* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electric Motor Controllers Starting Methods
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
War of the currents wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Brushless DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Commutator (electric) wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
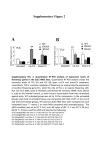
Electric Motor Controllers Starting Methods Explained Direct on line, Starting current: Method: Comment: MP300 6 -7 x FLC, reducing after 50% of motor full speed. Single contactor, hence low cost and reliable with rapid starting speed. Preferred starting method in Europe up to 100hp Star / Delta Starting current: Method: Transition Current: Comment: MP430, open transition star-delta 2 to 3 x FLC while in star, jumping to 6 times briefly. Three contactor reduced voltage (58%) start system Can be 2x locked rotor current (12 to 16 times FLA) Preferred starting method in Europe above 100hp Star / Delta Starting current: Method: Comment: MP435, closed transition star-delta 2-3 x FLC while in star, jumping to 6 times briefly. Four contactor and power resistor system Only used to avoid transition current on MP430 type Autotransformer Start current: Method: Comment: MP450 With 65% tap, 3.5 x FLC reducing after 60% of motor full speed Three contactors and power transformer Can be used when higher starting torques are required, compared to star-delta. Primary Resistor Start current: Method: Comment: MP400 3.5 – 4.5 x FLC reducing after 70% of motor full speed. Two contactors & power resistors to limit starting current Smooth starting for light loads. For a given starting current, much less starting torque is available, compared to MP430 or MP450. Resistors chosen so that the motor see 50% of voltage at start up. Electronic Soft Start Starting current: Method: MP700 3 to 4 times FLC Two contactors with soft start module. Once up to speed the soft starter is out of circuit. Designed to reduce mechanical stress at start up and stopping Current limit is factory set to 500% of FLC. Comment: Variable Frequency Drive Starting current, VFD mode Comment: MP800 Selectable, factory set to 1.3 times FLC Must have a by-pass system for when VFD fails, typically soft start or direct on line. Designed to vary motor speed to maintain a set pressure with varying suction pressure. NOTE: ALL controllers require direct on line emergency start, 6 to 7 times FLC. FLC=Full load current, LRC= Locked rotor current. Values shown are for guidance only, based on experiences with European electric motors. David Carter, 12th April 2011. Ref:engineeri…\MFP-MPxxx\starting-methods METRON ELEDYNE LIMITED 18 Autumn Park, Dysart Road, Grantham, LINCS. NG31 7DD. United Kingdom Telephone: +44 (0) 1476 516120 FAX: +44 (0) 1476 516121 email: [email protected] www.metroneledyne.co.uk