* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
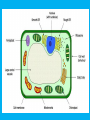
Introduction to Plants Botany and Ecology Warm Up: • Describe your experience growing plants throughout your life. Would you consider yourself to be a novice, intermediate, or experienced gardener? How do you think this will impact your performance in this course? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v =nJdLVua5z8E Botany • Comes from the Greek word for “Plant” • 1600’s: people began conducting experiments to see how plants grow Botany includes: • Plant systematics • Evolutionary history of plants • Plant anatomy and physiology • Plant morphology • Plant ecology • Plant genetics Why Study Plants? • Photosynthesis Sustains Life on Earth –Oxygen –Food • Medicines • Fuel, Shelter, Paper Products • Why else? 1. Plants are Multicellular Eukaryotes • Multicellular –Composed of many cells • Eukaryotes –Cells have a nucleus which contains the DNA 2. Almost all plants are capable of photosynthesis • Known as autotrophs • Make their own food • Distinguishes plants from mushrooms (not plants, kingdom Fungi) Plants to avoid when we work around the school grounds… Poison Ivy Stinging Nettle 3. Plants have cell walls composed of cellulose • Cellulose a.k.a. Fiber • A chain of glucose molecules • Gives structure and support to cell walls 4. Plants have 2 Adult Forms of reproduction • Spores –Reproductive cells that can reproduce asexually • Pollen and Egg (male and female parts) –Pollen fertilizes egg to produce an embryo (seed) that develops into an adult. A variety of seeds 5. Plants have a multicellular embryo protected within the female parent (seed) • Prevents embryo from drying out • Distinguishes plants from algae (even though they have chlorophyll most algae are classified as kingdom Protista) Some Plants We will Study • Gymnosperms –Non-flowering seed plants (ferns, pines) http://studyjams.scholastic.com/studyjams/ja ms/science/plants/plants-without-seeds.htm • Angiosperms –Flowering seed plants http://studyjams.scholastic.com/studyjams/jams/scie nce/plants/plant-with-seeds.htm In a seed plant… • The embryo is a miniature plant in an arrested state of development. It will begin to grow when conditions are favorable. • The endosperm is a built-in food supply which can be made up of proteins, carbohydrates, or fats. • The seed coat, a hard outer covering, protects the seed from disease and insects. It also prevents water from entering the seed and initiating germination before the proper time. Plant Cell Diagram • Color all of the cell organelles, following the directions colors for each structure. • Write the function of the following parts on your diagram: • Cell wall, plasma (cell) membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, nucleolus, chloroplast, mitochondrion, vacuole, ribosome, endoplasmic reticulum Warm Up • Recall the plant cell… –What 3 things make a plant cell different from an animal cell? Answers • They make their own food • No cell wall in animals • They contain chloroplasts Vascular Tissue System • What does “vascular” make you think of? Can you guess what this system does? • A continuous system of tissues that conduct water, minerals, and food Xylem • Brings water and mineral nutrients from the roots to the rest of the plants • Forms a tube for water transport Phloem • Moves sugars and other organic nutrients from the leaves to the rest of the plant • Photosynthesis takes place in the leaf, so the phloem transports it to where it’s needed Plants grow at Meristems! • Parts of the plant that grow through Cell Division! • Tips of roots, ends of branches Warm Up What part of a plant GROWS? A. The trunk, from the bottom up B. The roots, from the top down C. The branches, from the ends D. The roots, from the tips E. A & B F. C & D G. All of the above Leaf Characteristic Lab • Choose 5 different leaves to examine Draw a detailed diagram of each leaf. • What differences do you notice between the variety of leaves?