* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Abu Bakr
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
The Jewel of Medina wikipedia , lookup
Imamah (Shia) wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Medieval Muslim Algeria wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
Islamic socialism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Shia view of Ali wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
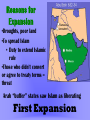
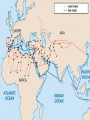
Spread of Islam Mrs. Kirkpatrick Soc. Studies 8 “This day I have perfected your religion for you and completed My favor to you. I have chosen Islam to be your faith.” The Faith •One true God – Allah •Idols must be rejected •Many opposed Muhammad; he Fled mecca for safety •Hijrah: journey to medina •Friend Abu Bakr saved him •Converted people from Medina •United Muslims • Unity • Ummah (religious community) – Single source of authority (Allah) • Military unity • Strong moral and ethical code • Equality How does Islam the Religion become Islam the Empire? Are You Ready? • According to Phase 1, how did Islam spread? • What are the 2 best pieces of evidence to support that Islam spread through conquest? •Islamic community established in Medina •Muhammad settled quarrels between Bedouin clans -Attracted many Bedouin followers •Meccan caravans raided •Battles between Muslims & Umayyad Clan followed - Muhammad was courageous soldier •Treaty (628) allowed visitation to Ka’ba Early Growth Momentum •Muhammad returned to Mecca • 10,000 accompanied him •destroyed idols in Ka’ba •Treated others mercifully •Mecca secured •eventually most of Umayyad Clan converted •Muhammed proclaimed as Prophet •controlled most of Arabian Peninsula Crisis 632: Muhammad dies •No successor •Opinion divided •Caliph = successor of Muhammad – not prophet, but leader of Muslim community Rightly Guided Who should lead after Muhammed? •Abu Bakr? - close friend, early follower - knew Bedouin tribes, tribal histories •Ali ? - cousin, son-in-law - too young to hold position of such responsibility Abu Bakr: 632-634 Abu Bakr elected Problem: 1. Arabic tribes strayed from ummah; some renounced faith • Resistence to paying zakat 2. False prophets appeared Solution: 1. military troops put down revolts; collected taxes 2. Abu Bakr said secession from Ummah was = to not believing in Allah Reasons for Expansion •Droughts, poor land •To spread Islam • Duty to extend Islamic rule •Those who didn’t convert or agree to treaty terms = threat Arab “buffer” states saw Islam as liberating First Expansion 634: Umar named by Abu Bakr as successor Expanded ummah Overthrew Persian Empire took parts of Byzantine Empire Expanded to parts of North African coast Umar Jihad Umar added strength to belief in (lesser) jihad Took city of Jerusalem Umar named 2 types of territory: - Dar al-Islam = land where Islam is practiced - Dar al-Harb = land from which attacks are launched against Islamic rule Battle of Qadisiya 636 Muslims vs. Sassanids •Muslims outnumbered but prevail •Lead to defeat of Persian Empire Government under Umar •Non-Muslims could practice own beliefs •Non-Muslims protected; called “dhimmi” •Both Muslims & non-Muslims taxed for police, education, army, etc. •Non-Muslim tax = jizya •Jerusalem shared by Muslims & non-Muslims •Garrison posts established Uthman • Umar assassinated by Persian rebels • Uthman appointed by council - was Muhammad’s son-in-law - was powerful member of Umayyad Clan • Uthman completed compiling the Qu’ran Muhammad Married to Khadijah Married to Aisha Zaynab Ruqayah Om Kolthoom Fatimah Married to cousin Al’Ass Married to Uthman Married to Uthman Married to Ali •Quraysh = tribe: Powerful in Mecca •Hashim = Clan of the Quraysh tribe • Muhammad = member of Quraysh tribe, Hashim clan •Umayyad = Clan of the Quraysh tribe •Powerful in Mecca after hijrah; managed Ka’ba trade Towards Crisis •Financial problems slowed pace of