* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Measuring Crest Factor
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
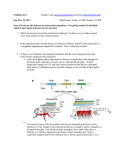
Application Note Measuring Crest Factor Yiu-Fai Kwan Microwave Engineer, Noisecom Abstract This document provides Noise Com’s method of measuring crest factor of a noise source using LeCroy Wavepro 7200 Oscilloscope. Measuring Crest Factor Crest Factor Procedure The Crest Factor (CF) is defined as the ratio of the peak amplitude of a waveform to its RMS value. It is a numerical value without units. The LeCroy Wavepro 7200 Oscilloscope is used for measuring crest factor. This is a four channel oscilloscope, any one channel can be used to perform the measurement. For the following instructions, channel 3 was chosen. 1. Turn the touch screen on. CF is the Crest Factor Vp is the peak voltage Vrms is the RMS voltage 2. Press the “3“ button under “VERTICAL”. 3. Press the “C3” box on screen (on lower left hand corner). Statistical evaluation of related occurring events present always certain kinds of distribution curves. Gaussian distribution, also known as normal distribution, is the most common way events take place. Most white noise sources provide Gaussian distribution of their spectral power. The randomness of noise sources requires a mathematical model that allows calculating the probability density of events. Gaussian distribution right and left of the mean probability is of equal size. Crest factor is also an important quantity for noise sources. It allows calculating the likelihood of unwanted events relative to the mean probability. Such renegade events may cause an overload of an amplifier input, distortion of a signal, or a bit error. Obviously, the fewer of those natural but unwanted events happen, the better. High quality white Gaussian noise sources offer crest factors of up to 18 dB, placing the probability of unwanted events far beyond reasonable measurement capabilities. Application Note 4. Set “Trace on” with a check mark and set the following parameters to: Volt/div = 1.00 V Offset = 0.00 V Bandwidth = full Coupling = DC50 ohm Averaging = 1 sweep Interpolation = Linear Deskew = 0 Probe Atten = divided by 1 Measuring Crest Factor 2 Figure 1 shows the Oscillscope display. 5. Next, press the “Timebase” box to adjust the following parameters: Time/div = 5.00 us Max sample Points = 500 kS Active Channel = 10GS/s Figure 1 Figure 2 shows the Oscillscope display. 6. Press “Math” under “Wavepilot “ on the panel. 7. On the touch screen, press “F1” and set a check mark to “Trace on”. Figure 2 Application Note Measuring Crest Factor 3 8. Set “Source 1” to “C3” and “Operator 1” to “ Histogram” (see Figure 3). 9. At the right side box on screen, press “Histogram” tab. Figure 3 10. Set “Buffer” value to max (2 billion) and “ # Bins” to max (2.00e+3) (see Figure 4). 11. Press “Clear Sweep” on the lower right corner panel. Now, the screen should have two curves. One is the output and the other one is the histogram of the output. 12. Press “Measure” under “Wavepilot”. 13. Set check mark on “Show Table” and “Statistics”. 14. Press “P1” tab and set “Source 1” to “C3”. Figure 4 Application Note Measuring Crest Factor 4 15. Set “Measure” to “Maximum” (see Figure 5). 16. Press “P2” and set “Source 1” to “C3”. Figure 5 17. Set “Measure” to “RMS” (see Figure 6). 18. Press “P3” and press “Math on Parameters”. Figure 6 Application Note Measuring Crest Factor 5 19. Choose the “Math Operator” to “Pn / Pm” (see Figure 7). 20. Make sure the “ON” box of P1, P2, & P3 has a check mark. 21. The max value of P3 is the crest factor ratio, which is the max of P1 divided by the mean of P2. Take the log of the max value of P3 and multiplied by 20. That would be the crest factor of the noise module in dB. In this case, the crest factor is 16.39 dB. Figure 7 Wireless Telecom Group Inc. 25 Eastmans Rd Parsippany, NJ United States Tel: +1 973 386 9696 Fax: +1 973 386 9191 www.noisecom.com © Copyright 2010 All rights reserved. Note: Specifications, terms and conditions are subject to change without prior notice.