* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CMV
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Cryptosporidiosis wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Diagnosis of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Cytomegalovirus
DR.K.RAJA
GHTM
CHENNAI
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
CMV IN IMMUNO COMPETENT PATIENTS
CMV IN IMMUNO COMPROMISED PATIENTS
CMV IN PREGNANT WOMEN
KEY POINTS
IN HIV CMV IS REACTIVATION OF LATENT INFECTION
HIV AND CMV COINFECTION – RAPID PROGRESSION OF HIV
CD4 - <50 – CMV IS ACTIVATED AND DISSEMINATED
IN PREGNANCY ONLY PRIMARY INFECTION CAUSES IN VITRO
TRANMISSION
NEONATES, INFECTED IN UTERO - RASHES, HEPATITIS,
GASTROENTERITIS AND A ORGAN SPECIFIC MALADIES.
SURVIVORS – HEARING LOSS, VISION IMPAIRMENT AND
MENTAL RETARDATION.
IN IMMUNO COMPETENT – FLU LIKE SYNDROME
AND REMAIN LATENT LIFE TIME
Human Cytomegalovirus
herpesvirus
betaherpesvirinae subfamily
CMV infected cells may become enlarged
(cytomegalia), showing intranuclear inclusions.
Virus Structure
Enveloped, slightly
pleomorphic
Spherical
120 – 200 nm in
diameter
Capsid
Envelope
Tegument
Genome
double stranded
DNA per virion
TRANSMISSION
Transmitted through infected bodily fluids
that come in contact with hands and then
are absorbed through the nose or mouth of
a susceptible person.
Transmission can also occur
– congenitally
- by sexual contact
- through blood transfusion
CMV may be shed in the bodily fluids
urine
saliva
blood
semen
breast milk
The shedding of virus
- intermittent
- without signs
-without causing symptoms.
CMV infection
High-risk groups:
(1) infection to the unborn baby during
pregnancy
(2) infection to people who work with children
(3) immunocompromised person:
a) organ transplant recipients
b) human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
C)undergoing hemodialysis
d) patients with cancer
CMV IN IMMUNO COMPETENT PERSONS
The primary infection
presents as mononucleosis-like syndrome
which soon resolves.
Most of them asymptomatic for life.
IN PREGNANCY
IN PREGNANCY WHEN A WOMEN WHO
HAS NEVER HAD CMV INFECTION
BECOMES INFECTED WITH CMV, THERE IS
A POTENTIAL RISK THAT AFTER BIRTH
THE INFANT MAY HAVE CMV-RELATED
COMPLICATIONS
NEONATES
NEONATES, INFECTED IN UTERO - RASHES,
HEPATITIS, GASTROENTERITIS AND A
ORGAN SPECIFIC MALADIES.
THE MOST COMMON OF WHICH ARE
ASSOCIATED WITH HEARING LOSS, VISUAL
IMPAIRMENT, OR DIMINISHED MENTAL
AND MOTOR CAPABILITIES.
INFANTS AND CHILDREN WHO ACQUIRE
CMV AFTER BIRTH HAVE FEW, IF ANY,
SYMPTOMS OR COMPLICATIONS.
CMV IN HIV INFECTION
Primary infection - rare in HIV as most have
been exposed to CMV
Latent CMV infection is activated
in advanced HIV disease.
CMV IN HIV
retinitis
oesophagitis
encephalitis
myelitis
radiculopathy
colitis
pneumonitis
adrenalitis
pancreatitis
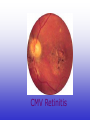
CMV Retinitis
small floaters
foggy or blurred vision
loss of central or peripheral vision
routine exam when the infectious
process is early and located in the
peripheral retina
loss of vision
retinal detachment
CMV Retinitis
PROGRESSION
CMV – COFACTOR IN THE PROGRESSION OF
HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS TYPE 1 (HIV-1)
DISEASE.
Laboratory tests
CMV antibody - paired serum samples
1) ELISA
2)fluorescence assays
3)indirect hemagglutination
4)latex agglutination
A virus culture
Tissue biopsy for culture
CMV blood culture ("buffy coat" culture)
CMV urine culture
CMV sputum cultures
ANTIGEN
CMV shell vial (a method of determining the
presence of CMV antigens)
BIOPSY
Biopsies of organs likely to be infected with CMV
Treatment
First line:
ganciclovir, powder for injection, 500 mg in vial
Adults: 5 mg/kg i.v twice a day for 14-21 days
Second line:
foscarnet, solution for injection, 24 mg/ml 250
ml, 500 ml
Adults: retinitis; 90 mg/kg i.v daily for 14-21
days for CMV
Adults: CMV oesophagitis; 90 mg/kg i.v twice a
day for 14-21 days
Maintenance
First Line:
ganciclovir, capsules, 250 mg
Adults: 1 g orally three times a day
Second Line:
ganciclovir, powder for injection, 500 mg in vial
Adults: 5 mg/kg i.v daily
Third line:
foscarnet, solution for injection, 24 mg/ml 250
ml, 500 ml
Adults: 90 mg/kg i.v daily
ALTERNATIVE TREATMENT
Valganciclovir 900mg bid po
Cidofovir 5mg/kg weekly
PROPHYLAXIS
Primary prophylaxis is generally not
recommended because of cost concerns,
inconvenience and the potential for
development of resistance
MAINTAINENCE
CD4+ cell counts > 100 for > 3 months as a
result of potent ART
Prevention
Simple hand washing with soap and
water is effective in removing the virus
from the hands.