conquest •Some Muslims rich from spoils; others claimed wealth was against religion - led to loyalties split between clans and ummah •Uthman accused of nepotism Open Conflict • Uthman replaced some governors of provinces with relatives – ensured loyalty • Rebels from Egypt went to Medina to protest • Rebels murdered Uthman • Civil war broke out after Uthman’s murder ALI • Ali named caliph = Muhammad’s cousin and son-inlaw • Umayyad clan (Uthman) clashed with Hashim clan (Ali) despite common faith – Some of Ali’s supporters were rebels against Uthman – Ali replaced governors appointed by Uthman with his own people Mu’awiya • Mu’awiya = governor of Syria - stirred up bad feelings - wanted revenge for Uthman - challenged Ali’s authority to rule - called himself caliph Battle of Siffin •Ali to move capital to Kufa (Iraq) •Ali’s armies fought Mu’awiya’s •Ummah intermediaries called on both to resign •Ali refused to follow decision Result? •Ali ruled as caliph in Persia & Iraq •Mu’awiya ruled as caliph in Syria & Egypt Civil War • Assassination attempts on both caliphs • Only Ali was killed • Led to more fighting about who succeeds as caliph Ali Mu’awiya Husan Yezid Gave up right to rule Hussein Killed at Karbala by Yezid’s troops Sunni/Shi’a Split Shi’as Believe leaders must be part of Muhammad’s bloodline Believe Muhammad chose Ali as his successor Do not recognize 1st caliphs (Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman) 12 Imams (starting with Ali) = rightful leaders of Islam Awaiting return of 12th Imam (al Mahdi) Hussein = martyr Sunni’s Believe any devout Muslim can become caliph Each Muslim has a direct relationship with Allah Believe Muhammed did not specify successor Recognize 1st caliphs as “rightly guided” Al-jama’ah = differences of opinion should be tolerated Sunni & Shi’a Modern Population A Closer Look http://www.cfr.org/peace-conflict-and-human-rights/sunni-shia-divide/p33176#!/?cid=otr-marketing_url-sunni_shia_infoguide Umayyad Dynasty 661-750 •Muwawiya begins dynasty after civil war •Spain conquered 711 •Central Asian strongholds – Samarkand •Capital moved to Damascus, Syria •Governors ruled provinces, though central control from Damascus •Attracted indigenous people who adapted Arab culture, converted to Islam Finances • 1/5th of all spoils collected by Muslims • Non-Muslims = dhimmis • Dhimmis paid security tax called jizya; other taxes - taxed at higher rate • Muslims paid zakat; other taxes at lower rate • Eventually only paid zakat! • $ went to canals, mosques construction, public projects -zakat went to supporting the poor Umayyad Decline • Umayyad rulers lived luxurious lifestyle • Policy of Arab superiority upset many • Taxed recent converts - violated laws of Qu’ran - most non-Arabs • Disgruntled groups united (Persians, Shi’as) through Abbasid family Abbasid Revolution •Those dissatisfied with Umayyad rule united over years of planning •Built army; lead revolt •Merv secured, then army pushed west •Kufa secured •Abul Abbas = 1st Abbasid caliph (749) The Abbasids 750-1206 •All Umayyad family executed after 750 •Only Abd al Rahman escaped to Spain; established Umayyad rule •Abbasids moved capital to Baghdad, Iraq Are You Ready? What made Muslims such superior traders? Golden Age 9th – 13 Centuries •Major contributions in sciences, law, industry, arts, agriculture, technology •House of Wisdom: Baghdad •Scholars came from all over to study •Classics preserved •New innovations Innovations Mathematics: Arabic Numerals Algebra Graph Paper Trade: Paper Checks Sufi’s Sufi’s = mystics • Followed life of poverty • Kept Muslims focused on Qu’ran • Active missionaries – Brought Islam to remote areas • Some felt Sufi rituals went against Qur’an Abbasid Decline •Leaders separated themselves from general population •Chose foreigners as advisors, officials •Turned away from Shi’a •Mamluk army replaced Persian and Arab army; caused resentment •Political, religious and cultural unity disintegrated