* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download metamorphic rocks 6-2
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Marine geology of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Provenance (geology) wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
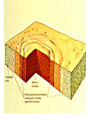
§6-2 “Metamorphic Rocks” Objectives: • Distinguish between regional and contact metamorphism. • Distinguish between foliated and nonfoliated metamorphic rocks and give an example of each. Metamorphism • Changing of one type of rock to another by heat & pressure or chemical processes. • Metamorphic rocks are formed from all 3 types of rocks. Contact Metamorphism • Magma rises into existing rocks & the heat causes changes in the minerals. Regional Metamorphism • Caused by tectonic activity at plate boundaries. • Friction creates immense heat & pressure which changes the chemical composition of a rock. Metamorphic Rock Video Clip Classification of Metamorphic Rocks Only 2 choices: • Foliate – Similar to layers – Also called “banding” • Nonfoliated – Similar to fracture Foliated Rocks – show layering or “banding” Nonfoliated Rocks – Crystals grow as rock heats up Limestone changes to Sandstone changes to Assignments • • • • Finish worksheet packet & have checked off. Look at metamorphic rocks in boxes. Go over worksheets Wednesday Test on Thursday in Computer Lab. – Field trip people test on paper Friday in class – Everyone else ch 12 vocab on Friday in class • STUDY – STUDY --- STUDY Page 191 –Blue Box #1 • If you were to start a rock collection, what 10 rocks would you like to include & why. • EXAMPLE: Moon Rock – because they are rare and I was born when the first astronauts landed on the moon