* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electrical Conduction PPT
Survey
Document related concepts
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
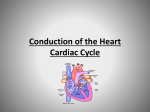
Electrical Conduction pathway of the heart: heart beat is regulated by electrical impulses SA node impulse begins in SA (sinoatrial node; normal rate 60 – 100 BPM) group of nerve cells located in right atrium “pacemaker” of the heart sends out electrical impulses that spread out over muscles in the atria electrical impulse causes atria to contract and push blood into ventricles electrical impulse then travels to AV (atrioventricular) node AV node group of cells located between atria and ventricles (normal rate 40 – 60 BPM) AV node sends electrical impulse through nerve fibers in the septum called the Bundle of His Bundle of His nerve fibers in the septum divides into right and left bundle branches Right and left bundle branches pathways that carry the electrical impulse down through the ventricles bundles continue to subdivide into network of nerve fibers throughout ventricles called Perkinje fibers Perkinje fibers final fibers on electrical conduction pathway (normal rate 20 – 40 BPM) spread electrical impulses to all of the muscle tissue in the ventricles ventricles then contract http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov /health/healthtopics/topics/hhw/electric al.html EKG or ECG (electrocardiogram) electrical conduction pattern occurs about every 0.8 seconds EKG or ECG (electrocardiogram): machine that monitors and records electrical impulses in the heart; used to detect abnormal heart activity or disease EKG p, qrs, t waves p wave: Atrial depolarization or contraction qrs complex: ventricular depolarization or contraction t wave: ventricular relaxation Cardiac cycle Conists of mechanical and electrical conduction Both must function properly for normal cardiac output