Uterine contractions stimulate oxytocin Negative feedback Increase in hormone inhibits further secretion Thyroid Stimulating Hormone produces T3/T4 Hormones Peptide hormones Water soluble Mostly protein Attach to cell membrane Trigger secondary messenger within cell Epinephrine, oxytocin, antidiuretic hormone (ADH), etc. Hormones Steroid hormones Water insoluble Cholesterol-based Cross into cell Bind to receptors in cytoplasm or nucleus Estrogen, testosterone, cortisol, etc. Pituitary Gland “Master Gland” Associated with & directed by hypothalamus Posterior & Anterior lobes Pituitary Gland Posterior Lobe Stores secretions from hypothalamus Oxytocin Uterine contractions Milk “let down” ADH Conserves water Kidney tubules reabsorb water Pituitary Gland Anterior Lobe Prolactin Breast development Stimulates & sustains milk production Pituitary Gland Anterior Lobe Growth Hormone (GH) Stimulates body cells to grow & divide Mostly young bones & muscles Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Thyroid gland growth Secretion of thyroid hormones Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) Adrenal gland growth Secretion of cortisol from adrenal gland Pituitary Gland Anterior Lobe Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) Stimulates estrogen secretion Stimulates egg production (females) Stimulates sperm production (males) Luteinizing Hormones Stimulates ovulaton Stimulates progesterone secretion (females) Stimulates testosterone secretion (males) Pituitary Gland Anterior Lobe MelanocyteStimulating Hormone (MSH) Stimulates melanocytes in skin Increases during human pregnancy Increases in amphibians in dark location Pituitary Gland Anterior Lobe Endorphins Natural pain-killers Sense of well-being Strenuous exercise, excitement, orgasm “Runner’s High” Thyroid Gland Regulates speed of all basic cellular processes Energy burning Protein synthesis Thyroxine (T4), Triiodothyronine (T3) Controls metabolism Affects growth Calcitonin Lowers blood calcium levels Increases deposit of calcium in bones Parathyroid Gland Calcium metabolism Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) Breaks down bone to release calcium Increases intestinal absorption Increases kidney retention Adrenal Gland Cortex Produces corticosteroids Mineralocorticoids Aldosterone—controls electrolytes through kidneys Glucocorticoids Cortisol—“stress hormone” Increases blood pressure & blood glucose Suppresses immune system Andgrogens Testosterone Cause masculine traits Adrenal Gland Medulla Hormones released under stress Controlled by sympathetic nervous system Epinephrine 80% of medullary hormones Increases heart rate, blood pressure, and blood sugar Increases sympathetic effects Norepinephrine 20% of medullary hormones Maintains blood pressure Thymus Gland Large in infant Increases until puberty Shrinks until adulthood Thymosin Normal development of immune system Pineal Gland Melatonin Regulates biological clock Regulates sleep cycle “Lower” vertebrates, cells resemble photoreceptor cells of eye May be triggered by light Pancreas Endocrine & exocrine Digestive enzymes Glucagon Breaks down glycogen to glucose Frees stored glycogen in liver Insulin Lowers blood glucose Increases uptake of glucose into body cells Ovaries Estrogen Female sexual characteristics Sperm maturation & libido in males Progesterone Prepares uterus for egg implantation Regulates menstrual cycle Testes Testosterone Male sexual characteristics Sexual behaviors “Male” behaviors Aggression Territoriality Other organs Kidneys Erythropoietin—stimulates red blood cell production Skin Calcidiol—inactive form of vitamin D Skeletal muscle Thrombopoietin—stimulates platelet formation Adipose (fat) Leptin—decrease appetite, increase metabolism Hormonal Imbalances Hypersecretion of GH Gigantism—in children Acromegaly—in adults Hormonal Imbalances Hyposecretion of GH Pituitary dwarfism—children, slow bone growth Hormonal Imbalances Hypothyroidism Fatigue Thin, brittle hair & nails Weight gain Poor muscle tone Goiter Inflammation of thyroid gland Can be due to iodine deficiency Hormonal Imbalances Hyperthyroidism Weight loss Ravenous appetite Irritability, anxiety Fatigue Hyperactivity Graves’ disease Protrusion of eyes Edema (fluid accumulation) Thickening of skin Goiter Hormonal Imbalances Diabetes insipidus Deficiency of ADH Increased urine output Chronic dehydration risk Diabetes mellitus Deficiency of insulin High blood glucose levels Type I—usually before age 20, pancreas cells stop producing, autoimmune Type II—usually after age 40, insulin levels normal, cells don’t respond to it Hormonal Imbalance Addison’s disease Adrenal gland produces insufficient glucocorticoids Low blood pressure Darkening of skin Vomiting, diarrhea Mood, personality changes Cushing’s disease Overproduction of glucocorticoids Weight gain Thin skin, often stretched Muscle weakness Hirsuitism (horses & humans) Hyperglycemia