* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download sgt2
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
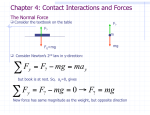
PHYS 211 MWF 9-9:50 & 11-11:50 Study Guide for Test #2 Chapters 5,6,7, & 8 Format will be similar to Test #1, consists of regular questions and problems. A. You should know the following: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Newton’s three laws of motion. Drawing Free-body diagrams. Solving problems with frictional forces. Solving circular motion problems. Work-Energy theorem. Solving problems using conservation of energy principles. Hooke’s law. B. You should be able to define the following: weight, work, power, kinetic energy, potential energy, mechanical energy, conservative, and non-conservative forces. C. The following equations will be provided if needed: 1. Equations of kinematics 1. 2. 1 x x0 (v v0 )t v v0 at 2 3. 4. v 2 v0 2a( x x0 ) 2 2b. Frictional forces: 1 CAv 2 2 1 5. Kinetic energy: K mv 2 2 4. Centripetal force: F 7. Elastic Potential Energy = U ( x) 1 2 kx 2 3. Drag force: D 8. ∆𝑈 = −𝑊 11. Work done by a variable force: W t Pins 1 2 at 2 dW dt Pins F v x x0 vt f S ,max S FN mv 2 R 6. Gravitational Potential energy = U ( y ) mgy 10. Work done by a constant force: W FdCos F d 12. Power: Pavg x x0 v0 t f k k FN 2a. Newton’s 2nd Law: 𝐹𝑛𝑒𝑡 = 𝑚𝑎 5. 𝑑𝑈 9. 𝐹(𝑟) = − 𝑑𝑟 1 2 at 2