* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Roots, Stems, Leaves, Tissues
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
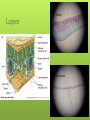
Roots, Stems, Leaves, Tissues BSC 2011L Review of difference between monocots and dicots Organization of Flowering Plants 3 vegetative organs that don’t have to do with reproduction: Root – anchor the plant, and absorb water and minerals Stem – supports leaves Leaves – carry on photosynthesis 3 major tissues of vegetative organs: Dermal tissue Ground tissues Outer protective coating of organ Interior of plant organ Vascular tissue Xylem (transports water) and phloem (transports sugars) Transports, supports Ground Tissue 3 cell types according to cell wall structure Parenchyma Large vacuoles Important roles: Collenchyma Photosynthesis in leaves Storage of proteins in fruits Storage of starch in roots Generally elongated Provide support to leaf petioles, nonwoody stems, growing organs Sclerenchyma Thickened cell walls for support Undergo programmed cell death often and offer support then (in wood and bark) Growth Primary Growth Increases Secondary length of plant Growth Increases girth of plant Growth - Apical Meristem Located at terminal end of stem, branches, root tip Continuous growth Growth – Lateral Meristem The roots and stems of some Eudicots develop secondary plant body – tissues referred to as wood and bark 2 Lateral Meristems Vascular Cambium – supplies cells of secondary xylem and phloem which eventually become wood and bark Cork cambium – waxy protective cells that become bark Root System Eudicot Root Monocot Root Roots Note location of: Root cap Zone of cell division Zone of elongation Zone of maturation Root Diversity Types of roots Taproots – main root is larger and often serves as food storage Fibrous roots – all of the roots approximately same size Stems Monocots Usually herbaceous (non-woody) Dicots Some are herbaceous Trees - woody Stems Dicot Monocot Stem Diversity Other examples: Rhizomes – horizontal underground stems that can give rise to new shoots Bamboo Bulbs – stems with many fleshy layers of leaves that store nutrients Lilies, onions Anatomy of woody stems – only in dicots Primary growth Apical Secondary meristem within termnial bud is active growth Vascular cambium is active Produces new xylem and phloem each year Build-up of this every year is called wood Woody Stems Leaves Dicot Monocot Leaves Petiole