* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ANCIENT AND CLASSICAL PERIOD IN WORLD HISTORY: FROM
Contemporary history wikipedia , lookup
Urban history wikipedia , lookup
Origins of society wikipedia , lookup
Ancient history wikipedia , lookup
Guns, Germs, and Steel wikipedia , lookup
History of the world wikipedia , lookup
Cradle of civilization wikipedia , lookup
Social history wikipedia , lookup
Neolithic Revolution wikipedia , lookup
Proto-Indo-Europeans wikipedia , lookup
Societal collapse wikipedia , lookup
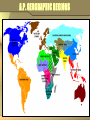
ANCIENT AND CLASSICAL PERIOD IN WORLD HISTORY: FROM THE DAWN OF TIME TO 600 C.E. CONTENT HISTORICAL GEOGRAPHY TO KNOW • Historic Regions • All AP Regions • Mesopotamia, Mesoamerica • Sudanic Africa (West African Sahel) • Historic States to Know • River Valley Civilizations • Amer-Indian geographic hearths • Classical Empires • Locations of world religions • Internal vs. External migration • Migration, Urbanization • Immigration • Movement in History • • • • • • Original spread of humans Indo-European Bantu Germanic and Viking Spread of world religions Polynesian A.P. GEOGRAPHIC REGIONS MODERN NATIONS TO KNOW THEMES • THEMES (P.E.R.S.I.A.N., S.C.R.I.P.T.E.D.) • • • • • • • • Social, Gender Structures including Labor Systems Cultural and Intellectual Structures Religious Structures Interactions: War, Diplomacy, Trade Political Culture, Political Organization, State Structures, Technology Economics Demography (geography) and Environment • OTHER • Change and Continuity over Time • Geography: Local and regional focus THE ANCIENT AND CLASSICAL PERIOD • PERIODIZATION • • • • What themes set a period apart? When did it begin, when did it end? Nature and causes of change Breaks and continuity within a time period • 1,000,000 BCE TO 600 CE • Prehistoric: 1 million to 4500 BCE or Stone age • Ancient: 4500 to 1000 BCE or Bronze Age • Classical: 1000 BCE to 600 CE or Iron Age • Breaks and Continuity within Period • Prehistoric: Rise of Humans, Hunter Gatherers • Ancient: Sedentary culture, domestications • Classical: Use of Iron THE FIVE THEMES • Relative Location • Know relative locations • Know locations of major states, cultures • Place • Physical • Know the major features of physical geography • Human • Know the cultural characteristics of states • Human Environment Interaction • Movement • History is the result of movement • Region • All history is regional until 1450 CE HUMAN ENVIRONMENT INTERACTION • PRE-SEDENTARY TIMES: ADAPT OR DIE • • • • • • • Climates diverse, man’s adaptations diverse Man arose in Africa, spread out to other continents Harshest climates around deserts, desert like conditions Environment often forced man to change As civilization advances, man begins to change surroundings Hunter-gather nature Slash and burn was the transition to sedentary agriculture • AGRICULTURAL SOCIETIES • Domestications • Farming • Herding • Sedentary civilization • PASTORAL SOCIETIES • Nomads and their flocks • Relationship to agricultural societies • DEMOGRAPHIC CHANGES WITH RISE OF CIVILIZATIONS • DEMOGRAPHIC STRESS • Overfarming and overhunting, deforestation, agriculture replaces plants LOCATION: EARLY GEOGRAPHIC SETTING • PRE-HISTORIC • The whole world in all settings • The first towns, cities arose in marginal zones • Some building materials • Some foods, resources, marginal water, and protection • ANCIENT RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS (HEARTHS) • Mesopotamia • Sumer • Assyria and Babylon • Nile River • Egyptian Kingdoms • Kush-Meroe • Indus River • Harrappan, Mohenjo Daro • Aryans • Yellow River • Xia • Shang LOCATION: LATER GEOGRAPHIC SETTING CLASSICAL • MEDITERRANEAN • Phoenicians, Jews, Persians • Greeks: Hellenes, Hellenistic Age • Romans: Republic and Empire • SOUTH ASIA • Persians and Greeks • Mauryans • Guptans • EAST ASIA • Zhou, • Qin, Han • CENTRAL ASIANS • OTHERS • Ghana, Axum-Ethiopia • Mayans, Toltecs, Aztecs • Incas and predecessors EARLY POLITICAL STRUCTURES • Paleolithic Structure • Small bands, generalized social equality • Led by best hunters, male or female • Neolithic • Sedentary villages • Village Councils, Elders, some hereditary chiefs • Much more patriarchal • Early Cities • • • • • Often city states Ceremonial Centers: Plazas, Temples Centralized rule of priests, kings, elite class Class structure usually based on land ownership Hereditary positions become common CHANGE OVER TIME STATE STRUCTURES • Small city states • Sumer, Indus, Xia • Phoenicians, Greeks • Olmecs, Mixtec, Zapotecs, Mayans • Small Regional State • Shang • Babylonia, Israel • Ghana, Kush, Axum • Early Theocratic Empires • Egyptian Old Kingdom, Middle Kingdom • Toltecs • Akkad • Shang, Zhou • Funan (SE Asia) EARLY CULTURE • PALEOLITHIC CULTURE • • • • Language, Religion Traditions and Institutions Occupations and Past-times Simple artifacts, art (cave paints, totems, jewelry) • TOOL MAKING CULTURE • Hunter Gathers had tools, only primitive • Neolithic technology become complex, varies • NEOLITHIC CULTURE • Social Revolution: hierarchy, gender relations • Technological Revolution: pottery, advanced tools, irrigation • NATURE OF CIVILIZATION • • • • • Writing is at the center of a cultural change Complex culture based on living in a city People packed more closely together Social mores reflect this change Artisans, toolmakers have great influence • SOPHISTICATION: Increased over time SOCIAL HIERARCHY • Patriarchal • Increasingly so over time • Social Class Differentiation • Superior vs. Inferior • Increasingly classes defined over time • Caste Systems • If classes become rigid, it is a caste system • Slavery • Common since dawn of history in all cultures • Rigidity depended on culture • Serfdom CHANGE OVER TIME EARLY SOCIAL • PALEOLITHIC: HUNTER GATHERER • • • • • • NEOLITHIC: SETTLED AGRICULTURE, DOMESTICATIONS • • • • • Domestication of plants and animals Shifting Agriculture and Migratory Farmers Nomadic Pastoralism Patriarchal society, patrilineal descent ; gender differences in work, farming ANCIENT: VILLAGE TO CIVILIZATION • • • • • • Gender equality, work equality Short life, Limited survival, foods Small groups, bands led by elders Religion: animist, afterlife Extended family Sedentary life led to rise of social classes Social differences, gender differences, Specialized occupations Rise of inequalities; rise of aristocrats, kings, priests; unfree labor inc. slavery, serfs Villages and a few cities Nuclear Family CLASSICAL • • • • Continuation of Ancient although trends heightened Classes often become rigid, rise of warriors, war leaders; castes Aristocracy, artisan, intellectual classes Gender differences pronounced and often codified in law CHANGE OVER TIME RELIGIONS • UNIVERSALIZING vs. ETHNIC RELIGIONS • MAJOR FEATURES OF EACH, WHERE ARE RELIGIONS LOCATED • OVERTIME: • • • RISE OF PERMANENT RELIGIOUS CASTE, MORAL CODES INCLUDING SOME CASTING ANIMISM/SHAMANISM TO GENERALIZED ANTRHOPOMORPHISM T0 POLYHEISM PHILOSOPHIES AND MONOTHEISMS DEVELOP AT END OF PERIOD • EARLY RELIGIONS • • • • • ANIMISM, SHAMANISM ANTHROPOMORPHIC POLYTHEISM ELABORATED POLYTHEISM WITH PRIESTS, RITUAL, DOGMA HINDUISM SHINTO • ETHICAL PHILOSOPHIES AND RELIGIONS BLEND • • • CHINESE RELIGIOUS COMPLEX: TAOISM, CONFUCIANISM, LEGALISM JAINISM, BUDDHISM HELLENIC PHILOSOPHY • MONOTHEISM: EXCLUSIVITY • • • JUDAISM CHRISTIANITY ISLAM TECHNOLOGY OVER TIME • The ability to make and use tools • Man has always been a toolmaker • Tools increasingly designed to meet specific needs • Simple to complex • Materials • • • • Bone, Stone, Wood; Mixture of Media Metallurgy, Metalworking: Copper, Bronze, Iron Include domestications as technology if necessary In many