* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Does frictional force depend on the size of the contact surface area?
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
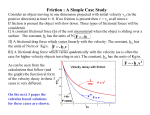
Does frictional force depend on the contact surface’s normal force? You will measure the frictional force (Ff) using two objects of different weights. We measure 𝐹𝑓 by indirect means. In the case when an object undergoes motion with a constant velocity, the 𝐹𝑓 is equal in magnitude and in an opposite direction to the applied force. Therefore, you measure the 𝐹𝑓 by measuring the applied force when the object is undergoing constant motion. You will complete this experiment in two parts. For each part, repeat the measurement of the 𝐹𝑓 a total of six times and calculate the average 𝐹𝑓 : Part 1. Measure the mass of the block. Measure its FN.Pull the block until it is moving at a constant velocity and measure the 𝐹𝑓 . Part 2. Add the weight to the block. Measure the mass of the combined block (with added weight). Measure its FN.Pull the combined block until it is moving at a constant velocity and measure the 𝐹𝑓 . Block: Block (with weight): mass of block: 𝑚1 = _____________ kg mass of block and weight: 𝑚2 = ________ kg normal force : 𝐹𝑁1 = _____________ N normal force : 𝐹𝑁2 = _____________ N i 1 2 3 4 5 6 𝐹𝑓 [N] ̅̅̅̅ 𝐹𝑓1 = ___________ N i 1 2 3 4 5 6 𝐹𝑓 [N] ̅̅̅̅ 𝐹𝑓2 = ___________ N What is the ratio between the block and combined block’s normal forces? 𝐹𝑁2 What is the ratio between the block and combine blocks’ frictional forces? 𝐹𝑓2 What do you conclude about the relationship between frictional force and normal force? 𝐹𝑁1 𝐹𝑓1 = = Does frictional force depend on the size of the contact surface area? You will measure the frictional force (Ff ) using two blocks with differently-sized contact surface areas (A). We measure 𝐹𝑓 by indirect means. In the case when an object undergoes motion with a constant velocity, the 𝐹𝑓 is equal in magnitude and in an opposite direction to the applied force. Therefore, you measure the 𝐹𝑓 by measuring the applied force when the object is undergoing constant motion. You will complete this experiment in two parts. For each part, repeat the measurement of the 𝐹𝑓 a total of six times and calculate the average 𝐹𝑓 : Part 1. Position the block so that its larger surface area is face-down. Measure the mass of the block. Pull the block until it is moving at a constant velocity and measure the 𝐹𝑓 . Part 2. Turn the block onto its side so that its smaller surface area is face-down. Measure the mass of the block. Pull the block until it is moving at a constant velocity and measure the 𝐹𝑓 . Larger area: Smaller area: Larger surface area: Smaller surface area: 𝐴1 = _____________ cm2 𝐴2 = _____________ cm2 i 1 2 3 4 5 6 𝐹𝑓 [N] ̅̅̅̅ 𝐹𝑓1 = ___________ N 𝐹𝑓 [N] i 1 2 3 4 5 6 ̅̅̅̅ 𝐹𝑓2 = ___________ N 𝑆2 What is the ratio between the blocks’ surface areas? What is the ratio between the blocks’ frictional forces? 𝐹𝑓2 = What do you conclude about the relationship between frictional force and the size of 𝑆1 = 𝐹 𝑓1 the contact surface? Does frictional force depend on the type of contact surfaces? You will measure the frictional force by using blocks with different types of contact surfaces. We measure 𝐹𝑓 by indirect means. In the case when an object undergoes motion with a constant velocity, the 𝐹𝑓 is equal in magnitude and in an opposite direction to the applied force. Therefore, you measure the 𝐹𝑓 by measuring the applied force when the object is undergoing constant motion. You will complete this experiment in two parts. For each part, repeat the measurement of the 𝐹𝑓 a total of six times and calculate the average 𝐹𝑓 : Part 1. Pull the wood block until it is moving at a constant velocity and measure the 𝐹𝑓 . Part 2. Pull the sandpaper-covered block until it is moving at a constant velocity and measure the 𝐹𝑓 . Wood – contact surface: i 1 2 3 4 5 6 𝐹𝑓 [N] ̅̅̅̅ 𝐹𝑓1 = ___________ N Sandpaper – contact surface: 𝐹𝑓 [N] i 1 2 3 4 5 6 ̅̅̅̅ 𝐹𝑓2 = ___________ N 𝐹 What is the ratio between the blocks’ frictional forces? 𝐹𝑓2 = What did you observe happens when the contact surface is changed? What do you conclude about the relationship between frictional force and the type of 𝑓1 contact surfaces?