* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download chapter 11 - courses.psu.edu
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Planned obsolescence wikipedia , lookup
Market analysis wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
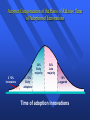
CHAPTER 11 DEVELOPING NEW MARKET OFFERINGS IMPORTANT TOPICS OF THIS CHAPTER What is a New Product? Challenges in New Product Development (NPD) Organizational Structure & NPD Stages & Management of NPD Diffusion & Adaption of New Products NEW PRODUCTS New-to-the-World Products(10%) New Product Lines/Functions/Applications (20%) Additions to Existing Product Lines(26%) Improvements and Revisions of Existing Products(26%) Repositioning(7%) Cost Reductions(11%) CAUSES OF NEW PRODUCT FAILURE Failure in Market Research Findings Overestimated Demand and Size of Market Design Failure Positioning Problem Ineffective Communication/Promotion High Development Cost/ Price Pressure from Competitors Poor Timing CAUSES OF NEW PRODUCT SUCCESS Technological Superiority Easy of Market Entry Competitive Advantage Size and Speed in Market growth Identifying Needs/Wants and Good Timing Effective Promotion/Communication Uniqueness of the Concept/Product Marketing and Managerial Synergy/Team Effort CHALLENGES IN NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT Shortage in New Product Ideas Fragmented Markets Social and Governmental Constraints High Development Cost Shortage of Cash/Capital Faster Development Time Shorter Product Life Cycle EFFECTIVE ORGANIZATIONAL ARRANGEMENTS Top Management: » R&D Budget. Organization for New-Product Development: » » » » Product managers New Product Managers New Product Committee New Product Departments: R&D. » New Product Venture Team THE NEW-PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT PROCESS Idea Generation: » Sources of new ideas: Customers’ needs and wants, scientists and engineers, competitors, sales force and channels, top management, universities and research firms. Idea Screening: » Idea manager » Idea committee: DROP-error GO-error THE NEW-PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT PROCESS Concept Development and Testing: » Concept development: Category concepts Product-positioning map Brand positioning map turns into brand concept » Concept testing Virtual reality. Customer-driven engineering: – Incorporating customer preferences into final engineering design. Expensive High price/oz. Bacon and eggs Pancakes Hot cereal Cold cereal Instant breakfast Inexpensive Low in calories b) Brand-positioning map (instant breakfast market) Brand C Brand B Brand A Low price/oz. High in calories (a) Product-positioning map (breakfast market) Quick Slow Product & Brand Positioning THE NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT PROCESS Marketing Strategy Development: » Size of market, structure, behavior, market share and short-run profit goals » Pricing and distribution strategy » Long-run sales and profit goals. Business Analysis: » Sales, cost and profit projections: Estimating total sales: – First-time sales. – Replacement sales. – Repeat sales. Estimating costs and profits: – Cost of goods sold, gross margin, gross contribution, net contribution, discounted contribution and pay back period, break-even analysis, risk analysis. THE NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT PROCESS Product Development: » Physical version of the product: Functional test (alpha testing) Customer test (beta testing) » Measuring consumer preferences: Rank-order. Paired comparison. Monadic rating. THE NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT PROCESS Market Testing: – Consumer-goods market testing: » Trial, first repeat, adoption and purchase frequency: sales-wave research-trying with no cost to consumer. simulated test marketing. controlled test marketing. test markets- reliable forecasts, testing the marketing mix: – how many cities. – which cities. – length of test. – what information to learn. – what action to take-trial and repurchase rate. Consumer-Goods Market Testing Simulated Test Market Test in a simulated shopping environment to a sample of Sales- consumers. Controlled Test Market A few stores that have agreed to carry new products for a fee. Wave Research Standard Test Market Test offering trail to a sample of consumers in successive periods. Full marketing campaign in a small number of representative cities. THE NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT PROCESS – Business goods market testing: » Alpha testing Measure and improve product performance. » Beta testing: Testing in customer’s site » Trade shows » Dealers’ showroom. Commercialization: – Timing: » First entry. » Parallel entry. » Late entry. NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT PROCESS Commercialization (cont.): » Geographical strategy: Single locality Regional National Global » Target-market prospects: Users Nonusers Opinion leaders » Strategic model: Critical path. THE CONSUMER ADOPTION PROCESS Early strategies: » Mass-market approach, » Heavy-user target market. Early adopter theory: » Time laps between exposure and trials. » Influence to early adopter: Media exposure. Early adopter as opinion leader. Stages in adoption: » » » » » Awareness. Interest. Evaluation. Trial. Adoption. THE CONSUMER ADOPTION PROCESS (CONT.) Factors influencing the adoption process: » People’s readiness: Adopter Categories: – Innovator(2.5%) – Early Adopters(13.5%), – Early Majority (34%), – Late Majority(34%). – Laggards(16%). » Personal Influence: More important at the evaluation stage, and on late adopters than the early adopters. Adopter Categorization of the Basis of Relative Time of Adoption of Innovations 34% Early majority 2 1/2% Innovators 13 1/2% Early adopters 34% Late majority 16% Laggards Time of adoption innovations INFLUENCING FACTORS TO ADOPTION PROCESS » Characteristics of the Innovation affect rate: Relative advantage Compatibility Complexity Divisibility Communicability » Organizations to Adopt Innovation: Environmental factors Organizational factors: – Progressiveness. – Size. – Pressure.