ways writing is a technology • Technology is specialization • Expands if group supports artisans who do not hunt, gather, farm • Irrigation systems requires team work leading to political structure • Know how inventions improved life CHANGE OVER TIME INTERACTIONS • War • • • • Not a new invention but rare in Pre-history History introduces scarcity, contest for it War becomes increasingly complex; warrior classes Technology effected war; empires are core of classical • Diplomacy • Similar to War • Contact between states led to diplomacy • First treaty was between Hittites, Egyptians • Trade • • • • The simplest way for cities to overcome failings Trade for what you do not have Most international trade was for luxury Commodities traded locally, internally • Exchanges: ideas, diseases • Migration of nomads, Bantus, Indo-Europeans • Interactions between nomads, sedentary MOVEMENT • Themes • Indigenous or Independent Development • Cultural Diffusion • Spread of Agriculture • Spread of Technology • Popular Movements • • • • • • Early Humans spread across globe Indo-European Migrations or “Chariot Peoples” Bantu Migrations Polynesian Migrations Xiong Nu or steppe peoples Germanic Peoples CLASSICAL ENDS • Reasons for Decline • External and Internal • Internal Decay vs. External popular forces • Aspects • Geographic, Demographic, Environment • Military, Political • Economic, Social • Decline in Given Areas • Mediterranean, South Asia, East Asia • Mesoamerica • That which remains • Classical cultures • Classical religions • Classical traditions • Interregional Networks: Trade, Spread of Religions • Movements of Bantu, Huns, Germans, Polynesian ESSAYS COMPARISONS AND SNAPSHOTS • Compare and contrast the development of institutions and traditions (political, social, economic, or intellectual) in any two of these classical civilizations: • • • • • • China India Greece Rome Mesoamerica Andes • Compare and contrast any two of these cultures: • • • • The Neolithic Revolutions Early civilization Pastoral nomadism Shifting agriculture COMPARISONS AND SNAPSHOTS • Compare major religions and philosophical systems including similarities in cementing a social hierarchy, e.g. Hinduism contrasted with Confucianism. • Compare the role of women in different belief - Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism and Confucianism • Compare and contrast the rise, development and spread of Buddhism and early Christianity. COMPARISONS AND SNAPSHOTS • Understand how and why the collapse of empire was more severe in Western Europe than it was in the Eastern Mediterranean, China, or South India • Compare the caste system to other systems of social inequality devised by ancient and Classical civilizations, including slavery COMPARISONS AND SNAPSHOTS • Compare societies and cultures that include cities with pastoral and nomadic societies. • Compare the development of traditions and institutions in major civilizations, e.g. Indian, Chinese, Greek • Describe interregional trading systems e.g. the Indian Ocean trade system and the Silk Road • Compare and contrast the intellectual accomplishments of the classical Chinese and Mediterranean civilizations (Hellenic, Hellenistic, and Roman). COMPARISONS AND SNAPSHOTS • Compare any two of the interregional trading systems: • • • • • Mesoamerica Mediterranean Southwest Asia South Asia East Asia • Compare and contrast the popular movements and settlement patterns of any two of these peoples: Indo-Europeans/Chariot Peoples, Germans, Polynesian, or Bantu. COMPARISONS AND SNAPSHOTS • Compare the political and social structures of two early civilizations using any two of the following: • Mesopotamia (Sumer through Persia) • Egypt (Old Kingdom through New Empire) • Indus Valley (Harappan to Aryan) • Shang Dynasty • Mesoamerica (Olmecs, Mayans, Toltecs) • Andean South America (Moche, Chan Chan)