* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What`s the function of
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Soil microbiology wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Living things in culture wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
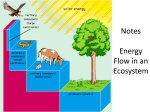
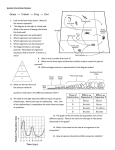
Grade 5- Evaluation sheet Choose: ____ 1. Human organs and organ systems each have specific functions, or jobs. Which pairing matches an organ with its main function? A. B. C. D. ____ biceps: structure jaw bone: balance lung: removal of oxygen vein: carrying away wastes 2. The following picture shows the human circulatory system. What is the function of the organ marked as X? A. B. C. D. ____ to filter blood to pump blood to add oxygen to the blood to remove carbon dioxide from the blood 3. Annabel is tired after playing softball with her friends. She goes home to relax. When Annabel relaxes, she can feel a steady, pulsing rhythm of pressure when she touches her wrist or neck. What is this pulse evidence of? A. bones moving as part of the skeletal system B. muscles flexing as part of the muscular system C. the stomach digesting food as part of the digestive system D. the heart pumping blood as part of the circulatory system 1 Grade 5- Evaluation sheet ____ 4. Body systems work together to supply cells with nutrients. Which list shows the path nutrients take in the body? A. B. C. D. ____ air - respiratory system - digestive system – cells air - respiratory system - circulatory system – cells food - digestive system - circulatory system – cells food - digestive system - respiratory system – cells 5. Your body makes countless movements each day. I Which body system allows the body to move? A. B. C. ____ 6. The movement of legs allows people to walk. Which three body systems work together closely to give the legs movement? A. B. C. D. 2 muscular, nervous, and skeletal digestive, muscular, and respiratory circulatory, digestive, and muscular circulatory, digestive, and respiratory Grade 5- Evaluation sheet ____ 7. The human skeletal system provides structure and support for the body. The following picture shows the basic structures of a plant. Which labeled plant structure is most similar in function to the human skeletal system? A. B. C. D. ____ A B C D 8. Which description tells how the circulatory and respiratory systems work together? A. The circulatory system takes up oxygen, while the respiratory system transports it to cells. B. The respiratory system takes up oxygen, while the circulatory system transports it to cells. C. The circulatory system takes up carbon dioxide, while the respiratory system transports it to cells. D. The respiratory system takes up carbon dioxide, while the circulatory system transports it to cells. ____ 9. Which organs support and protect the body, store minerals, and allow movement? A. B. C. D. Bones ligaments pancreas skin ____ 10. Through which organ system does food get to your cells? A. B. C. D. 3 the muscular system the circulatory system the excretory system the skeletal system Grade 5- Evaluation sheet ____ 11. The organ shown below, identified with an arrow, is a digestive organ. What happens when food reaches this organ? A. B. C. D. Acidic juices mix with the food. Food is stored, but no digestion occurs. The food is completely digested and absorbed into the bloodstream. The food is moved into the small intestine within two or three minutes. ____ 12. The digestive system changes the food we eat into usable and unusable materials. Where do unusable materials go until disposal? A. to the liver B. to the pancreas C. to the large intestine D. to the small intestine ____ 13. The small intestine contains tiny structures called villi. How do villi help the small intestine perform its function. A. They add acidic juices to food. B. They help eliminate solid wastes. C. They help the small intestine absorb nutrients. D. They help food move from the esophagus to the stomach. ____ 14. The urinary system is important to your body’s proper functioning. Which of these describes the function(s) of the urinary system? A. B. C. D. 4 aids in reproduction breaks down solid food stores important nutrients and vitamins regulates fluid balance and eliminates waste Grade 5- Evaluation sheet ____ 15. Where is urine stored prior to urination? A. B. C. D. Bladder Kidneys large intestine stomach ____ 16. The diagram below shows the parts of a human body system. Which body system is shown? A. B. C. D. circulatory digestive respiratory urinary ____ 17. Len was alone, in a strange place, in a new situation, feeling afraid. His body reacted by producing the hormone adrenalin. How did the adrenalin make Len feel? A. He began to feel happy and cheerful. B. He felt calm and at ease. C. He became shaky and his heart thumped. D. He didn’t feel any different. ____ 18. Which organ removes waste from the blood, controls the blood’s salt level, and helps conserve water? A. bladder B. small intestine C. kidneys D. liver ____ 19. Robert has grown taller again and needs larger clothes. Which gland produced the growth hormone that caused this change? A. adrenal B. pancreas C. pituitary D. thyroid ____ 20. What would happen if the urinary system organs stopped working properly? 