* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Campus Plant Handout
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
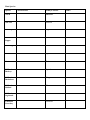
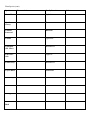
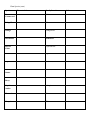
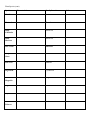
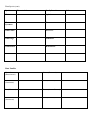
PLANT ADAPTATIONS ON CAMPUS INTRODUCTION The purpose of this lab is not to be able to identify every plant you see. The purpose of this lab is to learn how to identify the different adaptations a plant may have evolved for survival in a particular environment. In this lab, you will be responsible for learning the names and adaptations of the plants discussed during the tour of the campus and Wildlife Sanctuary. Leave Types Simple: Compound: Singly: Doubly: Venation: Pinnate: Palmate: Parallel: Leaf Arrangement: Alternate: Opposite: Whorled: Plant Species: Species Characteristics Family/Location Acacia Fabaceae Ash Tree Oleaceae Bladderpod Capparaceae Brazilian Pepper Anacardiaceae Black Sage Lamiaceae Bulrush Cyperaceae Cactus Cactaceae California Buckeye Sapindaceae California Buckwheat Polygonaceae California Redbud Fabaceae California Sagebrush Asteraceae California Sweet bay Lauraceae Other Plant Species (cont) Species Characteristics Family/Location Caster Bean Euphorbiaceae Catalina Cherry Rosaceae Catalina Ironwood Rosaceae Cattails Typhaceae Ceanothus (Mt. Lilac) Rhamnaceae Coast Live Oak Fagaceae Coffee berry Rhamnaceae Coyote Bush Asteraceae Elderberry Adoxaceae Encelia Asteraceae Eucalyptus Myrtaceae Flannel Bush Malvaceae Other Plant Species (cont) Species Characteristics Family/Location Fremont Cottonwood Salicaceae Fringe Tree Oleaceae Ginkgo Ginkgoaceae Horehound Lamiaceae Incense Cedar Cupressaceae Jacaranda Bignoniaceae Jojoba Simmondsiaceae Laurel Sumac Anacardiaceae Lemonade Berry Anacardiaceae Liquid Amber Altingiaceae Manzanita Ericaceae Mesquite Fabaceae Other Plant Species (cont) Species Characteristics Family/Location Mulefat Asteraceae Mustard Brassicaceae Palm, California Arecaceae Palm, Mexican Arecaceae Palo Verde Fabaceae Pampas Grass Poaceae Pine Tree Pinaceae Sago Palm Cycadaceae Southern Magnolia Magnoliaceae Sugar Bush Anacardiaceae Toyon Rosaceae Tree Tobacco Solanaceae Other Plant Species (cont) Species Characteristics Family/Location Walnut Juglandaceae Western Sycamore Plantaceae White Alder Betulaceae White Sage Lamiaceae Wild Radish Brassicaceae Willow Salicaceae Plant Families Mustard (Brassicaceae) Cactus (Cactaceae) Mint (Lamiaceae) Rose (Rosaceae) Pea (Fabaceae) Sumac (Anacardiaceae) Sunflower (Asteraceae) Grass (Poaceae) Other Plant Families When identifying flower parts, it is best to start on the outside of the flower and work towards the middle: Sepals: a modified leaf, part of the outermost of the four groups of flower parts. The sepals of a flower are collectively called the calyx and act as a protective covering of the inner flower parts in the bud. Sepals are usually green, but in some flowers (e.g., the lily and the orchid) they are the same color as the petals and may be confused with them, Petals: The whorl of petals is known collectively as the corolla [Lat.,=little crown]. The number of petals is usually constant within groups (e.g., five in the rose family), as are the numbers of the other organs. Stamens: The stamen (microsporophyll), is often called the flower's male reproductive organ. It is typically located between the central pistil and the surrounding petals. A stamen consists of a slender stalk (the filament) tipped by a usually bilobed sac (the anther) in which microspores develop as grains. Pistils: the female reproductive organ of flowering plants, consisting of an ovary, style (sometimes absent), and stigma. The carpels are separate or fused to form a single pistil Plant Family Mustard (Brassicaceae) Sepals 4 Petals Stamens 4 arranged in an 6 - 4 Tall & X or H 2 Short Pistils 1 5 United Petals – 2 lobes up, 3 down 5 forming Banner, Wings, and Keel 5 petals fused together 4 – 2 Long & 2 Short 2 United Usu. 10 (sometimes 5) 1 5 fused around pistil Stigmas Numerous Numerous Numerous Rose (Rosaceae) 5 5 Numerous 2 or more united carpels Numerous Sumac (Anacardiaceae) 5 5 5 or 10 1 Grass (Poaceae) Minimal Minimal 3 3 united carpels Mint (Lamiaceae) 5 United Pea (Fabaceae) 5 United Sunflower (Asteraceae) In a ring Cactus (Cactaceae) Others Seed pods - Radial pattern around the stalk called a raceme Stems are Square with opposite leaves, aromatic Pea-like pods and often pinnate leaves Composites with many small flowers in a disk Succulent plant with spines Oval, serated Leaves 3-lobed or pinnate leaves, single seeded red or white fruit Knee-like nodes on the flower stems Mustard (Brassicaceae) Mint (Lamiaceae) Pea (Fabaceae) Sunflower (Asteraceae) Rose (Rosaceae) Sumac (Anacardiaceae)