* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiac Cycle
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
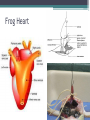
Cardiac Cycle Lab Cardiac cycle- the electrical and mechanical events that occur in one complete heart beat Today you will use a physiograph to record the cardiac cycle in a frog heart and: ▫ Measure and calculate the phases of the cardiac cycle. ▫ Determine the effects of temperature and chemicals on the heart ▫ Investigate the heart’s absolute refractory period and heart block Recording Equipment • Physiograph – records biological activity • Myograph – transducer that measures mechanical force produced by muscle contraction • Myogram – recording of muscle activity that can be measured and interpreted • Stimulator – sends electrical impulses to the muscle Cardiac Cycle • Consists of atrial systole/diastole, and ventricular systole/diastole which creates one complete heartbeat. • These phases are controlled by the contraction of myocardial cells which are stimulated by the autorhythmic cells. Frog Heart Force (g) Cardiac Cycle Atrial Systole Atrial Diastole Ventricular Systole Time (seconds) Ventricular Diastole Cardiac Cycle Effects of Temperature on Cardiac Muscle • Extreme cold- decrease heart rate • Extreme hot- increase heart rate Effects of Chemicals on Cardiac Muscle Chemicals affecting HR are “chronotropic” agents, while chemicals affecting contractile force are “inotropic” agents. ▫ Epinephrine- sympathomimetic, increases heart rate and contractile force. ▫ Acetylcholine- parasympathomimetic, decreases heart rate ▫ Atropine- parasympatholytic, increases heart rate Calculating Percent Change Post treatment – Pre treatment Pre treatment X 100 Absolute Refractory Period • Cardiac muscle tissue has a relatively long absolute refractory period. This: ▫ Prevents summation and tetany ▫ Ensures filling time for ventricles Extra Systole Compensatory Pause Heart Block • Heart block - occurs when the ventricles fail to respond to every depolarization of the SA node or the response is delayed. • Partial / Incomplete Block ▫ First-degree block: The interval between atrial contraction and ventricular contraction is prolonged. ▫ Second-degree block: The atrial to ventricular contraction ratio is altered. The action potentials are not strong enough to pass through to the ventricles every time. Can be a 2:1; 3:1; or 3:2 ratio of atrial to ventricular contractions. • Complete Block ▫ Third-degree block: The conduction between the atria and ventricles is completely blocked. There will be no correlation between atrial and ventricular contractions.