* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DE Vocabulary Unit 1.1 - Stratford High School
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Aluminium-conductor steel-reinforced cable wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electronic musical instrument wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Electronic paper wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Electrical wiring in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Dual in-line package wikipedia , lookup
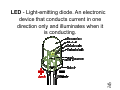
DE Vocabulary y Unit 1.1 Capacitor - An electrical device used to store electrical charge. Cold Solder Joint - A solder connection that is characterized by a grayish, porous appearance p pp due to excessive impurities in the solder, inadequate cleaning prior to soldering soldering, and/or the insufficient application of heat during soldering. soldering Digital Multimeter - Electronic test equipment that can perform multiple tasks. Typically yp y one capable p of measuring voltage, current, and resistance More sophisticated modern resistance. digital multimeters also measure capacitance inductance capacitance, inductance, current gain of transistors, and/or anything else th t can b that be measured d electronically. l t i ll Diode - A two terminal device that conducts in only one direction. Dual In-Line Package (DIP) - A very common IC package with two parallel rows of p pins intended to be inserted into a socket of through holes drilled in a printed circuit board board. Engineering Notation - A floating point system in which numbers are expressed p as p products consisting g of a number greater than one multiplied by an appropriate power of ten that is some multiple of three. Fuse - A protective device in the current path that melts or breaks when current exceeds a p predetermined maximum value. LED - Light-emitting diode. An electronic device that conducts current in one direction onlyy and illuminates when it is conducting. Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier (PLCC) A square IC package with leads on all four sides designed g for surface mounting on a circuit board. Printed Circuit Board - Insulating board containing conductive tracks for circuit connections. Resistor - Component made of material that opposes flow of current and therefore has some value of resistance. Resistor Color Code - Coding system of colored stripes on a resistor to indicate the resistor's value and tolerance. Scientific Notation - Numbers entered as a number from one to ten multiplied byy a p power of ten. SI Notation - Abbreviation of System International, a system of practical units based on the meter, kilogram, g second, ampere, Kelvin, mole, and candela. candela Seven-Segment Display - An array of seven independently controlled lightemitting g diodes ((LED)) or liquid q crystal y display (LCD) elements, shaped like a figure-8 figure 8, which can be used to display decimal digits and other characters by turning on the appropriate elements elements. Small Outline IC (SOIC) - An IC package similar to a DIP, but smaller, which is designed g for automatic placement and soldering on the surface of a circuit board board. Solder - Metallic alloy of tin and lead that is used to join two metal surfaces. Solder Bridge - The unwanted formation of a conductive path of solder between conductors. Soldering - Process of joining two metallic surfaces to make an electrical contact byy melting g solder ((usually y tin and lead) across them. Soldering Iron - Tool with an internal heating element used to heat surfaces being g soldered to the p point where the solder becomes molten. Tinning - The process of applying a thin coat of solder to materials prior to their being g soldered; for example, p application of a light coat of solder to the filaments of a conductor to hold the filaments in place prior to soldering the conductor conductor. Transistor - Term derived from "transfer resistor." Semiconductor device that can be used as an amplifier p or as an electronic switch.