* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download More Help with Gerunds and Infinitives Verbs that can have gerunds
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek verbs wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish verbs wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Hungarian verbs wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Split infinitive wikipedia , lookup
English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Finnish verb conjugation wikipedia , lookup
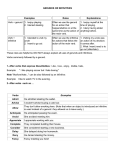
More Help with Gerunds and Infinitives Verbs that can have gerunds as their objects: (example: He denied stealing the car. In this case, “he” is the subject, “denied” is the verb, “stealing” is the gerund with “stealing the car” as the entire gerund phrase acting as the object—it answers what he denied.) Appreciate Deny Enjoy Mention Postpone Avoid Discuss Finish Mind Quit Delay Dislike Keep Miss Recall Recommend Resent Suggest Understand Verbs that are often used with infinitives: (verb + infinitive) (example: Hannah decided to go to college after all. In this case, “Hannah” is the subject, “decided” is the verb, and “to go” is the infinitive with “to go to college” as the entire infinitive phrase answering what Hannah decided.) Agree Appear Wait Decide Learn Plan Tend Seem Offer Intend Can/Can’t afford (verb + noun phrase + infinitive) (example: The teacher warned her student to be quiet during the test. In this examples, “the teacher” is the subject, “warned” is the verb, and “her student” is the noun phrase following the verb working as an indirect object with “to be” is the infinitive with “to be quiet” as the entire infinitive phrase answering what the student was warned by the teacher.) Cause Force Invite Persuade Teach Trust Convince Hire Order Remind Tell Warn (verb (+ noun phrase) + infinitive (example: I asked the police officer to show me his badge. In this example, “I” is the subject, “asked” is the verb, “the police officer” is the noun phrase, and “to show” is the infinitive.) Ask Choose Get Want Beg Expect Need Would like Verbs that can take a gerund or infinitive: (examples: I like to start new books but have a hard time finishing them. OR I like starting new books but have a hard time finishing them.) Begin Hate Love Start Prefer Continue Like Verbs that take a gerund or noun phrase + infinitive: (examples: The law does not allow swimming in this area. OR The law does not allow people to swim in this area). Advise Encourage Require Allow Permit Urge Adjectives often followed by infinitives: (example: The mother encouraged her daughter not to be hesitant about her first day of school. Afraid Ashamed Determined Fortunate Amazed Careful Disappointed Glad Anxious Delighted Eager Happy Hesitant Prepared Relieved Shocked Lucky Proud Reluctant Sorry Pleased Ready Sad Willing