Life in the Neolithic
... Originally, Childe believed that the settlement dated from around 500 BC. This interpretation was coming under increasing challenge by the time new excavations in 1972–73 settled the question. Radiocarbon results obtained from samples collected during these excavations indicates that occupation of S ...
... Originally, Childe believed that the settlement dated from around 500 BC. This interpretation was coming under increasing challenge by the time new excavations in 1972–73 settled the question. Radiocarbon results obtained from samples collected during these excavations indicates that occupation of S ...
/home/bea/Documents/Documents/WEA/HOs/Neolithic and Skara
... forced people to develop farming. By 9500–9000 BC, farming communities arose in the Levant and spread to Asia Minor, North Africa and North Mesopotamia. Early Neolithic farming was limited to a narrow range of plants, both wild and domesticated, which included einkorn wheat, millet and spelt, and th ...
... forced people to develop farming. By 9500–9000 BC, farming communities arose in the Levant and spread to Asia Minor, North Africa and North Mesopotamia. Early Neolithic farming was limited to a narrow range of plants, both wild and domesticated, which included einkorn wheat, millet and spelt, and th ...
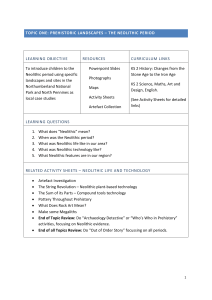
topic one: prehistoric landscapes – the neolithic
... The Neolithic period in Britain started around a thousand years later than the Neolithic period on the Continent. Mesolithic Britons may have been aware of farming for a long time before they decided to start doing it. The period preceding the Neolithic was called the Mesolithic, or “middle stone ag ...
... The Neolithic period in Britain started around a thousand years later than the Neolithic period on the Continent. Mesolithic Britons may have been aware of farming for a long time before they decided to start doing it. The period preceding the Neolithic was called the Mesolithic, or “middle stone ag ...
Around 2300 BCE nomadic pastoralists mixed with settled city
... “How did agricultural techniques spread from Southwest Asia to Europe after 7000 BCE?” The answer….? We already have the answer! “After 7000 BCE, agricultural techniques spread from Southwest Asia to Europe along the coastline of the Northern Mediterranean, and by travelers overland into northern E ...
... “How did agricultural techniques spread from Southwest Asia to Europe after 7000 BCE?” The answer….? We already have the answer! “After 7000 BCE, agricultural techniques spread from Southwest Asia to Europe along the coastline of the Northern Mediterranean, and by travelers overland into northern E ...
Kurgans, Ritual Sites, and Settlements Eurasian Bronze and Iron Age
... historical and archaeological sources, discusses nomadic migrations toward central and southern Europe during the early centuries AD. The next article considers the question of ThracoCimmerian migrations or assimilations on the great Hungarian plains. In northern Fennoscandia, archaeological finds i ...
... historical and archaeological sources, discusses nomadic migrations toward central and southern Europe during the early centuries AD. The next article considers the question of ThracoCimmerian migrations or assimilations on the great Hungarian plains. In northern Fennoscandia, archaeological finds i ...
Group 1 Olmec The Olmec were the first `major` civilization in Mexico
... Ohlones never developed agriculture or tilled the soil. Their staple diet consisted of crushed acorns, nuts, grass seeds, and berries, although other vegetation, hunted and trapped game, fish and seafood, were also important to their diet. These food sources were abundant in earlier times and mainta ...
... Ohlones never developed agriculture or tilled the soil. Their staple diet consisted of crushed acorns, nuts, grass seeds, and berries, although other vegetation, hunted and trapped game, fish and seafood, were also important to their diet. These food sources were abundant in earlier times and mainta ...
Learning About The Past
... sometimes referred to as AD and BC, respectively. BCE and CE are the modern system. Only BCE (BC) years have anything written after them, BCE (BC). Timelines are always divided into equal parts or time periods. Some are divided into 10 year periods (Decades), others into 100 year periods (Centuries) ...
... sometimes referred to as AD and BC, respectively. BCE and CE are the modern system. Only BCE (BC) years have anything written after them, BCE (BC). Timelines are always divided into equal parts or time periods. Some are divided into 10 year periods (Decades), others into 100 year periods (Centuries) ...
Todd_sample chapter_The early germans
... items of metalwork such as torques, brooches and other personal ornaments. It is not possible to estimate how regular these contacts with the Celtic world were. The uniformly high quality of the goods imported would readily support the idea that many of them were supplied through the medium of gift- ...
... items of metalwork such as torques, brooches and other personal ornaments. It is not possible to estimate how regular these contacts with the Celtic world were. The uniformly high quality of the goods imported would readily support the idea that many of them were supplied through the medium of gift- ...
ANCIENT AND CLASSICAL PERIOD IN WORLD HISTORY: FROM
... • Compare the role of women in different belief - Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism and Confucianism • Compare and contrast the rise, development and spread of Buddhism and early Christianity. ...
... • Compare the role of women in different belief - Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism and Confucianism • Compare and contrast the rise, development and spread of Buddhism and early Christianity. ...
The Development of Civilization in the Indus River Valley
... (terracotta figurines, simple dot designs) ...
... (terracotta figurines, simple dot designs) ...