* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 2 Test
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Hotspot Ecosystem Research and Man's Impact On European Seas wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
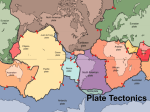
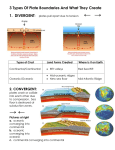
Name: ______________________________ Date: ________________ Marine Science Block: _______ UNIT 2 TEST REVIEW – OCEANS, SEA FLOOR FEATURES, BATHYMETRY & PLATE TECTONICS Topics to study: 1. Oceans a. Major oceans b. Locations of trenches & MOR c. Locations of seas 2. Ocean floor features / topography a. Continental Margin i. Continental Shelf ii. Continental Slope iii. Shelf Break (where shelf & slope meet) iv. Continental Rise v. Submarine Canyon b. Ocean Basin i. Abyssal Plain ii. Abyssal Hill iii. Seamount iv. Guyot v. Island vi. Hot Spots vii. Trenches viii. Mid Ocean Ridge (MOR) ix. Rift Valley 3. Bathymetry – how do we determine the topography of the ocean floor? SONAR 4. Plate Tectonics a. Continental Drift i. Alfred Wegener ii. Theory iii. Pangaea iv. Evidence 1. Puzzle-fit of continents 2. Similar rocks, mountains & fossils v. Why rejected b. Plate Tectonics i. Theory ii. Layers of Earth – core, mantle, crust (composition) 1. Oceanic crust – basalt (dense) 2. Continental crust – granite (less dense) iii. Lithosphere & asthenosphere (physical characteristics) iv. How many plates v. Evidence 1. Location of volcanoes & earthquakes 2. Magnetic patterns 3. Seafloor spreading (seafloor created at MOR, destroyed at trenches) 4. Older rocks away from MOR 5. Hot spot volcano patterns (Hawaiian islands) vi. Plate boundaries 1. Divergent Oceanic-Oceanic 2. Divergent Continental-Continental 3. Convergent Continental-Continental 4. Convergent Oceanic-Continental or Oceanic-Oceanic (Subduction) Unit 2 Test – Oceans, Sea Floor Features, Bathymetry & Plate Tectonics 71% Abyssal Plain Atlantic Ocean Basalt Below Sea Level Continental Drift Continental Margin Continental Rise Continental Shelf Continental Slope Denser Granite Guyot Ice comets & volcanoes Iceland Interconnected Lithosphere Major Ocean Basins Mantle Mid-Ocean Ridge Near Mid-Ocean Ridges Oceanic Ridge Older Older On Continents Pacific Ocean Recycled Sea Floor Spreading Smaller SONAR Southern Ocean Thinner Trench Trench Volcanoes & Earthquakes Younger Percent of Earth’s surface covered by water Smoothest part of the ocean The ocean that is getting wider What oceanic crust is made of How oceanic crust compares to continental crust Theory that continents were once joined together & broke apart Submerged part of the continent Feature at the base of a continent composed of sediments eroded from the continent Shallowest part of the continental margin Steepest part of the continental margin How oceanic crust compares to continental crust What continental crust is made of Large, extinct volcano with a flat top Origin of the ocean Where the mid-ocean ridge rises above sea level Mid-ocean ridges Crust & upper mantle that “floats” on the asthenosphere Arctic, Atlantic, Indian, Pacific, Southern Semi-solid layer of silicon, magnesium & iron, below the crust Divergent plate boundary Where youngest seafloor rocks are found Sea floor is created How continents compare in age to seafloor Age of rocks as you move away from a mid-ocean ridge Where the oldest rock of the planet are found Largest & deepest ocean What happens to seafloor at a trench Occurs at mid-ocean ridges & where new sea floor is created How continental topography compares to oceanic bathymetry Technology that sends sound waves that bounce off the ocean floor to map the ocean’s features Body of water surrounding Antarctica How oceanic crust compares to continental crust Sea floor recycled/destroyed Occurs when an ocean plate sinks back in to the asthenosphere Occur at mid-ocean ridges How oceanic crust compares to continental crust 2