* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 6.1.1.A AtomicStructurex
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
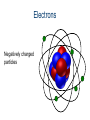
Atomic Structure Atomic Structure • • • • • • • Elements Atoms Components of an Atom Atomic Number Periodic Table of Elements Electrons Electron Orbits Elements The simplest form of matter Atoms The smallest piece of an element that contains all properties of that element Components of an Atom Nucleus The center portion of an atom containing the protons and neutrons Protons Positively charged atomic particles Neutrons Uncharged atomic particles Atomic Number The atomic number is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. The atomic number identifies the element. How many protons are in this nucleus? Periodic Table of Elements NASA Which element has 4 protons? Electrons For this unit, we mainly care about electrons in atoms. Why? It is important to understand the “how and why” of the movement of electrons to understand electricity. Electrons Negatively charged particles Electrons Models of the Atom 3D Bohr’s Model 2D Electrons •The electrons reside in the electron cloud •The clouds are divided into 7 energy levels •Electrons “reside” in lowest energy levels whenever possible. Electrons Areas within each energy level where electrons move around the nucleus of an atom are known as Electron Orbitals. There are four different type of orbitals, each type able to contain different numbers of electrons Sharp Principal Diffuse Fundamental Electrons Energy Level Types of Orbitals S orbitals can hold up to 2 electrons P orbitals can hold up to 6 electrons D orbitals can hold up to 10 electrons F orbitals can hold up to 14 electrons 1 Types of Maximum Orbitals Electrons 1 2 (S) 2 2 8 (S & P) 3 3 18 (S, P, D) 4 4 32 (S, P, D & F) 5 4 32 (S, P, D & F) 6 3 18 (S, P, D) 7 2 (S & P) 8 Electrons Electrons will not completely fill all the orbitals in an energy level before moving up to another level. Because of this, There are never more than 8 electrons in the highest energy level! The electrons in the highest energy level of an atom are called the Valence Electrons Orbital Filling order: 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p 5s 4d 5p 6s 4f 5d 6p 7s 5f 6d 7p Electron Orbits Atoms work to have their valence level either filled (8) or empty(0) of electrons. How many electrons are in the valence level? 1 Copper has a loose hold on this electron, so it can easily be moved Electron Orbits Atoms like to have their valence level either filled (8) or empty(0) of electrons. How many electrons are in the valence level? 6 Sulfur has space to gain two electrons in its valence level. What does all this have to do with Electricity? The number of valence electrons in an atom will determine if an element will allow electricity to flow. The ability of an atom to draw electrons to itself (away from its neighbors) is called Electronegativity. Conductors and Insulators Conductors Insulators Electrons flow easily between atoms Electron flow is difficult between atoms 1-3 valence electrons in outer orbit 5-8 valence electrons in outer orbit Low Electronegativity High Electronegativity Good Conductors: Silver, Copper, Gold, Aluminum . . . Examples: Mica, Glass, Rubber, Plastic . . . Conductors and Insulators Identify conductors and insulators Conductors Insulators Metals, Non-Metals, & Metalloids Metals, Non-Metals, & Metalloids Good Conductors Poor Conductors Poor Insulators Good Insulators Shiny Dull Luster Brittle Malleable Combination of metal and non-metal properties Low Density High Density Conduct heat & electricity better than insulators, but not Melt at lower temps as Electronegativity good as metals Low Solids Semi-conductors High Electronegativity Semiconductors •Include Carbon, Germanium, and Silicon •Contain 4 valence electrons •Neither a good insulator, nor a good conductor, but can be made a better conductor through doping. •Needed for transistors and microchips •Silicon is most often used in electronic applications •Silicon is an insulator at room temperature but becomes a conductor when heated Electron Flow in Conductors An atom will lose a valence electron when “pushed” by an electron from another atom. Electron Flow Electricity is created as electrons collide and transfer from atom to atom. Play Animation Image Resources Microsoft, Inc. (2008). Clip Art. Retrieved September 10, 2008, from http://office.microsoft.com/en-us/clipart/default.aspx National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). (n.d.). Genesis: Search for origins. Retrieved September 10, 2008, from http://genesismission.jpl.nasa.gov/educate/scimodule/cosmic/ptable. html