5 Grade 5- Evaluation sheet A. B. C. D. Waste products would build up. The body would not digest solid food. The liver would take over and the person would not be affected. Blood would stop moving around the body. ____ 21. The nutrients you eat are passed to the bloodstream, where your cells can use them. How do nutrients in digested food reach the bloodstream? A. B. C. D. They are absorbed by the large intestine. They pass from the esophagus into the blood. They pass from the small intestine through tiny blood vessels into the blood. They are absorbed into the bloodstream through structures in the stomach wall. ____ 22. A domain is the broadest classification of living things. Which of the following names the three known domains? A. B. C. D. Eukarya, Bacteria, Archaea Animalia, Chordata, Mammalia family, genus, species Plantae, Fungi, Protista ____ 23. Which statement best explains how living organisms are classified into the three domains by their differences? A. The main characteristics for classifying organisms into domains is whether they have vascular tissue, are vertebrates, or absorb food from their environment. B. Animals are in one domain. Plants are in another domain. Protists and fungi are in a third domain. C. One domain contains all the complex organisms. The other two domains contain simple, single-celled organisms with no nucleus. D. The three domains are classified as organisms that are microscopic, reproductive, or visible. ____ 24. A large classification of living things is made of up organisms that have many cells and use sunlight to make food. Which kingdom is the classification for such organisms? A. B. C. D. 6 Animals Bacteria plants fungi Grade 5- Evaluation sheet ____ 25. Four organisms are pictured below. Which of the following best describes the classification these organisms are examples of? A. B. C. D. different mammals different invertebrates different kingdoms different species ____ 26. The organisms below are members of one of the six kingdoms of living things. What do these organisms have in common with all the other members of this kingdom? A. B. C. D. They are microscopic. They feed on dead or decayed materials. They live in extreme environments and get energy from strange resources. They may look or act like plants, animals, or fungi. ____ 27. Miguel had a white navy bean, a red lentil bean, a white lima bean, and a black bean. He used a diagram like the following to classify the four beans according to their physical characteristics. This type of classification chart is best known as what? A. B. C. D. an order of classes a dichotomous key a subdivision a classification code ____ 28. Mrs. Kim’s class was identifying different species of plants. Which of the following best describes a species? 7 Grade 5- Evaluation sheet A. B. C. D. the next more specific classification following an order a group in which organisms of different kinds are closely related a unique kind of organism another name for a family or genus ____ 29. Scientists organize living things into a number of different levels of classification. As you continue down the levels of classification, which of the following is true? A. B. C. D. Each level refers to a unique kind of organism. The members of each classification level have more and more differences. The organisms are grouped more and more by their behavior. The organisms are more and more closely related to each other. ____ 30. Emma’s class was studying vertebrates. Which of the following are examples of vertebrates? A. B. C. D. ferns, conifers, mosses brittle stars, sea stars, basket stars camels, falcons, frogs crabs, grasshoppers, jellyfish ____ 31. Among these four living things, which two are most likely to have the most physical characteristics in common? A. B. C. D. the tree and the lizard the bear and the lizard the human and the bear the lizard and the human ____ 32. Scientists classify living things into three domains and six kingdoms. Which of the following best describes characteristics of the protist kingdom? A. may be plant-like, animal-like, or fungus-like B. do not make food from sunlight; feed on dead or decayed materials C. are vascular or nonvascular D. are vertebrates or invertebrates ____ 33. Some organisms break down dead things for food. Which word describes these organisms? 8 Grade 5- Evaluation sheet A. B. C. D. consumers decomposers herbivores producers ____ 34. How are decomposers like consumers? A. B. C. D. They provide energy to producers. They must capture prey in order to survive. They can make their own energy from sunlight. They get their energy from producers or other consumers. ____ 35. Look at the desert scene pictured below. To picture all of the types of organisms listed below, which types would you need to add to the scene? A. B. C. D. consumers, decomposers herbivores, producers producers, herbivores scavengers, producers ____ 36. In the carbon dioxide-oxygen cycle, which organisms take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen as part of the process of making food? A. B. C. D. animals consumers plants plants and animal ____ 37. What is the primary source of energy for this organism? A. carbon dioxide 9 Grade 5- Evaluation sheet B. oxygen C. soil D. sunlight ____ 38. What is the process that plants use to produce food? A. B. C. D. carbon dioxide photosynthesis chloroplast sunlight ____ 39. This producer uses a molecule called chlorophyll. Which need does chlorophyll help to meet? A. B. C. D. making food releasing oxygen absorbing soil nutrients taking in carbon dioxide ____ 40. Which type of organism makes its own food? A. B. C. D. consumer decomposer producer scavenger ____ 41. In a forest food chain, what is the connection between the sun and a tree? A. B. C. D. The sun helps chlorophyll turn oxygen into carbon dioxide. The tree shades animals from the sun and gives them nutrients. The sun heats up the ground so the tree’s roots can take in water. The tree uses the sun’s energy to make food through photosynthesis. ____ 42. Which of the following is an example of a producer? A. a caterpillar 10 Grade 5- Evaluation sheet B. a robin C. a tree D. a worm ____ 43. Which of the following does a plant use in the process of photosynthesis? A. B. C. D. oxygen, sugar, and