* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 11.6 Patterns in Evolution TEKS 7B, 7D, 7E, 7F The student is
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Coevolution wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
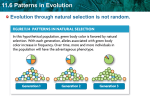
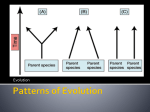
11.6 Patterns in Evolution TEKS 7B, 7D, 7E, 7F The student is expected to: 7B analyze and evaluate scientific explanations concerning any data of sudden appearance, stasis, and sequential nature of groups in the fossil record; 7D analyze and evaluate how the elements of natural selection, including inherited variation, the potential of a population to produce more offspring than can survive, and a finite supply of environmental resources, result in differential reproductive success; 11.6 Patterns in Evolution TEKS 7B, 7D, 7E, 7F (continued) 7E analyze and evaluate the relationship of natural selection to adaptation and to the development of diversity in and among species; 7F analyze and evaluate the effects of other evolutionary mechanisms, including genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and recombination 11.6 Patterns in Evolution KEY CONCEPT Evolution occurs in patterns. TEKS 7B, 7D, 7E, 7F 11.6 Patterns in Evolution TEKS 7B, 7D, 7E, 7F Evolution through natural selection is not random. • Natural selection can have direction. • The effects of natural selection add up over time. 11.6 Patterns in Evolution • Convergent evolution describes evolution toward similar traits in unrelated species. TEKS 7B, 7D, 7E, 7F 11.6 Patterns in Evolution TEKS 7B, 7D, 7E, 7F • Divergent evolution describes evolution toward different traits in closely related species. kit fox red fox ancestor How do convergent and divergent evolution illustrate the directional nature of natural selection? 11.6 Patterns in Evolution TEKS 7B, 7D, 7E, 7F Species can shape each other over time. • Two or more species can evolve together through coevolution. – evolutionary paths become connected – species evolve in response to changes in each other 11.6 Patterns in Evolution TEKS 7B, 7D, 7E, 7F • Coevolution can occur in beneficial relationships. 11.6 Patterns in Evolution TEKS 7B, 7D, 7E, 7F • Coevolution can occur in competitive relationships, sometimes called evolutionary. 11.6 Patterns in Evolution TEKS 7B, 7D, 7E, 7F Species can become extinct. • Extinction is the elimination of a species from Earth. • Background extinctions occur continuously at a very low rate. – occurs at roughly the same rate as speciation – usually affects a few species in a small area – caused by local changes in environment 11.6 Patterns in Evolution TEKS 7B, 7D, 7E, 7F • Mass extinctions are rare but much more intense. – destroy many species at global level – thought to be caused by catastrophic events – at least five mass extinctions in last 600 million years 11.6 Patterns in Evolution TEKS 7B, 7D, 7E, 7F Speciation often occurs in patterns. • A pattern of punctuated equilibrium exists in the fossil record. – theory proposed by Eldredge and Gould in 1972 – episodes of speciation occur suddenly in geologic time – followed by long periods of little evolutionary change – revised Darwin’s idea that species arose through gradual transformations 11.6 Patterns in Evolution TEKS 7B, 7D, 7E, 7F • Many species evolve from one species during adaptive radiation. – ancestral species diversifies into many descendent species – descendent species usually adapted to wide range of environments