* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Complexity and Stability - Powerpoint for Nov. 2.
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Drought refuge wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
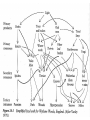
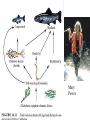
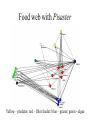
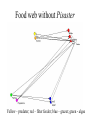
The Nature of Communities and Ecosystems Stability A stable community or ecosystem is one that has the ability to replace itself – exist in place for more than one generation Components of Stability 2 major components: 1) resistance - the ability of a community or ecosystem to avoid disturbance - how most people think of stability 2) resilience - the speed with which a community or ecosystem returns to its former state following a disturbance that has displaced it from its initial condition Ecosystems and Stability Grassland – South Africa Rainforest – Puerto Rico Additional Components of Stability • Local stability describes the tendency of a community to return to its original state following a small disturbance • Global stability describes the tendency of a community to return to its original state following a large disturbance Adaptive Capacity of an Ecosystem Adaptive Capacity of an Ecosystem Adaptive Capacity of an Ecosystem - Chesapeake Bay Adaptive Capacity in 3D Current Adaptive Capacity From Local vs. Global Stability • dynamically fragile - a community which is stable only within a narrow range of environmental conditions • dynamically robust - a community which is stable within a wide range of environmental conditions Complexity and Stability Current understanding - no clear relation between complexity and stability 1) complex, fragile communities of relatively constant environments (the tropical rainforests) are more susceptible to outside, unnatural disturbances than are simpler, more robust communities which experience regular climatic fluctuations (most temperate communities) 2) In stable environments you would expect to find K selected species (high competitive ability, high survivorship, low reproductive output) and such species will resist disturbance 3) In unstable environments you would expect to find r selected species (low competitive ability, low survivorship, but high reproductive output) that have little resistance but high resilience Why is the World Green? Boreal Forest Outlined in Green Spiny Water Flea Spiny Water Flea Invasion Spiny Water Flea Current Distribution Spiny Water Flea Food Web Mary Power Eel River with steelhead Eel River without steelhead Direct and Indirect Effects • Direct effects - effect of 1 species on another resulting from physical interaction between the two – interference competition, inadvertant interference, mutualisms, parasitism, predatorprey • Indirect effects - an effect of one species on another that is not caused by a physical interaction between the two - these can only happen when more than two species are present Pisaster starfish Pisaster and Mytilus californianus Food web with Pisaster Yellow – predator; red – filter feeder; blue – grazer; green - algae Mytilus californianus Food web without Pisaster Yellow – predator; red – filter feeder; blue – grazer; green - algae Strong vs. Weak Interactors 1) Non-interactors - species does not affect population of those species with which it interacts 2) weak interactors - species only influences those species with which it interacts directly - effects may be large 3) strong interactors - species that directly and indirectly effects other species - these species are the most important in the community or ecosystem because a change in their numbers may cause changes in the entire ecosystem – keystone species Aerial view Of 1989 Yellowstone Fire Disturbance and Succession Disturbance • Disturbance - any agent which causes complete or partial destruction of the community resulting in the creation of bare space • Disturbance agents: both physical and biological processes may cause disturbances, though we usually focus on physical processes • Physical - fires, ice storms, floods, drought, high winds, landslides, large waves • Biological - severe grazing, predation, disease, things that inadvertently kill organisms - digging and burrowing Wind Damage – July 4, 1999 Derecho Wildfire – Southern California October 22, 2007