water sunlight, oxygen, and sugar water, carbon dioxide, and sunlight carbon dioxide, sugar, and sunlight ____ 44. A robin’s diet includes earthworms, small insects, and berries. How should a robin be classified? A. B. C. D. carnivore herbivore omnivore producer ____ 45. What are the products of photosynthesis? A. B. C. D. oxygen and water sugars and oxygen sugars and carbon dioxide carbon dioxide and chlorophyll ____ 46. What are fungi in a forest food chain? A. carnivores B. decomposers C. omnivores D. predators ____ 47. Ecosystems have producers, consumers, and decomposers. Why are decomposers important in an ecosystem? A. They are herbivores and keep down the population of plants. B. They are carnivores and keep down the population of animals. C. They produce more food for other organisms. D. They break down dead plants and animals. ____ 48. Erin needs to complete the chart below. Decomposers Facts about . . . Producers Consumers Which statement belongs in the “Decomposers” column? A. eat plants 11 Grade 5- Evaluation sheet B. eat plants and/or animals C. use photosynthesis to make food D. return nutrients to the soil ____ 49. Which of these things can function as a decomposer? A. bread B. leaves C. fungus D. rotting meat ____ 50. The picture shows a food chain. The arrows show how energy flows from one living thing to the next. In this food chain, what would be a possible energy source for the bacteria? A. all the animals B. all the organisms C. only the hawk D. only the predators ____ 51. In a rotting-log ecosystem, how are the fungi that grow on dead bark and the beetles that eat the wood alike? A. They are producers. B. They are the energy source. C. They are the decomposers. D. They are predators. ____ 52. A tree in the forest grows old and dies. It gradually falls apart inside, and finally falls over. In time, fungus is visible on the fallen log. What is this process called? A. decomposition B. ecosystem C. molding D. producing ____ 53. Alex notices a small spot of fungus growing on an orange in the back of his refrigerator. He doesn’t eat the orange. He looks at the orange again a week later. Which of these is he most likely to observe? A. The fungus has gone away. B. The fungus has not changed. C. The fungus has grown larger. D. The fungus has changed color. ____ 54. Which of these happens during the time a fallen log is decomposing? 12 Grade 5- Evaluation sheet A. B. C. D. The fallen log slowly begins to die. The fallen log continues to produce food. The materials in the log combine into new, complex parts. The materials in the log are broken into smaller, simpler parts. ____ 55. Jackson and Kathryn were assigned to observe the growth of fungus on a hamburger bun. They sprayed half of the bun with water and sealed it in a plastic bag. They left the other half of the bun dry and sealed it in a different plastic bag. Over time, what did they observe? A. B. C. D. Mold grew faster on the dry bun. Mold grew the same on both buns. Mold did not grow inside sealed bags. Mold grew faster on the moistened bun. ____ 56. During the decomposition process, the wastes of living organisms and the remains of dead organisms are broken down and their nutrients are returned to the soil. What is the most important cause of decomposition? A. B. C. D. air sunlight scavengers bacteria and fungi ____ 57. Below is a diagram of a basic food web. What is the best word to put in to replace the letter X? A. decomposers B. first-level consumers C. predators D. second-level consumers ____ 58. Which of these is a decomposer? A. bread B. heat C. mold D. water ____ 59. A forest contains many different kinds of plants and animals. All living things eventually die, yet the forest floor is not piled high with their remains. Which organisms are most responsible for cleaning up the remains of dead plants and animals? 13 Grade 5- Evaluation sheet A. B. C. D. producers and consumers consumers and scavengers producers and decomposers scavengers and decomposers ____ 60. The picture below shows a food chain. The arrows show how energy flows from one living thing to the next. Notice the bacteria at the end of the food chain. Why are bacteria shown at the end of the food chain? A. B. C. D. They are producers, and make food from sunlight. They are consumers, and feed off of the dead hawk. They are decomposers, and break down the dead hawk. They are consumers, and the smallest organisms in this chain. Complete: 1- The …skeletal…system supports the body 2- It joins between 2 bones …ligaments… while …tendons…… connects muscle to bone 3- The ball and socket joints allow …circular……… movement 4- The respiratory system brings in …oxygen……… and the releases …carbon dioxide…… 5- The …skeletal … system and the …muscular… system allow movement 6- The …heart… pumps the blood to all body organs 7- ……Heart… and ……stomach walls……… are involuntary muscles 8- Two tubes are connected to trachea are called …bronchi… 9- Joints… is the space between 2 bones 10- The broadest unit of classification …domains.... 11- …Chlorophyll…. Absorbs sunlight so plants can made their food. 14 Grade 5- Evaluation sheet 12- Organisms that break down wastes and food remains are ….decomposers… What’s the function of: 1-Bones:…supports body-protects organs-store minerals-allow movement…………....….. 2-Muscle:……………………allow movement…………………………………………… 3-Heart:…………………pump blood to the body………………………………………... 4-Trachea:……………carry oxygen to the lungs………………………………………… 5-plateletes:……………stop bleeding………….…………………………………………. - - 15 Explain why humans are classified as omnivores and how that is different from being a carnivore or an herbivore Humans eat plants and animals Why scientist classify organism. to study them and know how they are related OR to ease their study